Update Webex Cisco Windows to version 44.11.0.31172
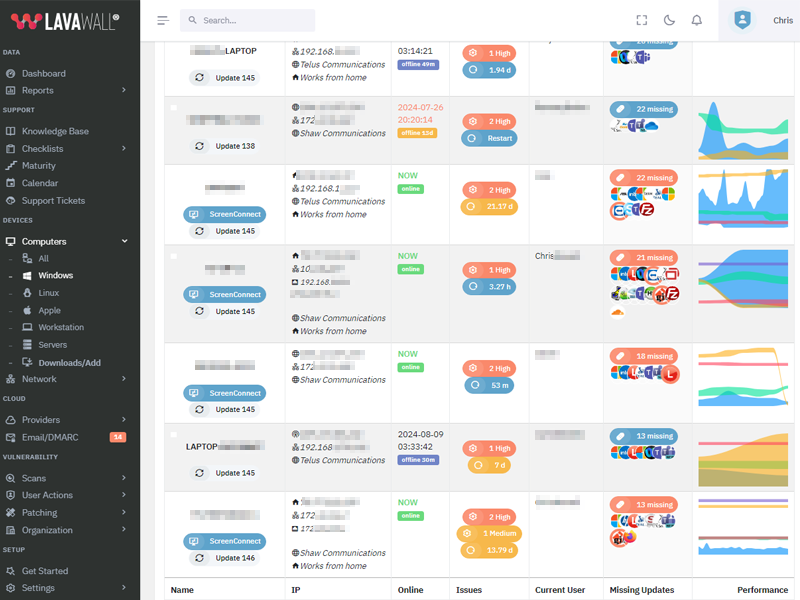
What patches are you missing?
CVE Vulnerabilities for Webex Cisco Windows
| CVE | Published | Severity | Details | Exploitability | Impact | Vector |
| CVE‑2023‑20180 | 2023‑07‑07 20:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in the web interface of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attack on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to insufficient CSRF protections for the web interface on an affected system. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user of the interface to click a malicious link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to perform arbitrary actions. These actions could include joining meetings and scheduling training sessions. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑20134 | 2023‑04‑05 18:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple vulnerabilities in the web interface of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct a stored cross-site scripting (XSS) attack or upload arbitrary files as recordings. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑20133 | 2023‑07‑07 20:15:10 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in the web interface of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct a stored cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against a user of the interface. This vulnerability exists because of insufficient validation of user-supplied input in Webex Events (classic) programs, email templates, and survey questions. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to click a malicious link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive, browser-based information. | 2 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑20132 | 2023‑04‑05 18:15:08 | MEDIUM (5) | Multiple vulnerabilities in the web interface of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to conduct a stored cross-site scripting (XSS) attack or upload arbitrary files as recordings. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. | 2 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑20852 | 2022‑08‑10 09:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple vulnerabilities in the web interface of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow a remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack or a frame hijacking attack against a user of the web interface. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑20820 | 2022‑08‑10 09:15:08 | MEDIUM (5) | Multiple vulnerabilities in the web interface of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow a remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack or a frame hijacking attack against a user of the web interface. For more information about these vulnerabilities, see the Details section of this advisory. | 2 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑20778 | 2022‑04‑21 19:15:08 | MEDIUM (6) | A vulnerability in the authentication component of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against a user of the web-based interface. This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input by the web-based interface of the authentication component of Cisco Webex Meetings. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user of the interface to click a maliciously crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive, browser-based information. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑40128 | 2021‑11‑04 16:15:10 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in the account activation feature of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to send an account activation email with an activation link that points to an arbitrary domain. This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied parameters. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted HTTP request to the account activation page of Cisco Webex Meetings. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to send to any recipient an account activation email that contains a tampered activation link, which could direct the user to an attacker-controlled website. | 4 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑34743 | 2021‑10‑21 03:15:07 | HIGH (7) | A vulnerability in the application integration feature of Cisco Webex Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to authorize an external application to integrate with and access a user's account without that user's express consent. This vulnerability is due to improper validation of cross-site request forgery (CSRF) tokens. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by convincing a targeted user who is currently authenticated to Cisco Webex Software to follow a link designed to pass malicious input to the Cisco Webex Software application authorization interface. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause Cisco Webex Software to authorize an application on the user's behalf without the express consent of the user, possibly allowing external applications to read data from that user's profile. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑1544 | 2021‑06‑04 17:15:10 | MEDIUM (6) | A vulnerability in logging mechanisms of Cisco Webex Meetings client software could allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain access to sensitive information. This vulnerability is due to unsafe logging of application actions. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by logging onto the local system and accessing files containing the logged details. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to gain access to sensitive information, including meeting data and recorded meeting transcriptions. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑1467 | 2021‑04‑08 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings for Android could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to modify the avatar of another user. This vulnerability is due to improper authorization checks. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted request to the Cisco Webex Meetings client of a targeted user of a meeting in which they are both participants. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to modify the avatar of the targeted user. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑1420 | 2021‑04‑08 04:15:13 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in certain web pages of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to modify a web page in the context of a user's browser. The vulnerability is due to improper checks on parameter values in affected pages. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to follow a crafted link that is designed to pass HTML code into an affected parameter. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to alter the contents of a web page to redirect the user to potentially malicious websites, or the attacker could use this vulnerability to conduct further client-side attacks. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑1372 | 2021‑02‑17 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (6) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App and Webex Productivity Tools for Windows could allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain access to sensitive information on an affected system. This vulnerability is due to the unsafe usage of shared memory by the affected software. An attacker with permissions to view system memory could exploit this vulnerability by running an application on the local system that is designed to read shared memory. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to retrieve sensitive information from the shared memory, including usernames, meeting information, or authentication tokens. Note: To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must have valid credentials on a Microsoft Windows end-user system and must log in after another user has already authenticated with Webex on the same end-user system. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑1351 | 2021‑02‑17 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (6) | A vulnerability in the web-based interface of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against a user of the web-based interface of the affected service. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input by the web-based interface of the affected service. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user of the interface to click a maliciously crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the context of the affected interface or access sensitive, browser-based information. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑1311 | 2021‑01‑13 22:15:22 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in the reclaim host role feature of Cisco Webex Meetings and Cisco Webex Meetings Server could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to take over the host role during a meeting. This vulnerability is due to a lack of protection against brute forcing of the host key. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted requests to a vulnerable Cisco Webex Meetings or Webex Meetings Server site. A successful exploit would require the attacker to have access to join a Webex meeting, including applicable meeting join links and passwords. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to acquire or take over the host role for a meeting. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑1310 | 2021‑01‑13 22:15:22 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in the web-based management interface of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to redirect a user to an untrusted web page, bypassing the warning mechanism that should prompt the user before the redirection. This vulnerability is due to improper input validation of the URL parameters in an HTTP request. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to click a crafted link. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to redirect a user to a malicious website, bypassing the Webex URL check that should result in a warning before the redirection to the web page. Attackers may use this type of vulnerability, known as an open redirect attack, as part of a phishing attack to convince users to unknowingly visit malicious sites. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑1221 | 2021‑02‑04 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in the user interface of Cisco Webex Meetings and Cisco Webex Meetings Server Software could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to inject a hyperlink into a meeting invitation email. The vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by entering a URL into a field in the user interface. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to generate a Webex Meetings invitation email that contains a link to a destination of their choosing. Because this email is sent from a trusted source, the recipient may be more likely to click the link. | 2 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3604 | 2020‑11‑06 19:15:16 | HIGH (8) | Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerabilities are due to insufficient validation of certain elements of a Webex recording that is stored in the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a user a malicious ARF or WRF file through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file with the affected software on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑3603 | 2020‑11‑06 19:15:16 | HIGH (8) | Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerabilities are due to insufficient validation of certain elements of a Webex recording that is stored in the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a user a malicious ARF or WRF file through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file with the affected software on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑3588 | 2020‑11‑06 19:15:15 | HIGH (8) | A vulnerability in virtualization channel messaging in Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App for Windows could allow a local attacker to execute arbitrary code on a targeted system. This vulnerability occurs when this app is deployed in a virtual desktop environment and using virtual environment optimization. This vulnerability is due to improper validation of messages processed by the Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App. A local attacker with limited privileges could exploit this vulnerability by sending malicious messages to the affected software by using the virtualization channel interface. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to modify the underlying operating system configuration, which could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code with the privileges of a targeted user. Note: This vulnerability can be exploited only when Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App is in a virtual desktop environment on a hosted virtual desktop (HVD) and is configured to use the Cisco Webex Meetings virtual desktop plug-in for thin clients. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑3573 | 2020‑11‑06 19:15:15 | HIGH (8) | Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerabilities are due to insufficient validation of certain elements of a Webex recording that is stored in the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a user a malicious ARF or WRF file through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file with the affected software on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑3541 | 2020‑09‑04 03:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in the media engine component of Cisco Webex Meetings Client for Windows, Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App for Windows, and Cisco Webex Teams for Windows could allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain access to sensitive information. The vulnerability is due to unsafe logging of authentication requests by the affected software. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by reading log files that are stored in the application directory. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to gain access to sensitive information, which could be used in further attacks. | 1 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑3502 | 2020‑08‑17 18:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Multiple vulnerabilities in the user interface of Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to obtain restricted information from other Webex users. These vulnerabilities are due to improper input validation of parameters returned to the application from a web site. An attacker with a valid Webex account could exploit these vulnerabilities by persuading a user to follow a URL that is designed to return malicious path parameters to the affected software. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain restricted information from other Webex users. | 2 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3501 | 2020‑08‑17 18:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Multiple vulnerabilities in the user interface of Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to obtain restricted information from other Webex users. These vulnerabilities are due to improper input validation of parameters returned to the application from a web site. An attacker with a valid Webex account could exploit these vulnerabilities by persuading a user to follow a URL that is designed to return malicious path parameters to the affected software. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain restricted information from other Webex users. | 2 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3441 | 2020‑11‑18 19:15:12 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings and Cisco Webex Meetings Server could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to view sensitive information from the meeting room lobby. This vulnerability is due to insufficient protection of sensitive participant information. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by browsing the Webex roster. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to gather information about other Webex participants, such as email address and IP address, while waiting in the lobby. | 4 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3440 | 2020‑08‑26 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App for Windows could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to overwrite arbitrary files on an end-user system. The vulnerability is due to improper validation of URL parameters that are sent from a website to the affected application. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to follow a URL to a website that is designed to submit crafted input to the affected application. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to overwrite arbitrary files on the affected system, possibly corrupting or deleting critical system files. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3361 | 2020‑06‑18 03:15:14 | CRITICAL (10) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings and Cisco Webex Meetings Server could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to gain unauthorized access to a vulnerable Webex site. The vulnerability is due to improper handling of authentication tokens by a vulnerable Webex site. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted requests to a vulnerable Cisco Webex Meetings or Cisco Webex Meetings Server site. If successful, the attacker could gain the privileges of another user within the affected Webex site. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3347 | 2020‑06‑18 03:15:14 | MEDIUM (6) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App for Windows could allow an authenticated, local attacker to gain access to sensitive information on an affected system. The vulnerability is due to unsafe usage of shared memory that is used by the affected software. An attacker with permissions to view system memory could exploit this vulnerability by running an application on the local system that is designed to read shared memory. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to retrieve sensitive information from the shared memory, including usernames, meeting information, or authentication tokens that could aid the attacker in future attacks. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑3345 | 2020‑07‑16 18:15:18 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in certain web pages of Cisco Webex Meetings and Cisco Webex Meetings Server could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to modify a web page in the context of a browser. The vulnerability is due to improper checks on parameter values within affected pages. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to follow a crafted link that is designed to pass HTML code into an affected parameter. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to alter the contents of a web page to redirect the user to potentially malicious web sites, or the attacker could leverage this vulnerability to conduct further client-side attacks. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3342 | 2020‑06‑18 03:15:14 | HIGH (9) | A vulnerability in the software update feature of Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App for Mac could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerability is due to improper validation of cryptographic protections on files that are downloaded by the application as part of a software update. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to go to a website that returns files to the client that are similar to files that are returned from a valid Webex website. The client may fail to properly validate the cryptographic protections of the provided files before executing them as part of an update. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the user. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3263 | 2020‑06‑18 03:15:12 | HIGH (8) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute programs on an affected end-user system. The vulnerability is due to improper validation of input that is supplied to application URLs. The attacker could exploit this vulnerability by persuading a user to follow a malicious URL. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the application to execute other programs that are already present on the end-user system. If malicious files are planted on the system or on an accessible network file path, the attacker could execute arbitrary code on the affected system. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3194 | 2020‑04‑15 21:15:35 | HIGH (8) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Microsoft Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Microsoft Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerability exists due to insufficient validation of certain elements with a Webex recording stored in either the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or the Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a user a malicious ARF or WRF file through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file with the affected software on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑3182 | 2020‑03‑04 19:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in the multicast DNS (mDNS) protocol configuration of Cisco Webex Meetings Client for MacOS could allow an unauthenticated adjacent attacker to obtain sensitive information about the device on which the Webex client is running. The vulnerability exists because sensitive information is included in the mDNS reply. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by doing an mDNS query for a particular service against an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to gain access to sensitive information. | 3 | 1 | ADJACENT_NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3155 | 2020‑03‑04 19:15:13 | HIGH (7) | A vulnerability in the SSL implementation of the Cisco Intelligent Proximity solution could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to view or alter information shared on Cisco Webex video devices and Cisco collaboration endpoints if the products meet the conditions described in the Vulnerable Products section. The vulnerability is due to a lack of validation of the SSL server certificate received when establishing a connection to a Cisco Webex video device or a Cisco collaboration endpoint. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by using man in the middle (MITM) techniques to intercept the traffic between the affected client and an endpoint, and then using a forged certificate to impersonate the endpoint. Depending on the configuration of the endpoint, an exploit could allow the attacker to view presentation content shared on it, modify any content being presented by the victim, or have access to call controls. This vulnerability does not affect cloud registered collaboration endpoints. | 2 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑3128 | 2020‑03‑04 19:15:12 | HIGH (8) | Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Microsoft Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Microsoft Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerabilities are due to insufficient validation of certain elements within a Webex recording that is stored in either the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or the Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a malicious ARF or WRF file to a user through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑3127 | 2020‑03‑04 19:15:12 | HIGH (8) | Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Microsoft Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Microsoft Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerabilities are due to insufficient validation of certain elements within a Webex recording that is stored in either the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or the Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a malicious ARF or WRF file to a user through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑27126 | 2020‑11‑18 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (6) | A vulnerability in an API of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct cross-site scripting attacks. The vulnerability is due to improper validation of user-supplied input to an application programmatic interface (API) within Cisco Webex Meetings. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by convincing a targeted user to follow a link designed to submit malicious input to the API used by Cisco Webex Meetings. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to conduct cross-site scripting attacks and potentially gain access to sensitive browser-based information from the system of a targeted user. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑1948 | 2019‑08‑21 19:15:16 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings Mobile (iOS) could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to gain unauthorized read access to sensitive data by using an invalid Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate. The vulnerability is due to insufficient SSL certificate validation by the affected software. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by supplying a crafted SSL certificate to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to conduct man-in-the-middle attacks to decrypt confidential information on user connections to the affected software. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑1677 | 2019‑02‑07 19:29:00 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in Cisco Webex Meetings for Android could allow an unauthenticated, local attacker to perform a cross-site scripting attack against the application. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of the application input parameters. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a malicious request to the Webex Meetings application through an intent. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute script code in the context of the Webex Meetings application. Versions prior to 11.7.0.236 are affected. | 2 | 3 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑1674 | 2019‑02‑28 18:29:02 | HIGH (9) | A vulnerability in the update service of Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App and Cisco Webex Productivity Tools for Windows could allow an authenticated, local attacker to execute arbitrary commands as a privileged user. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied parameters. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by invoking the update service command with a crafted argument. An exploit could allow the attacker to run arbitrary commands with SYSTEM user privileges. While the CVSS Attack Vector metric denotes the requirement for an attacker to have local access, administrators should be aware that in Active Directory deployments, the vulnerability could be exploited remotely by leveraging the operating system remote management tools. This vulnerability is fixed in Cisco Webex Meetings Desktop App Release 33.6.6 and 33.9.1 releases. This vulnerability is fixed in Cisco Webex Productivity Tools Release 33.0.7. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑16001 | 2019‑11‑26 04:15:13 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in the loading mechanism of specific dynamic link libraries in Cisco Webex Teams for Windows could allow an authenticated, local attacker to perform a DLL hijacking attack. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker would need to have valid credentials on the Windows system. The vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of the resources loaded by the application at run time. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by crafting a malicious DLL file and placing it in a specific location on the targeted system. The malicious DLL file would execute when the vulnerable application is launched. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the target machine with the privileges of another user account. | 2 | 3 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑15960 | 2019‑11‑26 03:15:12 | MEDIUM (5) | A vulnerability in the Webex Network Recording Admin page of Cisco Webex Meetings could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to elevate privileges in the context of the affected page. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must be logged in as a low-level administrator. The vulnerability is due to insufficient access control validation. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by submitting a crafted URL request to gain privileged access in the context of the affected page. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to elevate privileges in the Webex Recording Admin page, which could allow them to view or delete recordings that they would not normally be able to access. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑15287 | 2020‑09‑23 01:15:13 | HIGH (8) | Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Microsoft Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Microsoft Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerabilities exist due to insufficient validation of certain elements with a Webex recording stored in either the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or the Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a user a malicious ARF or WRF file through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file with the affected software on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑15285 | 2020‑09‑23 01:15:13 | HIGH (8) | Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Microsoft Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Microsoft Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerabilities exist due to insufficient validation of certain elements with a Webex recording stored in either the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or the Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a user a malicious ARF or WRF file through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file with the affected software on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑15283 | 2020‑09‑23 01:15:12 | HIGH (8) | Multiple vulnerabilities in Cisco Webex Network Recording Player for Microsoft Windows and Cisco Webex Player for Microsoft Windows could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. The vulnerabilities exist due to insufficient validation of certain elements with a Webex recording stored in either the Advanced Recording Format (ARF) or the Webex Recording Format (WRF). An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending a user a malicious ARF or WRF file through a link or email attachment and persuading the user to open the file with the affected software on the local system. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the affected system with the privileges of the targeted user. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2018‑0390 | 2018‑07‑18 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in the web framework of Cisco Webex could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a Document Object Model-based (DOM-based) cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against the user of the web interface of an affected system. The vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation of certain parameters that are passed to the affected software by using the HTTP POST method. An attacker who can submit malicious scripts to the affected user interface element could execute arbitrary script or HTML code in the user's browser in the context of the affected site. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvj33287. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑0357 | 2018‑06‑07 21:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in the web framework of Cisco WebEx could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against the user of the web interface of an affected system. The vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation of certain parameters that are passed to the affected software via the HTTP GET and HTTP POST methods. An attacker who can convince a user to follow an attacker-supplied link could execute arbitrary script or HTML code in the user's browser in the context of an affected site. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvi71274. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑0356 | 2018‑06‑07 21:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | A vulnerability in the web framework of Cisco WebEx could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against the user of the web interface of an affected system. The vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation of certain parameters that are passed to the affected software via the HTTP GET and HTTP POST methods. An attacker who can convince a user to follow an attacker-supplied link could execute arbitrary script or HTML code in the user's browser in the context of an affected site. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvi63757. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑0264 | 2018‑05‑02 22:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A vulnerability in the Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player for Advanced Recording Format (ARF) files could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the system of a targeted user. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending the user a link or email attachment with a malicious ARF file and persuading the user to follow the link or open the file. Successful exploitation could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the user's system. This vulnerability affects Cisco WebEx Business Suite meeting sites, Cisco WebEx Meetings sites, Cisco WebEx Meetings Server, and Cisco WebEx ARF players. The following client builds of Cisco WebEx Business Suite (WBS31 and WBS32), Cisco WebEx Meetings, and Cisco WebEx Meetings Server are affected: Cisco WebEx Business Suite (WBS31) client builds prior to T31.23.4, Cisco WebEx Business Suite (WBS32) client builds prior to T32.12, Cisco WebEx Meetings with client builds prior to T32.12, Cisco WebEx Meeting Server builds prior to 3.0 Patch 1. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvh85410, CSCvh85430, CSCvh85440, CSCvh85442, CSCvh85453, CSCvh85457. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑0112 | 2018‑04‑19 20:29:00 | MEDIUM (6) | A vulnerability in Cisco WebEx Business Suite clients, Cisco WebEx Meetings, and Cisco WebEx Meetings Server could allow an authenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on a targeted system. The vulnerability is due to insufficient input validation by the Cisco WebEx clients. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by providing meeting attendees with a malicious Flash (.swf) file via the file-sharing capabilities of the client. Exploitation of this vulnerability could allow arbitrary code execution on the system of a targeted user. This affects the clients installed by customers when accessing a WebEx meeting. The following client builds of Cisco WebEx Business Suite (WBS30, WBS31, and WBS32), Cisco WebEx Meetings, and Cisco WebEx Meetings Server are impacted: Cisco WebEx Business Suite (WBS31) client builds prior to T31.23.2, Cisco WebEx Business Suite (WBS32) client builds prior to T32.10, Cisco WebEx Meetings with client builds prior to T32.10, Cisco WebEx Meetings Server builds prior to 2.8 MR2. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvg19384, CSCvi10746. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑0104 | 2018‑01‑04 06:29:00 | HIGH (9) | A vulnerability in Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player for Advanced Recording Format (ARF) files could allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the system of a targeted user. The attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending the user a link or email attachment with a malicious ARF file and persuading the user to follow the link or launch the file. Successful exploitation could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the user's system. This vulnerability affects Cisco WebEx Business Suite meeting sites, Cisco WebEx Meetings sites, Cisco WebEx Meetings Server, and Cisco WebEx ARF players. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvg78853, CSCvg78856, CSCvg78857. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑0103 | 2018‑01‑04 06:29:00 | HIGH (9) | A Buffer Overflow vulnerability in Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player for Advanced Recording Format (ARF) files could allow a local attacker to execute arbitrary code on the system of a user. The attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending the user a link or email attachment with a malicious ARF file and persuading the user to follow the link or launch the file. Successful exploitation could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on the user's system. This vulnerability affects Cisco WebEx Business Suite meeting sites, Cisco WebEx Meetings sites, Cisco WebEx Meetings Server, and Cisco WebEx ARF players. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvg78835, CSCvg78837, CSCvg78839. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑6753 | 2017‑07‑25 19:29:00 | HIGH (9) | A vulnerability in Cisco WebEx browser extensions for Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the affected browser on an affected system. This vulnerability affects the browser extensions for Cisco WebEx Meetings Server, Cisco WebEx Centers (Meeting Center, Event Center, Training Center, and Support Center), and Cisco WebEx Meetings when they are running on Microsoft Windows. The vulnerability is due to a design defect in the extension. An attacker who can convince an affected user to visit an attacker-controlled web page or follow an attacker-supplied link with an affected browser could exploit the vulnerability. If successful, the attacker could execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the affected browser. The following versions of the Cisco WebEx browser extensions are affected: Versions prior to 1.0.12 of the Cisco WebEx extension on Google Chrome, Versions prior to 1.0.12 of the Cisco WebEx extension on Mozilla Firefox. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvf15012 CSCvf15020 CSCvf15030 CSCvf15033 CSCvf15036 CSCvf15037. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑17428 | 2018‑03‑05 18:29:00 | HIGH (7) | Cavium Nitrox SSL, Nitrox V SSL, and TurboSSL software development kits (SDKs) allow remote attackers to decrypt TLS ciphertext data by leveraging a Bleichenbacher RSA padding oracle, aka a ROBOT attack. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑12372 | 2017‑11‑30 09:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A "Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player Remote Code Execution Vulnerability" exists in Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player for Advanced Recording Format (ARF) and WebEx Recording Format (WRF) files. A remote attacker could exploit this by providing a user with a malicious ARF or WRF file via email or URL and convincing the user to launch the file. Exploitation of this could cause an affected player to crash and, in some cases, could allow arbitrary code execution on the system of a targeted user. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvf57234, CSCvg54868, CSCvg54870. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑12371 | 2017‑11‑30 09:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A "Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player Remote Code Execution Vulnerability" exists in Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player for Advanced Recording Format (ARF) and WebEx Recording Format (WRF) files. A remote attacker could exploit this by providing a user with a malicious ARF or WRF file via email or URL and convincing the user to launch the file. Exploitation of this could cause an affected player to crash and, in some cases, could allow arbitrary code execution on the system of a targeted user. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvf49650, CSCvg54853, CSCvg54856, CSCvf49697, CSCvg54861, CSCvf49707, CSCvg54867. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑12370 | 2017‑11‑30 09:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A "Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player Remote Code Execution Vulnerability" exists in Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player for Advanced Recording Format (ARF) and WebEx Recording Format (WRF) files. A remote attacker could exploit this by providing a user with a malicious ARF or WRF file via email or URL and convincing the user to launch the file. Exploitation of this could cause an affected player to crash and, in some cases, could allow arbitrary code execution on the system of a targeted user. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCvf38060, CSCvg54836, CSCvf38077, CSCvg54843, CSCvf38084, CSCvg54850. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑12369 | 2017‑11‑30 09:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A "Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player Out-of-Bounds Vulnerability" exists in Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player for Advanced Recording Format (ARF) and WebEx Recording Format (WRF) files. A remote attacker could exploit this by providing a user with a malicious ARF or WRF file via email or URL and convincing the user to launch the file. Exploitation of this could cause an affected player to crash and, in some cases, could allow arbitrary code execution on the system of a targeted user. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCve30208, CSCve30214, CSCve30268. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑12368 | 2017‑11‑30 09:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A "Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player Remote Code Execution Vulnerability" exists in Cisco WebEx Network Recording Player for Advanced Recording Format (ARF) and WebEx Recording Format (WRF) files. A remote attacker could exploit this by providing a user with a malicious ARF or WRF file via email or URL and convincing the user to launch the file. Exploitation of this could cause an affected player to crash and, in some cases, could allow arbitrary code execution on the system of a targeted user. Cisco Bug IDs: CSCve10584, CSCve10591, CSCve11503, CSCve10658, CSCve11507, CSCve10749, CSCve10744, CSCve11532, CSCve10762, CSCve10764, CSCve11538. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6384 | 2015‑12‑05 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | The Cisco WebEx Meetings application before 8.5.1 for Android improperly initializes custom application permissions, which allows attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted application, aka Bug ID CSCuw86442. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |


Get the IT stuff done that nobody wants to do.
Patch more applications, achieve compliance, and prevent problems while reducing stress with Lavawall®.
Security First
A security tool by security auditors. From Passkeys and Argon2i to source validation and MVSP principles, Lavawall® has you covered.
Constant Improvement
More features and more security added nearly every day.
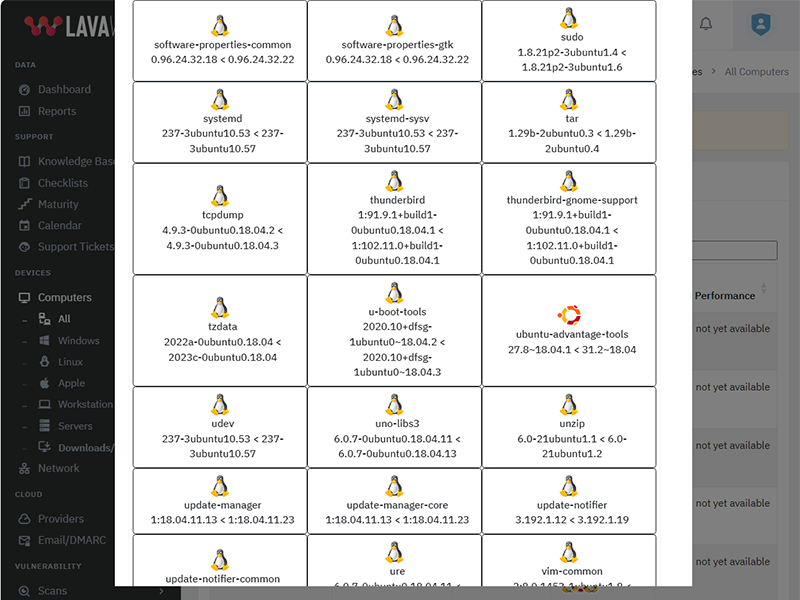
More patchable programs added every week
While Ninite and other patching tools have had the same patch offerings for decades, we're monitoring stats to keep adding the most useful prorgams.
Details matter
From wrapping TLS communications in extra encryption and uninstalling remote support tools when they aren't used to detailed statistical analysis of system and network performance, Lavawall® goes in-depth.
Chromium extensions and Notification Validation
Lavawall® goes beyond patches and breach detection. We also monitor for risky Chromium extensions and allowed notifications that might be part of a phishing or ransomware attack.
