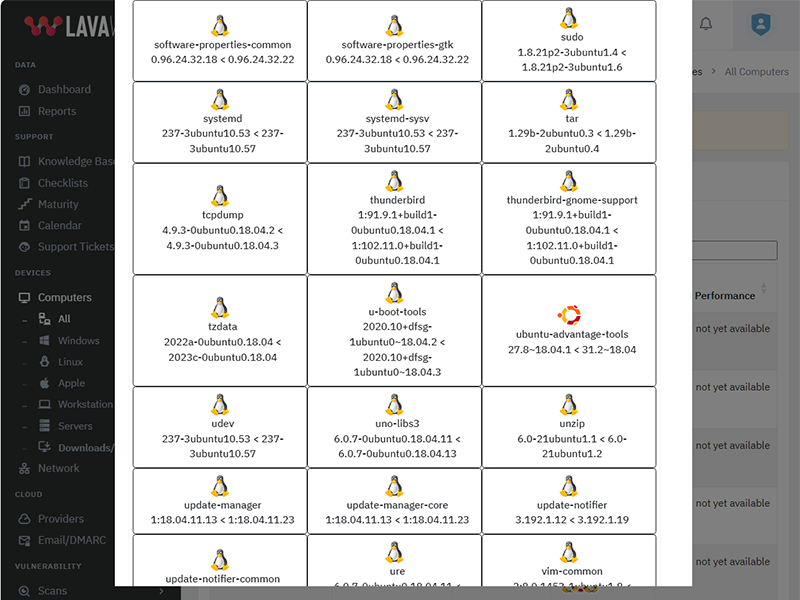
Update Google Chrome to version 132.0.6834.111
What patches are you missing?
CVE Vulnerabilities for Google Chrome
| CVE | Published | Severity | Details | Exploitability | Impact | Vector |
| CVE‑2025‑0437 | 2025‑01‑15 11:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read in Metrics in Google Chrome prior to 132.0.6834.83 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑9966 | 2024‑10‑15 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in Navigations in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.58 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 4 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑9965 | 2024‑10‑15 21:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in DevTools in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 130.0.6723.58 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑9964 | 2024‑10‑15 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Payments in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.58 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform UI spoofing via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑9963 | 2024‑10‑15 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.58 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑9962 | 2024‑10‑15 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Permissions in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.58 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑9958 | 2024‑10‑15 21:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in PictureInPicture in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.58 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑9954 | 2024‑10‑15 21:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in AI in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.58 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8909 | 2024‑09‑17 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in UI in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 129.0.6668.58 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8908 | 2024‑09‑17 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 129.0.6668.58 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8907 | 2024‑09‑17 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient data validation in Omnibox in Google Chrome on Android prior to 129.0.6668.58 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (XSS) via a crafted set of UI gestures. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8906 | 2024‑09‑17 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 129.0.6668.58 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8639 | 2024‑09‑11 14:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Autofill in Google Chrome on Android prior to 128.0.6613.137 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8638 | 2024‑09‑11 14:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.137 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8637 | 2024‑09‑11 14:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Media Router in Google Chrome on Android prior to 128.0.6613.137 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8636 | 2024‑09‑11 14:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.137 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8198 | 2024‑08‑28 23:15:06 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.113 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8194 | 2024‑08‑28 23:15:06 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.113 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8193 | 2024‑08‑28 23:15:05 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.113 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8035 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8034 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Custom Tabs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑8033 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebApp Installs in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious application to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7981 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Views in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7980 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient data validation in Installer in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a local attacker to perform privilege escalation via a crafted symbolic link. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2024‑7979 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient data validation in Installer in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a local attacker to perform privilege escalation via a crafted symbolic link. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2024‑7978 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Data Transfer in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7977 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient data validation in Installer in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a local attacker to perform privilege escalation via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2024‑7976 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in FedCM in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7975 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Permissions in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7974 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in V8 API in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7973 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7972 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7971 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7969 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7968 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker who had convinced the user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7967 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Fonts in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7966 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7965 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7964 | 2024‑08‑21 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Passwords in Google Chrome on Android prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7550 | 2024‑08‑06 21:16:04 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7536 | 2024‑08‑06 21:16:04 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7535 | 2024‑08‑06 21:16:04 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7534 | 2024‑08‑06 21:16:04 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Layout in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7533 | 2024‑08‑06 21:16:04 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sharing in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 127.0.6533.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7532 | 2024‑08‑06 21:16:04 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7255 | 2024‑08‑01 18:15:27 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read in WebTransport in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7005 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:51 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to bypass discretionary access control via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7004 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:51 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to bypass discretionary access control via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7003 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:51 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in FedCM in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7001 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:51 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in HTML in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑7000 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:51 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in CSS in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6999 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:51 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in FedCM in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6998 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:50 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in User Education in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6997 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:50 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tabs in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6996 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:50 | LOW (3) | Race in Frames in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 2 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6995 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:50 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in Fullscreen in Google Chrome on Android prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6994 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:50 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Layout in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6991 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:50 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Dawn in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6990 | 2024‑08‑01 18:15:27 | HIGH (9) | Uninitialized Use in Dawn in Google Chrome on Android prior to 127.0.6533.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6989 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:50 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Loader in Google Chrome prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6988 | 2024‑08‑06 16:15:50 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Downloads in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 127.0.6533.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6103 | 2024‑06‑20 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Dawn in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6102 | 2024‑06‑20 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in Dawn in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6101 | 2024‑06‑20 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.114 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑6100 | 2024‑06‑20 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.114 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5847 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:56 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5846 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5845 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Audio in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5844 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5843 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5842 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Browser UI in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5841 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5840 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | MEDIUM (7) | Policy bypass in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to bypass discretionary access control via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5839 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate Implementation in Memory Allocator in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5838 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5837 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5836 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate Implementation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to execute arbitrary code via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5835 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Tab Groups in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5834 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:55 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Dawn in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5833 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:54 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5832 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:54 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Dawn in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5831 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:54 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Dawn in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5830 | 2024‑06‑11 21:15:54 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 126.0.6478.54 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5500 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Sign-In in Google Chrome prior to 1.3.36.351 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑5274 | 2024‑05‑28 15:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 125.0.6422.112 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑4947 | 2024‑05‑15 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 125.0.6422.60 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑4761 | 2024‑05‑14 16:17:36 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.207 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑4671 | 2024‑05‑14 15:44:16 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Visuals in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.201 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑4058 | 2024‑05‑01 13:15:52 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.78 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3839 | 2024‑04‑17 08:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in Fonts in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.60 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3838 | 2024‑04‑17 08:15:10 | MEDIUM (6) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.60 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious app to perform UI spoofing via a crafted app. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2024‑3837 | 2024‑04‑17 08:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in QUIC in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.60 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3834 | 2024‑04‑17 08:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.60 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3176 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3175 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient data validation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform privilege escalation via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3174 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3173 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in Updater in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform OS-level privilege escalation via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3172 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3171 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 122.0.6261.57 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI gestures. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3170 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3169 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.139 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3168 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 122.0.6261.57 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3159 | 2024‑04‑06 15:15:27 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.105 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3158 | 2024‑04‑06 15:15:27 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑3156 | 2024‑04‑06 15:15:27 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑2884 | 2024‑07‑16 23:15:24 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.139 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑2631 | 2024‑03‑20 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in iOS in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.58 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑2630 | 2024‑03‑20 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in iOS in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.58 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑2629 | 2024‑03‑20 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in iOS in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.58 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑2628 | 2024‑03‑20 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.58 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted URL. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑2627 | 2024‑03‑20 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Canvas in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.58 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑2626 | 2024‑03‑20 17:15:07 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in Swiftshader in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.58 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑2625 | 2024‑03‑20 17:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Object lifecycle issue in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.58 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑1284 | 2024‑02‑07 00:15:56 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.160 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑1283 | 2024‑02‑07 00:15:56 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.160 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑12382 | 2024‑12‑12 01:40:29 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Translate in Google Chrome prior to 131.0.6778.139 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑12381 | 2024‑12‑12 01:40:29 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 131.0.6778.139 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑1077 | 2024‑01‑30 22:15:53 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Network in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.139 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑1060 | 2024‑01‑30 22:15:53 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Canvas in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.139 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑1059 | 2024‑01‑30 22:15:53 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Peer Connection in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.139 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit stack corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑10231 | 2024‑10‑22 22:15:04 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.69 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑10230 | 2024‑10‑22 22:15:04 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.69 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑10229 | 2024‑10‑22 22:15:03 | HIGH (8) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 130.0.6723.69 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0814 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Payments in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0813 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Reading Mode in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0812 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0811 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to leak cross-origin data via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0810 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to leak cross-origin data via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0809 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to bypass Autofill restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0808 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Integer underflow in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0807 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Web Audio in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0806 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Passwords in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0805 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted domain name. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0804 | 2024‑01‑24 00:15:08 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient policy enforcement in iOS Security UI in Google Chrome prior to 121.0.6167.85 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 4 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0519 | 2024‑01‑16 22:15:38 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.224 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0518 | 2024‑01‑16 22:15:38 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.224 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0517 | 2024‑01‑16 22:15:38 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.224 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0333 | 2024‑01‑10 22:15:51 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient data validation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.216 allowed an attacker in a privileged network position to install a malicious extension via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 2 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0225 | 2024‑01‑04 02:15:29 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebGPU in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.199 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0224 | 2024‑01‑04 02:15:29 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.199 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0223 | 2024‑01‑04 02:15:29 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.199 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2024‑0222 | 2024‑01‑04 02:15:29 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.199 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑7024 | 2023‑12‑21 23:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.129 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6707 | 2023‑12‑14 22:15:45 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in CSS in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.109 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6706 | 2023‑12‑14 22:15:45 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in FedCM in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.109 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6705 | 2023‑12‑14 22:15:45 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.109 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6704 | 2023‑12‑14 22:15:44 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in libavif in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.109 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted image file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6703 | 2023‑12‑14 22:15:44 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.109 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6702 | 2023‑12‑14 22:15:44 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.109 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6512 | 2023‑12‑06 02:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Web Browser UI in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof the contents of an iframe dialog context menu via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6511 | 2023‑12‑06 02:15:07 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass Autofill restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6510 | 2023‑12‑06 02:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Media Capture in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.62 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6509 | 2023‑12‑06 02:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Side Panel Search in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.62 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6508 | 2023‑12‑06 02:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Media Stream in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6351 | 2023‑11‑29 12:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in libavif in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.199 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted avif file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6350 | 2023‑11‑29 12:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in libavif in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.199 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted avif file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6348 | 2023‑11‑29 12:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in Spellcheck in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.199 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6347 | 2023‑11‑29 12:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.199 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6346 | 2023‑11‑29 12:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.199 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6345 | 2023‑11‑29 12:15:07 | CRITICAL (10) | Integer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.199 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑6112 | 2023‑11‑15 18:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.159 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5997 | 2023‑11‑15 18:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Garbage Collection in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.159 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5996 | 2023‑11‑08 20:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.123 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5859 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Picture In Picture in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted local HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5858 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebApp Provider in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5857 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially execute arbitrary code via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5856 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Side Panel in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5855 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Reading Mode in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI gestures. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5854 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Profiles in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI gestures. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5853 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5852 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Printing in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI gestures. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5851 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5850 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted domain name. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5849 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in USB in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5487 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Fullscreen in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5486 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Input in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5485 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker to bypass autofill restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5484 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5483 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Intents in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5482 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in USB in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5481 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5480 | 2023‑11‑01 18:15:10 | MEDIUM (6) | Inappropriate implementation in Payments in Google Chrome prior to 119.0.6045.105 allowed a remote attacker to bypass XSS preventions via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5479 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass an enterprise policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5478 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5477 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Installer in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a local attacker to bypass discretionary access control via a crafted command. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5476 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink History in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5475 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass discretionary access control via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5474 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5473 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (6) | Use after free in Cast in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5472 | 2023‑10‑25 18:17:44 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Profiles in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.117 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5346 | 2023‑10‑05 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.149 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5218 | 2023‑10‑11 23:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Site Isolation in Google Chrome prior to 118.0.5993.70 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5217 | 2023‑09‑28 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in vp8 encoding in libvpx in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.132 and libvpx 1.13.1 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5187 | 2023‑09‑28 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.132 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑5186 | 2023‑09‑28 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Passwords in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.132 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4909 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Interstitials in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4908 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Picture in Picture in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4907 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4906 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass Autofill restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4905 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4904 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass Enterprise policy restrictions via a crafted download. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4903 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Custom Mobile Tabs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4902 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Input in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4901 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4900 | 2023‑09‑12 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Custom Tabs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 117.0.5938.62 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate a permission prompt via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4863 | 2023‑09‑12 15:15:24 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in libwebp in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.187 and libwebp 1.3.2 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4764 | 2023‑09‑05 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in BFCache in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.179 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4763 | 2023‑09‑05 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Networks in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.179 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4762 | 2023‑09‑05 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.179 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4761 | 2023‑09‑05 22:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds memory access in FedCM in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.179 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4572 | 2023‑08‑29 20:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in MediaStream in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.140 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4431 | 2023‑08‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds memory access in Fonts in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.110 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4430 | 2023‑08‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Vulkan in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4429 | 2023‑08‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Loader in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4428 | 2023‑08‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds memory access in CSS in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.110 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4427 | 2023‑08‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.110 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4369 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in Systems Extensions in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 116.0.5845.120 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass file restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4368 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass an enterprise policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4367 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass an enterprise policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4366 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4365 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Fullscreen in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4364 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Permission Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4363 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebShare in Google Chrome on Android prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of a dialog URL via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4362 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Mojom IDL in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process and gained control of a WebUI process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4361 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome on Android prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass Autofill restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 4 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4360 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Color in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4359 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in App Launcher in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof elements of the security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 4 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4358 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DNS in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4357 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in XML in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file access restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4356 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Audio in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker who has convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4355 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4354 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4353 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4352 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4351 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Network in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker who has elicited a browser shutdown to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4350 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Fullscreen in Google Chrome on Android prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4349 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Device Trust Connectors in Google Chrome prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4078 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to inject scripts or HTML into a privileged page via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4077 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to inject scripts or HTML into a privileged page via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4076 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted WebRTC session. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4075 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Cast in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4074 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink Task Scheduling in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4073 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in ANGLE in Google Chrome on Mac prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4072 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read and write in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4071 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Visuals in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4070 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (8) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4069 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑4068 | 2023‑08‑03 01:15:12 | HIGH (8) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.170 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3742 | 2023‑12‑20 16:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in ADB in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a local attacker to bypass device policy restrictions via physical access to the device. (Chromium security severity: High) | 1 | 6 | PHYSICAL |
| CVE‑2023‑3740 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:34 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Themes in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to potentially serve malicious content to a user via a crafted background URL. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3739 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:34 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Chromad in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 115.0.5790.131 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted shell script. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3738 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3737 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Notifications in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of media notifications via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3736 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Custom Tabs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3735 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Web API Permission Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3734 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Picture In Picture in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3733 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:32 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebApp Installs in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3732 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3731 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Diagnostics in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 115.0.5790.131 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3730 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Groups in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3729 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Splitscreen in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 115.0.5790.131 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interactions. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3728 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:31 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3727 | 2023‑08‑01 23:15:31 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 115.0.5790.98 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3598 | 2023‑07‑28 21:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read and write in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3497 | 2023‑07‑03 17:15:10 | MEDIUM (5) | Out of bounds read in Google Security Processor firmware in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a local attacker to perform denial of service via physical access to the device. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 1 | 4 | PHYSICAL |