Extended Cloud Security
Extend the security features of Cloudflare, Microsoft, Google, Sophos, and other cloud providers to create a Lavawall® of protection
Secure Remote Management
Even if you used breached remote management tools like ScreenConnect through Lavawall® when it was vulnerable, your computers stayed safe because we only install the agent when it needs to be used.
Integrations and automation
Easily deploy, monitor, and analyze security tools like Huntress, AutoElevate, and Sophos. Magically gain details from ZenDesk, ConnectWise, Datto, Panorama9, Microsoft, and Google.
Human and automated support
Get immediate fixes, user notifications, admin notifications -- and even security-certified human level 3 support when our advanced statistical analysis confirms a problem or anomaly.
| 2024‑10‑30 | 0.12.8.195 | Mac update refinements |
| 2024‑10‑25 | 0.12.3.190 | |
| 2024‑10‑21 | 0.12.0.187 | Macos implementaiton, linux and windows improvements |
| 2024‑10‑16 | 0.11.128.186 | Linux stats and system information improvements, improvements for application shutdown |
| 2024‑09‑12 | 0.11.113.171 | CPU Optimizations and Packages reliability improvements |
| 2024‑09‑05 | 0.11.106.164 | Phased deployment enhancements |
| 2024‑09‑04 | 0.11.103.161 | |
| 2024‑09‑02 | 0.11.102.160 | CPU Optimizations and Packages reliability improvements |
| 2024‑08‑30 | 0.11.99.157 | CPU Optimizations and Packages reliability improvements |
| 2024‑08‑29 | 0.11.98.156 | CPU utilization and console event optimization |
| 2024‑08‑28 | 0.11.97.155 | Reliability to detect unusual updates like redistributables. |
| 2024‑08‑27 | 0.11.96.154 | |
| 2024‑08‑26 | 0.11.95.153 | Faster response for reboot requests |
| 2024‑08‑20 | 0.11.92.150 | Additional package upgrade pre-requisites |
| 2024‑08‑15 | 0.11.89.147 | |
| 2024‑08‑06 | 0.11.87.145 | |
| 2024‑07‑26 | 0.11.83.141 | Add resiliency for MAC duplicates and uptime |
| 2024‑07‑25 | 0.11.82.140 | Changes to facilitate cross-platform use. Bitlocker and Windows key refinements |
| 2024‑07‑15 | 0.11.80.138 | Antivirus and temperature added to configuration checks |
| 2024‑07‑15 | 0.11.79.137 | Add configuration checks for execution policy and secure boot |
| 2024‑07‑11 | 0.11.77.135 | load balancing refinements |
| 2024‑07‑10 | 0.11.76.134 | Add additional load balancing and data residency capabilities, add randomness to recurring task timings to decrease server load |
| 2024‑07‑05 | 0.11.74.132 | changes to graph and residual work on user imporsonation |
| 2024‑07‑04 | 0.11.73.131 | Add configuration checks for execution policy and secure boot. |
| 2024‑07‑03 | 0.11.72.130 | Enhanced event log monitoring |
| 2024‑07‑02 | 0.11.71.129 | Add details to Windows updates, enhanced risk metrics for application patches |
| 2024‑06‑19 | 0.11.65.123 | Update resiliancy and garbage collection |
| 2024‑06‑13 | 0.11.60.118 | Enhanced logging |
| 2024‑06‑12 | 0.11.55.113 | Include the primary drive serial number; MAC addresses for built-in wireless, Bluetooth, and ethernet into the device hash to restore uninstalled and reinstalled devices in cases where the motherboard serial is not unique |
| 2024‑06‑07 | 0.11.54.112 | Patch and package uninstall data addition |
| 2024‑06‑05 | 0.11.47.105 | refine per-user registry application listing |
| 2024‑06‑02 | 0.11.45.103 | uninstall and reinstall refinements, refine local logging, refine self-update and uninstall timing |
| 2024‑05‑30 | 0.11.21.79 | various bug fixes and improvements |
| 2024‑05‑28 | 0.11.16.74 | Error logging, registration, and uninstall improvements. |
| 2024‑05‑24 | 0.11.14.72 | applied changes for devices and login commands, changes for registration as well |
| 2024‑05‑22 | 0.11.13.71 | Add Windows computer model, improve Operating System parsing |
| 2024‑05‑21 | 0.11.11.69 | Added additional states for Windows update, flexibility for non-standard program file configurations, support for network diagrams at the switch level, details for Windows editions |
| 2024‑05‑21 | 0.11.10.68 | Add specific cases for Defender patterns and Composer versions. |
| 2024‑05‑17 | 0.11.3.61 | Change Log storage location to c:\program files\Lavawall |
| 2024‑05‑17 | 0.11.1.59 | self-update improvements. |
| 2024‑05‑16 | 0.8.0.55 | error log reporting and management. |
| 2024‑05‑15 | 0.7.0.54 | Websocket resiliency improvements |
| 2024‑05‑09 | 0.6.0.53 | Error log reporting and management. |
| 2024‑05‑01 | 0.5.44.52 | Even more improvements to scheduler |
| 2024‑04‑24 | 0.5.41.49 | Install compatibility with Sandbox |
| 2024‑04‑22 | 0.5.21.29 | Project property changes to enable automated compilation with new features. |
| 2024‑04‑20 | 0.5.20.28 | Add motherboard serial number and company reassignment |
| 2024‑04‑11 | 0.5.4.12 | Automate release notes as part of build process |
| 2024‑04‑03 | 0.5.3.11 | Websocket and service enhancements |
| 2024‑03‑21 | 0.5.2.10 | Enhance zip file validation |
NOTE: changes after June 2024 are incorportated into the Windows Changelog as the codebases for Windows, Linux, and Mac were combined
| 2024‑05‑20 | 253 | Added cleanup of old .json files during a re-install |
| 2024‑05‑13 | 252 | Added apt-get update to install |