| CVE‑2023‑3422 | 2023‑06‑26 21:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Guest View in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.198 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3421 | 2023‑06‑26 21:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Media in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.198 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3420 | 2023‑06‑26 21:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.198 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3217 | 2023‑06‑13 18:15:22 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebXR in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.133 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3216 | 2023‑06‑13 18:15:22 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.133 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3215 | 2023‑06‑13 18:15:22 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.133 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3214 | 2023‑06‑13 18:15:22 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Autofill payments in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.133 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑3079 | 2023‑06‑05 22:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2941 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to spoof the contents of the UI via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2940 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass file access restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2939 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient data validation in Installer in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a local attacker to perform privilege escalation via crafted symbolic link. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2023‑2938 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Picture In Picture in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2937 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Picture In Picture in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2936 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2935 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2934 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2933 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2932 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2931 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2930 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2929 | 2023‑05‑30 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Swiftshader in Google Chrome prior to 114.0.5735.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2726 | 2023‑05‑16 19:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in WebApp Installs in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.126 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious web app to bypass install dialog via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2725 | 2023‑05‑16 19:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Guest View in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.126 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2724 | 2023‑05‑16 19:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.126 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2723 | 2023‑05‑16 19:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.126 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2722 | 2023‑05‑16 19:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Autofill UI in Google Chrome on Android prior to 113.0.5672.126 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2721 | 2023‑05‑16 19:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.126 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2468 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in PictureInPicture in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to obfuscate the security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2467 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Prompts in Google Chrome on Android prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed a remote attacker to bypass permissions restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2466 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2465 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2464 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in PictureInPicture in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to perform an origin spoof in the security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2463 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Full Screen Mode in Google Chrome on Android prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed a remote attacker to hide the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2462 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed a remote attacker to obfuscate main origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2461 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in OS Inputs in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to enage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2460 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:09 | HIGH (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass file access checks via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2459 | 2023‑05‑03 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 113.0.5672.63 allowed a remote attacker to bypass permission restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2458 | 2023‑05‑12 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ChromeOS Camera in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 113.0.5672.114 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2457 | 2023‑05‑12 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in ChromeOS Audio Server in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 113.0.5672.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted audio file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2314 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2313 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Sandbox in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform arbitrary read/write via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2312 | 2023‑08‑15 18:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Offline in Google Chrome on Android prior to 116.0.5845.96 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2311 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2137 | 2023‑04‑19 04:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in sqlite in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.137 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2136 | 2023‑04‑19 04:15:32 | CRITICAL (10) | Integer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.137 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2135 | 2023‑04‑19 04:15:32 | HIGH (8) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.137 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to enable specific preconditions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2134 | 2023‑04‑19 04:15:31 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in Service Worker API in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.137 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2133 | 2023‑04‑19 04:15:31 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in Service Worker API in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.137 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑2033 | 2023‑04‑14 19:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.121 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1823 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in FedCM in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1822 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1821 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in WebShare in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to potentially hide the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1820 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Browser History in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1819 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1818 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Vulkan in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1817 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1816 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Picture In Picture in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform navigation spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1815 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Networking APIs in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1814 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:07 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to bypass download checking via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1813 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:07 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass file access restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1812 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in DOM Bindings in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1811 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Frames in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1810 | 2023‑04‑04 22:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Visuals in Google Chrome prior to 112.0.5615.49 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1534 | 2023‑03‑21 21:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.110 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1533 | 2023‑03‑21 21:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebProtect in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1532 | 2023‑03‑21 21:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read in GPU Video in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1531 | 2023‑03‑21 21:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1530 | 2023‑03‑21 21:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1529 | 2023‑03‑21 21:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Out of bounds memory access in WebHID in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a malicious HID device. (Chromium security severity: High) | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1528 | 2023‑03‑21 21:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Passwords in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.110 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1236 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Internals in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the origin of an iframe via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1235 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:11 | MEDIUM (6) | Type confusion in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1234 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1233 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Resource Timing in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information from API via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1232 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Resource Timing in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from API via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1231 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome on Android prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof the contents of the omnibox via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1230 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebApp Installs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious WebApp to spoof the contents of the PWA installer via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1229 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Permission prompts in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1228 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1227 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Core in Google Chrome on Lacros prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1226 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Web Payments API in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1225 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Navigation in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1224 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Web Payments API in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1223 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Autofill in Google Chrome on Android prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1222 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Web Audio API in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1221 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1220 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in UMA in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1219 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Metrics in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1218 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1217 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Stack buffer overflow in Crash reporting in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1216 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker who had convienced the user to engage in direct UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1215 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in CSS in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1214 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑1213 | 2023‑03‑07 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Swiftshader in Google Chrome prior to 111.0.5563.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0941 | 2023‑02‑22 20:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.177 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0933 | 2023‑02‑22 20:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.177 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0932 | 2023‑02‑22 20:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 110.0.5481.177 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0931 | 2023‑02‑22 20:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Video in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.177 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0930 | 2023‑02‑22 20:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Video in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.177 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0929 | 2023‑02‑22 20:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Vulkan in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.177 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0928 | 2023‑02‑22 20:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.177 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0927 | 2023‑02‑22 20:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Web Payments API in Google Chrome on Android prior to 110.0.5481.177 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0705 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in Core in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker who had one a race condition to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0704 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy and proxy settings via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0703 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via UI interactions. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0702 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in Data Transfer in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0701 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via UI interaction . (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0700 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Download in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0699 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in GPU in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page and browser shutdown. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0698 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0697 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Full screen mode in Google Chrome on Android prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0696 | 2023‑02‑07 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 110.0.5481.77 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0474 | 2023‑01‑30 09:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in GuestView in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.119 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a Chrome web app. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0473 | 2023‑01‑30 09:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in ServiceWorker API in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0472 | 2023‑01‑30 09:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0471 | 2023‑01‑30 09:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebTransport in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0141 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0140 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in in File System API in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file system restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0139 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Downloads in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to bypass download restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0138 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in libphonenumber in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0137 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Platform Apps in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0136 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in in Fullscreen API in Google Chrome on Android prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to execute incorrect security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0135 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Cart in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via database corruption and a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0134 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Cart in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via database corruption and a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0133 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in in Permission prompts in Google Chrome on Android prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to bypass main origin permission delegation via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0132 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in in Permission prompts in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to force acceptance of a permission prompt via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0131 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in in iframe Sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file download restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0130 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in in Fullscreen API in Google Chrome on Android prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0129 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Network Service in Google Chrome prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page and specific interactions. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2023‑0128 | 2023‑01‑10 20:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Overview Mode in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 109.0.5414.74 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4955 | 2023‑08‑04 20:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass file access restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4926 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 109.0.5414.119 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4925 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in QUIC in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to perform header splitting via malicious network traffic. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4924 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4923 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | LOW (3) | Inappropriate implementation in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed an attacker in a privileged network position to perform a man-in-the-middle attack via malicious network traffic. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 1 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4922 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to perform UI spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4921 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4920 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4919 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Base Internals in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4918 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in UI in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4917 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Notifications in Google Chrome on Android prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker to obscure the full screen notification via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4916 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Media in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4915 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in URL Formatting in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.134 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4914 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in PrintPreview in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4913 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to spoof extension storage via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4912 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in MathML in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4911 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4910 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4909 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (6) | Inappropriate implementation in XML in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform an ASLR bypass via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4908 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in iFrame Sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4907 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Uninitialized Use in FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4906 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4452 | 2023‑08‑25 15:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in crosvm in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4440 | 2022‑12‑14 06:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Profiles in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.124 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4439 | 2022‑12‑14 06:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Aura in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 108.0.5359.124 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4438 | 2022‑12‑14 06:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink Frames in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.124 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4437 | 2022‑12‑14 06:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Mojo IPC in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.124 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4436 | 2022‑12‑14 06:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink Media in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.124 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4262 | 2022‑12‑02 21:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.94 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4195 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to bypass Safe Browsing warnings via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4194 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4193 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file system restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4192 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Live Caption in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4191 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sign-In in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via profile destruction. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4190 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in Directory in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file system restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4189 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4188 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in CORS in Google Chrome on Android prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4187 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4186 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass Downloads restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4185 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Navigation in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the modal dialogue via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4184 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to bypass autofill restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4183 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Popup Blocker in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4182 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Fenced Frames in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to bypass fenced frame restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4181 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Forms in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4180 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4179 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Audio in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4178 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4177 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install an extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension and UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4176 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Lacros Graphics in Google Chrome on Chrome OS and Lacros prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via UI interactions. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4175 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Camera Capture in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4174 | 2022‑11‑30 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 108.0.5359.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4135 | 2022‑11‑25 01:15:10 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in GPU in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.121 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑4025 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Paint in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data outside an iframe via a crafted HTML page. (Chrome security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3890 | 2022‑11‑09 04:15:10 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in Crashpad in Google Chrome on Android prior to 107.0.5304.106 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3889 | 2022‑11‑09 04:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.106 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3888 | 2022‑11‑09 04:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebCodecs in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.106 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3887 | 2022‑11‑09 04:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Web Workers in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.106 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3886 | 2022‑11‑09 04:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Speech Recognition in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.106 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3885 | 2022‑11‑09 04:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.106 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3863 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (6) | Use after free in Browser History in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chrome security severity: High) | 2 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3842 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:11 | HIGH (8) | Use after free in Passwords in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.125 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3723 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:20 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3661 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:20 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to leak cross-origin data via a crafted Chrome extension. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3660 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Full screen mode in Google Chrome on Android prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to hide the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3659 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Accessibility in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3658 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Feedback service on Chrome OS in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3657 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3656 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in File System in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file system restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3655 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Media Galleries in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3654 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Layout in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3653 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Vulkan in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3652 | 2022‑11‑01 23:15:19 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 107.0.5304.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3450 | 2022‑11‑09 19:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Peer Connection in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3449 | 2022‑11‑09 19:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.119 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3448 | 2022‑11‑09 19:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Permissions API in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.119 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3447 | 2022‑11‑09 19:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Custom Tabs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 106.0.5249.119 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3446 | 2022‑11‑09 19:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebSQL in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3445 | 2022‑11‑09 19:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3444 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:22 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass File System restrictions via a crafted HTML page and malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3443 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:22 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass File System restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3373 | 2022‑11‑01 03:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.91 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3370 | 2022‑11‑01 03:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Custom Elements in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.91 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3318 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:22 | MEDIUM (4) | Use after free in ChromeOS Notifications in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to reboot Chrome OS to potentially exploit heap corruption via UI interaction. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3317 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:22 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3316 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:22 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass security feature via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3315 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:22 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3314 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:22 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in logging in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised a WebUI process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3313 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:22 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in full screen in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3312 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:21 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in VPN in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a local attacker to bypass managed device restrictions via physical access to the device. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 1 | 4 | PHYSICAL |
| CVE‑2022‑3311 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:21 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in import in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised a WebUI process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3310 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:21 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in custom tabs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed an attacker who convinced the user to install an application to bypass same origin policy via a crafted application. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3309 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:21 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in assistant in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI gestures to potentially perform a sandbox escape via specific UI gestures. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3308 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:21 | HIGH (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3307 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:21 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3306 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:21 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in survey in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3305 | 2022‑11‑01 20:15:21 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in survey in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3304 | 2022‑11‑01 19:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in CSS in Google Chrome prior to 106.0.5249.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3201 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:14 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in DevTools in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 105.0.5195.125 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3200 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Internals in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3199 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Frames in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3198 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3197 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3196 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3195 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Storage in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.125 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3075 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Insufficient data validation in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.102 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3071 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Strip in Google Chrome on Chrome OS, Lacros prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3058 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sign-In Flow in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3057 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in iframe Sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3056 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Content Security Policy in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3055 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Passwords in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3054 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3053 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Pointer Lock in Google Chrome on Mac prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to restrict user navigation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3052 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Window Manager in Google Chrome on Chrome OS, Lacros prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3051 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Exosphere in Google Chrome on Chrome OS, Lacros prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3050 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebUI in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3049 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in SplitScreen in Google Chrome on Chrome OS, Lacros prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3048 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Chrome OS lockscreen in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a local attacker to bypass lockscreen navigation restrictions via physical access to the device. | 1 | 6 | PHYSICAL |