| 2024‑05‑06 | 248 | Allow restart to use /var/run/reboot-required if needrestart is not installed |
| 2024‑04‑22 | 239 | Improve internal update and version tracking |
| 2024‑04‑15 | 235 | Add support for Yum packages |
| 2024‑04‑08 | 233 | Align patching with Windows patch reporting |
| 2024‑04‑02 | 228 | Add support for needrestart |
| 2024‑03‑04 | 224 | Schedule restarts |
| 2024‑03‑25 | 221 | Add support for apt packages |
| 2024‑03‑18 | 212 | Implement release management |
| 2024‑03‑11 | 202 | Add user login monitoring |
| 2024‑03‑04 | 189 | Enhance installation reliability |
| 2024‑02‑26 | 187 | Exapand triggers to identify if the instance needs to be restarted |
| 2024‑02‑19 | 146 | Improve compatibility for non-AWS instances |
| 2024‑02‑14 | 138 | Add self-uninstall capabilities |
| 2024‑02‑12 | 135 | Enhance scheduling flexibility |
| 2024‑02‑07 | 132 | Add kernel version tracking |
| 2024‑02‑05 | 124 | Add device hash to cryptographic self-update script validation |
| 2024‑01‑29 | 107 | Enhance encryption of patch data |
| 2024‑01‑22 | 98 | Improve how available storage is calculated |
| 2024‑01‑15 | 97 | Move initial tasks from installation file to sub scripts |
| 2024‑05‑21 | 91 | Improve multi-distribution compatibility |
| 2024‑05‑21 | 79 | Improve encryption reliability |
| 2023‑12‑11 | 68 | Enhance cryptographic validation of new scripts before updating |
| 2023‑11‑20 | 62 | Add inner layer of AES encryption in case TLS inspection doesn't allow for a secure connection |
| 2023‑11‑27 | 56 | Additional base cases for resiliancy |
| 2023‑11‑20 | 54 | Additional headers added to authentication process during installation. |
| 2023‑11‑20 | 53 | Enhanced key management |
| 2023‑11‑15 | 51 | Add insecure installation parameter to allow installation in environments with TLS inspection or other machine-in-the-middle situations. |
| 2023‑11‑06 | 42 | Enhance redundant encryption during installation. |
| 2023‑10‑30 | 33 | Improve install-over compatibility |
| 2023‑10‑23 | 18 | Add reboot configuration and scheduling |
| 2023‑10‑23 | 17 | Add self-updating functionality. |
| 2023‑10‑16 | 15 | Add Linux patching information for apt |
| 2023‑10‑09 | 14 | Collect system information |
| 2023‑10‑09 | 13 | Add Linux distribution information |
| 2023‑09‑30 | 12 | Add memory monitoring |
| 2023‑09‑30 | 10 | Add hardware information |
| 2023‑09‑23 | 9 | Add AWS information |
| 2023‑09‑23 | 8 | Add customized schedule capability for configuration updates |
| 2023‑09‑23 | 7 | Add support for package monitoring using package and dpkg logs |
| 2023‑09‑16 | 6 | Add storage data configuration gathering |
| 2023‑09‑16 | 5 | Add CPU information |
Lavawall® was built from the ground up with these concerns and the Minimum Viable Secure Product requirements in mind.
Some of the controls we implemented include:
- PassKeys as the preferred primary authentication at no additional cost
- Single Sign-on using modern, maintained, and industry-standard protocols for all customers at no additional cost
- Multi-Factor Authentication as a non-negotiable default
- Encrypting communications the same way as TLS again within the TLS tunnel, so we can allow TLS inspection without breaking like Huntress or disclosing security vulnerabilities to eavesdroppers.
- Encouraging external vulnerability reports and customer testing
- Passwords checked against popular disclosed passwords, hashed before they leave your computer, and then stored using Argon2id
- Not requiring the use of passwords at all. We consider them a temporary backup authentication in case you can't use passkeys or SSO.
Lavawall® databases and front-end systems are hosted with AWS in Montréal, Québec, Canada.
We send emails through AWS in Ireland and dedicated servers in Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
We send text messages for additional identity verification through Twilio in the United States.
We store executables and pass requests through Cloudflare at your nearest edge location.
We use Cloudflare for risk management, turnstile, and web application firewall services.
We use LeadPages for landing pages.
We use Google and Facebook for analytics on our public-facing pages, but they do not have access to the console.
We integrate with third-party tools, such as Microsoft, Google, Huntress, Screen Connect, Axcient, and Datto in their respective locations. However, you must initiate these integrations through single sign-on or by enabling them in your Lavawall® console.
Active security by design
Lavawall® is under active development with the latest release on
5+
Interfaces
350+
Monitored Applications
7+
System Metrics
Actively manage your IT with Lavawall®
Patching
Updates Beyond Windows
Lavawall® prevents the 80% of breaches and failed audits due to missing patches and updates.
You can reduce application patching delays from 67 days to nearly immediate with the 350+ applications that Lavawall® monitors and patches.
Patch release monitoring
Monitor everything without having to select packages or “managed applications”
Patch impact classification
Standard and optional Windows patches
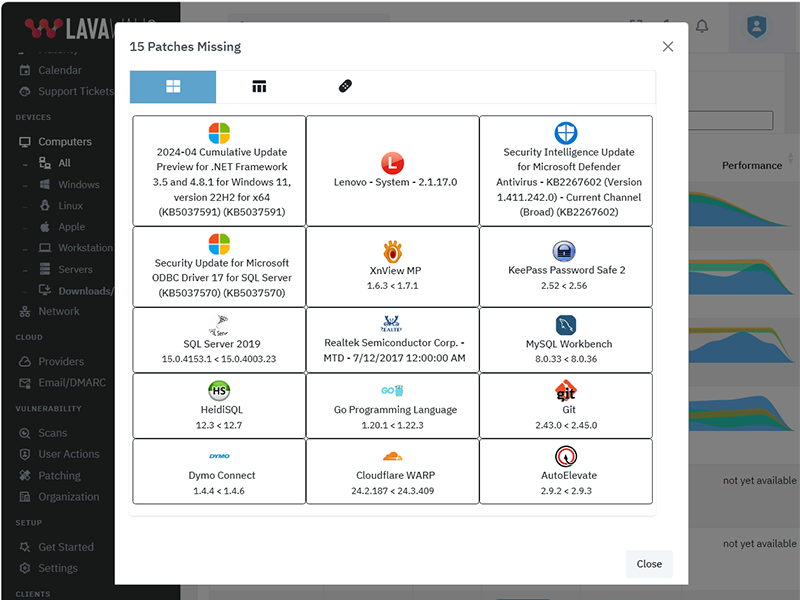
The above listing includes products that Lavawall® monitors through public information and/or proprietary statistical analysis.