| CVE‑2022‑3047 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass downloads policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3046 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Browser Tag in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3045 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3044 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Site Isolation in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3043 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Screen Capture in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3042 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PhoneHub in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3041 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebSQL in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3040 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Layout in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3039 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebSQL in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑3038 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Network Service in Google Chrome prior to 105.0.5195.52 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2998 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Browser Creation in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker who had convinced a user to engage in a specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2861 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to inject arbitrary scripts into WebUI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2860 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Cookies in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker to bypass cookie prefix restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2859 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Chrome OS Shell in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2858 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sign-In Flow in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2857 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2856 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker to arbitrarily browse to a malicious website via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2855 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2854 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2853 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Downloads in Google Chrome on Android prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2852 | 2022‑09‑26 16:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in FedCM in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2743 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in Window Manager in Google Chrome on Chrome OS and Lacros prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to perform an out of bounds memory write via crafted UI interactions. (Chrome security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2742 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Exosphere in Google Chrome on Chrome OS and Lacros prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted UI interactions. (Chrome security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2624 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2623 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Offline in Google Chrome on Android prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2622 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to bypass download restrictions via a crafted file. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2621 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2620 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebUI in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2619 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Settings in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to inject scripts or HTML into a privileged page via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2618 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Internals in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to bypass download restrictions via a malicious file . | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2617 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2616 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2615 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Cookies in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2614 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sign-In Flow in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2613 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Input in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to enage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2612 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Side-channel information leakage in Keyboard input in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2611 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Fullscreen API in Google Chrome on Android prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2610 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Background Fetch in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2609 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Nearby Share in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2608 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Overview Mode in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2607 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Strip in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2606 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Managed devices API in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to enable a specific Enterprise policy to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2605 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in Dawn in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2604 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2603 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 104.0.5112.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2587 | 2022‑08‑12 20:15:09 | CRITICAL (10) | Out of bounds write in Chrome OS Audio Server in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 102.0.5005.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted audio metadata. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2481 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Views in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.134 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via UI interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2480 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Service Worker API in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.134 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2479 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in File in Google Chrome on Android prior to 103.0.5060.134 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious app to obtain potentially sensitive information from internal file directories via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2478 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.134 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2477 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Guest View in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.134 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2415 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2399 | 2022‑07‑28 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebGPU in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2296 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Chrome OS Shell in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 103.0.5060.114 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via direct UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2295 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2294 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2165 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in URL formatting in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2164 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | MEDIUM (6) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass discretionary access control via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2163 | 2022‑07‑28 02:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Cast UI and Toolbar in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.134 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via UI interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2162 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file system access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2161 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebApp Provider in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific UI interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2160 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information from a user's local files via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2158 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2157 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Interest groups in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2156 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Core in Google Chrome prior to 103.0.5060.53 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2011 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.115 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2010 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | CRITICAL (9) | Out of bounds read in compositing in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.115 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2008 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Double free in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.115 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑2007 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebGPU in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.115 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1919 | 2022‑07‑28 01:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Codecs in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1876 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1875 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1874 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome on Mac prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to bypass downloads protection policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1873 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in COOP in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1872 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass downloads policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1871 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass file system policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1870 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in App Service in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1869 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1868 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1867 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Data Transfer in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted clipboard content. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1866 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tablet Mode in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1865 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension and specific user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1864 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebApp Installs in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension and specific user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1863 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Groups in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension and specific user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1862 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass profile restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1861 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sharing in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to enage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1860 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in UI Foundations in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1859 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Performance Manager in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1858 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via specific user interaction. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1857 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file system restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1856 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in User Education in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension or specific user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1855 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Messaging in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1854 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1853 | 2022‑07‑27 22:15:09 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Indexed DB in Google Chrome prior to 102.0.5005.61 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1641 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Web UI Diagnostics in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1640 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sharing in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1639 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1638 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in V8 Internationalization in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1637 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Web Contents in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1636 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Performance APIs in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1635 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Permission Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1634 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Browser UI in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker who had convinced a user to engage in specific UI interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1633 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sharesheet in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 101.0.4951.64 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific UI interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1501 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in iframe in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1500 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in Dev Tools in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1499 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (6) | Inappropriate implementation in WebAuthentication in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1498 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in HTML Parser in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1497 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Input in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of cross-origin websites via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1496 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in File Manager in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific and direct user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1495 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Downloads in Google Chrome on Android prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the APK downloads dialog via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1494 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient data validation in Trusted Types in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to bypass trusted types policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1493 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Dev Tools in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific and direct user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1492 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient data validation in Blink Editing in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1491 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific and direct user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1490 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Browser Switcher in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1489 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in UI Shelf in Google Chrome on Chrome OS, Lacros prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1488 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to leak cross-origin data via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1487 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Use after free in Ozone in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via running a Wayland test. | 4 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1486 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1485 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Use after free in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1484 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Web UI Settings in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1483 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebGPU in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1482 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1481 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sharing in Google Chrome on Mac prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1479 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1478 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1477 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Vulkan in Google Chrome prior to 101.0.4951.41 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1364 | 2022‑07‑26 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 Turbofan in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.127 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1314 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1313 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in tab groups in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1312 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:11 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in storage in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1311 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in shell in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1310 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in regular expressions in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1309 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:11 | CRITICAL (10) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1308 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in BFCache in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1307 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in full screen in Google Chrome on Android prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1306 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in compositing in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1305 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in storage in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1232 | 2022‑07‑25 14:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1146 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Resource Timing in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1145 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interaction and profile destruction. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1144 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific input into DevTools. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1143 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific input into DevTools. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1142 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific input into DevTools. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1141 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in File Manager in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user gesture. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1139 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Background Fetch API in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1138 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Web Cursor in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to obscure the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1137 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to leak potentially sensitive information via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1136 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific set of user gestures. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1135 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Shopping Cart in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via standard feature user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1134 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1133 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC Perf in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1132 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (6) | Inappropriate implementation in Virtual Keyboard in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a local attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via physical access to the device. | 1 | 5 | PHYSICAL |