Although we do have a partner relationship with some of the listed products and companies, they do not necessarily endorse Lavawall® or have integrations with our systems.
Learn More
Flexible Term; Flexible Service
Flexibility for your dynamic business
You need to get your arms around compliance and security and don't want to get locked into “high watermark” monthly invoices or multi-year contracts.
Pay-as-you-need monthly pricing
DIY, full management, and coaching options
CMMI, PCI, SOC2, Canadian Cybersecurity, Minimum Viable Secure Product, and other compliance support
Choose the plan that's right for you
Simple pricing. No hidden fees. Advanced features for you business.
Month
Annual
Get 2 months free with Annual!
DIY
Security-focused RMM
C$3.25 /computer/Month
C$32.50 /computer/Year
-
1 computer
or 1 of the following cloud integrations:
AWS, Axcient, Connectwise, Datto, Google, Huntress, M365, Sophos Central integrations
(each integration counts as 1 computer) -
50+ application patches
-
30-day Logs
-
Security configuration monitoring
-
Anomaly detection
-
CMMI, MVSP, CyberCanda compliance
-
Lavawall® support
-
Sophos MDR: C$13.50/desktopSophos MDR: C$162/desktop
-
Huntress: C$5.40/deviceHuntress: C$64.80/device
-
Available white-label support for end users
-
Level 3+ IT support for IT
-
Weekly IT coaching sessions
Managed Security & Support
Unlimited end-user support
C$160 /user/Month
C$1,600 /user/Year
-
1 computer/user
Additional devices charged at DIY prices -
AWS, Axcient, Connectwise, Datto, Google, Huntress, M365, Sophos Central integrations
-
350+ application patches
-
90-day Logs
-
Security configuration monitoring
-
Anomaly detection
-
CMMI, MVSP, CyberCanda compliance
-
Lavawall® support
-
Sophos MDR Essentials
-
Huntress
-
White-label email and phone support for end users
-
Level 3+ IT support for IT
-
Weekly IT coaching sessions
-
Automatic discount and upgrade to Support & Coaching after 15 users
Support & Coaching
Improve your IT performance
$2,250 /Month
$22,500 /Year
-
25 computers included
Additional computers charged at DIY prices -
AWS, Axcient, Connectwise, Datto, Google, Huntress, M365, Sophos Central integrations
-
350+ application patches
-
90-day Logs
-
Security configuration monitoring
-
Anomaly detection
-
CMMI, MVSP, CyberCanda compliance
-
Lavawall®-only support
-
Sophos MDR Essentials
-
Huntress
-
White-label email and phone support for 15 users included Additional: C$150/user Additional: C$1,500/user
-
L3 IT support for IT
-
Weekly IT coaching sessions
Frequently Asked Questions
If you can not find answer to your question in our FAQ, you can always contact us or email us. We will answer you shortly!
General Questions
- Two years after a missing Plex Media Server led to the LastPass breach, the
Remote Monitorign and Management (RMM) tools availabel for Manged IT Service Providers (MSPs)
still didn't monitor for it.
Going through industry-specific applications, we noticed many were missing from the big RMM and patching providers. MSPs, insurance providers, and organizations that put their cleints at risk need to know about these risks, which lead to the largest number of critical audit findings and breaches - After 20 years of writing the same audit findings about system configurations, Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliance, and missing patches, our technical co-founder wanted to make it easier fo avoid these findings
- The existing risk visibility tools for insurance underwriters took a shallow look at Internet-facing risks. They -- along with all businesses -- need a deeper view of the threats that could actually lead to breaches.
- Domain risks
- Operating System (OS) patches
- Application patches
- Network vulnerabilities
- Cloud vulnerabilities
- OS configurations
- Axcient*
- Cloudflare
- Connectwise Screen Connect
- Datto RMM
- FreshDesk*
- Huntress
- Microsoft 365
- Panorama9
- ZenDesk
You can use your own logo for the console and notifications. You can also use a CNAME to automatically brand your console.
Note: you cannot currently re-proxy the CNAME to Lavawall® through Cloudflare.
Lavawall® supports the following operating systems:
Lavawall® does not currently support non systemd distributions, such as Devuan, Artix Linux, PCLinuxOS, OpenWRT, and DD-WRT. However, we will support them by the end of 2024.
In June 2024, we combined the Windows and Linux systems for a consistent experience. This added support for RedHat and MacOS.
Privacy & Security
However, we do allow passwords and use passwords as part of the zero-knowledge encryption for your clients' sensitive data, such as Bitlocker keys and Personally-Identifiable Information (PII).
These passwords use Argon2id slow hashes with individual salts and peppers.
We have added an additional secure tunnel that mimics the TLS process within the public TLS tunnel. This extra tunnel provides authentication and privacy for the workstations and the Lavawall® servers to prevent attacks such as the one that took down Solar Winds.
Remote access is not enabled for read-only and audit situations.
Get In Touch
Have a quick question and don't want to talk? Send us a quick note with the form below and we'll reply within one business day.
NW Calgary:
ThreeShield Information Security Corporation
600 Crowfoot Crescent N.W., Suite 340
Calgary, Alberta
T3G 0B4
SE Calgary:
ThreeShield Information Security Corporation
105, 11500 - 29th St. SE
Calgary, Alberta
T2Z 3W9
Canada