| CVE‑2022‑1131 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Cast UI in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1130 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient validation of trust input in WebOTP in Google Chrome on Android prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker to send arbitrary intents from any app via a malicious app. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1129 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Full Screen Mode in Google Chrome on Android prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1128 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Web Share API in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed an attacker on the local network segment to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1127 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in QR Code Generator in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1125 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Portals in Google Chrome prior to 100.0.4896.60 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑1096 | 2022‑07‑23 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0980 | 2022‑07‑22 17:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in New Tab Page in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0979 | 2022‑07‑22 17:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome on Android prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0978 | 2022‑07‑22 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0977 | 2022‑07‑21 23:15:09 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Browser UI in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0976 | 2022‑07‑21 23:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in GPU in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0975 | 2022‑07‑21 23:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0974 | 2022‑07‑21 23:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Splitscreen in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0973 | 2022‑07‑21 23:15:09 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0972 | 2022‑07‑21 23:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0971 | 2022‑07‑21 23:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink Layout in Google Chrome on Android prior to 99.0.4844.74 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0809 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in WebXR in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0808 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Chrome OS Shell in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in a series of user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0807 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0806 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Data leak in Canvas in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in screen sharing to potentially leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0805 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Browser Switcher in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0804 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Full screen mode in Google Chrome on Android prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to hide the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0803 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Permissions in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to tamper with the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0802 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Full screen mode in Google Chrome on Android prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to hide the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0801 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (6) | Inappropriate implementation in HTML parser in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to bypass XSS preventions via a crafted HTML page. (Chrome security severity: Medium) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0800 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Cast UI in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0799 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Installer in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to perform local privilege escalation via a crafted offline installer file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0798 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in MediaStream in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0797 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0796 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Media in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0795 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in Blink Layout in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0794 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebShare in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0793 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Cast in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension and engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0792 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0791 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0790 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Cast UI in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0789 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 99.0.4844.51 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0610 | 2022‑04‑05 00:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Gamepad API in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.102 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0609 | 2022‑04‑05 00:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Animation in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.102 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0608 | 2022‑04‑05 00:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.102 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0607 | 2022‑04‑05 00:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in GPU in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.102 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0606 | 2022‑04‑05 00:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.102 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0605 | 2022‑04‑05 00:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Webstore API in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.102 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension and convinced a user to enage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0604 | 2022‑04‑05 00:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Tab Groups in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.102 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension and engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0603 | 2022‑04‑05 00:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in File Manager in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 98.0.4758.102 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0470 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0469 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Cast in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0468 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Payments in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0467 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Pointer Lock in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0466 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Inappropriate implementation in Extensions Platform in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0465 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0464 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0463 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via user interaction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0462 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Scroll in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0461 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Policy bypass in COOP in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to bypass iframe sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 4 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0460 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Window Dialogue in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0459 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Screen Capture in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process and convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0458 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Thumbnail Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0457 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0456 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Web Search in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via profile destruction. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0455 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Full Screen Mode in Google Chrome on Android prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0454 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0453 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Reader Mode in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0452 | 2022‑04‑05 01:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 98.0.4758.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0337 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in File System API in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information via a crafted HTML page. (Chrome security severity: High) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0311 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Task Manager in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0310 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Task Manager in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user interactions. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0309 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0308 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Data Transfer in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0307 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Optimization Guide in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interaction to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0306 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0305 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Service Worker API in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0304 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0302 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0301 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (8) | Heap buffer overflow in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2022‑0300 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Text Input Method Editor in Google Chrome on Android prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0298 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Scheduling in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0297 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Vulkan in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0296 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Printing in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to engage is specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0295 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to engage is specific user interactions to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0294 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Push messaging in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0293 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Web packaging in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0292 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Fenced Frames in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0291 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Storage in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0290 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Site isolation in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0289 | 2022‑02‑12 02:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Safe browsing in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0120 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Passwords in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak cross-origin data via a malicious website. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0118 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebShare in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially hide the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0117 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Policy bypass in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0116 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Compositing in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0115 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Uninitialized use in File API in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0114 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds memory access in Blink Serial API in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page and virtual serial port driver. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0113 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0112 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Browser UI in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to display missing URL or incorrect URL via a crafted URL. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0111 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to incorrectly set origin via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0110 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0109 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0108 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0107 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in File Manager API in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0106 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to perform specific user gesture to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0105 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0104 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0103 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0102 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0101 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to perform specific user gesture to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user gesture. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0100 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Media streams API in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0099 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sign-in in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to perform specific user gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user gesture. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0098 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Screen Capture in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to perform specific user gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user gestures. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0097 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | CRITICAL (10) | Inappropriate implementation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to to potentially allow extension to escape the sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2022‑0096 | 2022‑02‑12 00:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Storage in Google Chrome prior to 97.0.4692.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4324 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Google Update in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.93 allowed a remote attacker to read arbitrary files via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4323 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to access local files via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4322 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to execute arbitrary code via a crafted Chrome Extension. (Chromium security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4321 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Policy bypass in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4320 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4319 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4318 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Object corruption in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4317 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4316 | 2023‑07‑29 00:15:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Cast UI in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to spoof browser UI via a crafted HTML page. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4102 | 2022‑02‑11 23:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4101 | 2022‑02‑11 23:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Swiftshader in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4100 | 2022‑02‑11 23:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Object lifecycle issue in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4099 | 2022‑02‑11 23:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Swiftshader in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4098 | 2022‑02‑11 23:15:08 | HIGH (7) | Insufficient data validation in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.110 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4079 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted WebRTC packets. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4078 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4068 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in new tab page in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4067 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in window manager in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4066 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Integer underflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4065 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4064 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in screen capture in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4063 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4062 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in BFCache in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4061 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4059 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in loader in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4058 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4057 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in file API in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4056 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in loader in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4055 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4054 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4053 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in UI in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑4052 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in web apps in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.93 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38022 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in WebAuthentication in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38021 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in referrer in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38020 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in contacts picker in Google Chrome on Android prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38019 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38018 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38017 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in iframe sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38016 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in background fetch in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38015 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in input in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38014 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Swiftshader in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38013 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in fingerprint recognition in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised a WebUI renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38012 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38011 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in storage foundation in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38010 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in service workers in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38009 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in cache in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38008 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38007 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38006 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in storage foundation in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38005 | 2021‑12‑23 01:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in loader in Google Chrome prior to 96.0.4664.45 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38004 | 2021‑11‑23 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.69 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38003 | 2021‑11‑23 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.69 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38002 | 2021‑11‑23 22:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Web Transport in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.69 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38001 | 2021‑11‑23 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.69 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑38000 | 2021‑11‑23 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 95.0.4638.69 allowed a remote attacker to arbitrarily browser to a malicious URL via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37999 | 2021‑11‑23 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient data validation in New Tab Page in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.69 allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML in a new browser tab via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37998 | 2021‑11‑23 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Garbage Collection in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.69 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37997 | 2021‑11‑23 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sign-In in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.69 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to sign into Chrome to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37996 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a malicious file. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑37995 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in WebApp Installer in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially overlay and spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37994 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in iFrame Sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37993 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDF Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37992 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37991 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Race in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37990 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (6) | Inappropriate implementation in WebView in Google Chrome on Android prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted app. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑37989 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to abuse content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37988 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Profiles in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to engage in specific gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37987 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Network APIs in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37986 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Settings in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to engage with Dev Tools to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37985 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker who had convinced a user to allow for connection to debugger to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37984 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37983 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Dev Tools in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37982 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Incognito in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37981 | 2021‑11‑02 22:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 95.0.4638.54 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37980 | 2021‑11‑02 21:15:08 | HIGH (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially bypass site isolation via Windows. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37979 | 2021‑11‑02 21:15:08 | HIGH (9) | heap buffer overflow in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.81 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to browse to a malicious website to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37978 | 2021‑11‑02 21:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37977 | 2021‑11‑02 21:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Garbage Collection in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37976 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Memory in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.71 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37975 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.71 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37974 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Safebrowsing in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.71 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37973 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Portals in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.61 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37972 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read in libjpeg-turbo in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37971 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Web Browser UI in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37970 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37969 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (8) | Inappropriate implementation in Google Updater in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to perform local privilege escalation via a crafted file. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑37968 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Background Fetch API in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37967 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Background Fetch API in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37966 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Compositing in Google Chrome on Android prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37965 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Background Fetch API in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37964 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | LOW (3) | Inappropriate implementation in ChromeOS Networking in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed an attacker with a rogue wireless access point to to potentially carryout a wifi impersonation attack via a crafted ONC file. | 2 | 1 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑37963 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Side-channel information leakage in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37962 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Performance Manager in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37961 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37959 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Task Manager in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to enage in a series of user gestures to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37958 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in Navigation in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to inject scripts or HTML into a privileged page via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37957 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebGPU in Google Chrome prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑37956 | 2021‑10‑08 22:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Offline use in Google Chrome on Android prior to 94.0.4606.54 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30633 | 2021‑10‑08 21:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Indexed DB API in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30632 | 2021‑10‑08 21:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30630 | 2021‑10‑08 21:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30629 | 2021‑10‑08 21:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Permissions in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30628 | 2021‑10‑08 21:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Stack buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit stack corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30627 | 2021‑10‑08 21:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in Blink layout in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30626 | 2021‑10‑08 21:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30625 | 2021‑10‑08 21:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Selection API in Google Chrome prior to 93.0.4577.82 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user the visit a malicious website to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30604 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.159 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30603 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Data race in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.159 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30602 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.159 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to visit a malicious website to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30601 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.159 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30600 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Printing in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.159 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30599 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.159 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30598 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.159 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30597 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in Browser UI in Google Chrome on Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.131 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via physical access to the device. | 1 | 6 | PHYSICAL |
| CVE‑2021‑30596 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Navigation in Google Chrome on Android prior to 92.0.4515.131 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30594 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in Page Info UI in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.131 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via physical access to the device. | 1 | 6 | PHYSICAL |
| CVE‑2021‑30593 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds read in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.131 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30592 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Tab Groups in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.131 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30591 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.131 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30590 | 2021‑08‑26 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.131 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30589 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Sharing in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted click-to-call link. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30588 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30587 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Compositing in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30586 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in dialog box handling in Windows in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30585 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in sensor handling in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30584 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Downloads in Google Chrome on Android prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30583 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in image handling in iOS in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30582 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Animation in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30581 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30580 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Android intents in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious application to obtain potentially sensitive information via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30579 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in UI framework in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30578 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Uninitialized use in Media in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30577 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Installer in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to perform local privilege escalation via a crafted file. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑30576 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30575 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30574 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in protocol handling in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30573 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in GPU in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30572 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30571 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | CRITICAL (10) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30569 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in sqlite in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30568 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30567 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to open DevTools to potentially exploit heap corruption via specific user gesture. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30566 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Stack buffer overflow in Printing in Google Chrome prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit stack corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30565 | 2021‑08‑03 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Tab Groups in Google Chrome on Linux and ChromeOS prior to 92.0.4515.107 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30564 | 2021‑08‑03 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebXR in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.164 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30563 | 2021‑08‑03 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.164 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30562 | 2021‑08‑03 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebSerial in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.164 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30561 | 2021‑08‑03 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.164 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30560 | 2021‑08‑03 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink XSLT in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.164 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30559 | 2021‑08‑03 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.164 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30558 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:10 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in content security policy in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. (Chrome security severity: Medium) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30557 | 2021‑07‑02 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in TabGroups in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.114 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30556 | 2021‑07‑02 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30555 | 2021‑07‑02 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Sharing in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.114 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page and user gesture. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30554 | 2021‑07‑02 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30553 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Network service in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30552 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30551 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30550 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30549 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Spell check in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30548 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Loader in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30547 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30546 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30545 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30544 | 2021‑06‑15 22:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in BFCache in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.101 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30543 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30542 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30541 | 2021‑08‑03 19:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.164 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30540 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in payments in Google Chrome on Android prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30539 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient policy enforcement in content security policy in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30538 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in content security policy in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30537 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in cookies in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass cookie policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30536 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds read in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit stack corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30535 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Double free in ICU in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30534 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in iFrameSandbox in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30533 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in PopupBlocker in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted iframe. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30532 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Content Security Policy in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30531 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Content Security Policy in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30530 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30529 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30528 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAuthentication in Google Chrome on Android prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process of a user who had saved a credit card in their Google account to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30527 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30526 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in TabStrip in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30525 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in TabGroups in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30524 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in TabStrip in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30523 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted SCTP packet. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30522 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30521 | 2021‑06‑07 20:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Autofill in Google Chrome on Android prior to 91.0.4472.77 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30520 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30519 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Payments in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious payments app to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30518 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Reader Mode in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30517 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30516 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in History in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30515 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in File API in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30514 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30513 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30512 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Notifications in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30511 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds read in Tab Groups in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30510 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Aura in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30509 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page and a crafted Chrome extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30508 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Media Feeds in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to enable certain features in Chrome to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30507 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Offline in Google Chrome on Android prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑30506 | 2021‑06‑04 18:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Incorrect security UI in Web App Installs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 90.0.4430.212 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a web application to inject scripts or HTML into a privileged page via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21233 | 2021‑04‑30 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 90.0.4430.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21232 | 2021‑04‑30 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Dev Tools in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21231 | 2021‑04‑30 21:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21230 | 2021‑04‑30 21:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21229 | 2021‑04‑30 21:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in downloads in Google Chrome on Android prior to 90.0.4430.93 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21228 | 2021‑04‑30 21:15:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.93 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21227 | 2021‑04‑30 21:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.93 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21226 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.85 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21225 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.85 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21224 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.85 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21223 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | CRITICAL (10) | Integer overflow in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.85 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21222 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.85 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21221 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21220 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.128 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21219 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | MEDIUM (6) | Uninitialized data in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑21218 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | MEDIUM (6) | Uninitialized data in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑21217 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:09 | MEDIUM (6) | Uninitialized data in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑21216 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21215 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21214 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Network API in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21213 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebMIDI in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21212 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Network Config UI in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially compromise WiFi connection security via a malicious WAP. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21211 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Navigation in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21210 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Network in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially access local UDP ports via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21209 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in storage in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21208 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in QR scanner in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed an attacker displaying a QR code to perform domain spoofing via a crafted QR code. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21207 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in IndexedDB in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑21206 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.128 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21205 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigation in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21204 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21203 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21202 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑21201 | 2021‑04‑26 17:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in permissions in Google Chrome prior to 90.0.4430.72 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21200 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:10 | MEDIUM (5) | Out of bounds read in WebUI Settings in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. (Chrome security severity: Low) | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21199 | 2021‑04‑09 22:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Aura in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21198 | 2021‑04‑09 22:15:18 | HIGH (7) | Out of bounds read in IPC in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21197 | 2021‑04‑09 22:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in TabStrip in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21196 | 2021‑04‑09 22:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in TabStrip in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21195 | 2021‑04‑09 22:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21194 | 2021‑04‑09 22:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in screen sharing in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.114 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21193 | 2021‑03‑16 15:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21192 | 2021‑03‑16 15:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in tab groups in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21191 | 2021‑03‑16 15:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21190 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Uninitialized data in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21189 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:18 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in payments in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21188 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21187 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:18 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in URL formatting in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21186 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:18 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in QR scanning in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed an attacker who convinced the user to scan a QR code to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted QR code. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21185 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:18 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain sensitive information via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21184 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:18 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in performance APIs in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21183 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in performance APIs in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21182 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigations in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21181 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Side-channel information leakage in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21180 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in tab search in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21179 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Network Internals in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21178 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Compositing in Google Chrome on Linux and Windows prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21177 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21176 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in full screen mode in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21175 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Site isolation in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21174 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Referrer in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21173 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Side-channel information leakage in Network Internals in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21172 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21171 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in TabStrip and Navigation in Google Chrome on Android prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21170 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Loader in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21169 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21168 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in appcache in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21167 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21166 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Data race in audio in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21165 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Data race in audio in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21164 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in Chrome on iOS in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21163 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in Reader Mode in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page and a malicious server. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21162 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21161 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in TabStrip in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21160 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21159 | 2021‑03‑09 18:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in TabStrip in Google Chrome prior to 89.0.4389.72 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21157 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Web Sockets in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21156 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted script. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21155 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in Tab Strip in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21154 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in Tab Strip in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21153 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Stack buffer overflow in GPU Process in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21152 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Media in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21151 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Payments in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21150 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Downloads in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21149 | 2021‑02‑22 22:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Stack buffer overflow in Data Transfer in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 88.0.4324.182 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21148 | 2021‑02‑09 16:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.150 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21147 | 2021‑02‑09 15:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed a local attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21146 | 2021‑02‑09 15:15:14 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21145 | 2021‑02‑09 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Fonts in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21144 | 2021‑02‑09 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Tab Groups in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21143 | 2021‑02‑09 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21142 | 2021‑02‑09 15:15:14 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Payments in Google Chrome on Mac prior to 88.0.4324.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21141 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass file extension policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21140 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Uninitialized use in USB in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a local attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via via a USB device. | 1 | 6 | PHYSICAL |
| CVE‑2021‑21139 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in iframe sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21138 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a local attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted file. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑21137 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from disk via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21136 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in WebView in Google Chrome on Android prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21135 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Performance API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21134 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Page Info in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21133 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to download files to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21132 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | CRITICAL (10) | Inappropriate implementation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21131 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21130 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21129 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21128 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21127 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21126 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21125 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient policy enforcement in File System API in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21124 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | CRITICAL (10) | Potential user after free in Speech Recognizer in Google Chrome on Android prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21123 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in File System API in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to bypass filesystem restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21122 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21121 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in Omnibox in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21120 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebSQL in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21119 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Media in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21118 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21117 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:15 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Cryptohome in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a local attacker to perform OS-level privilege escalation via a crafted file. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2021‑21116 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in audio in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21115 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | CRITICAL (10) | User after free in safe browsing in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21114 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21113 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21112 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21111 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | CRITICAL (10) | Insufficient policy enforcement in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21110 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in safe browsing in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21109 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in payments in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21108 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21107 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in drag and drop in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2021‑21106 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:15 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6576 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in offscreen canvas in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.102 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6575 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:16 | HIGH (8) | Race in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.102 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6574 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:16 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient policy enforcement in installer in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 85.0.4183.102 allowed a local attacker to potentially achieve privilege escalation via a crafted binary. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑6573 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:16 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in video in Google Chrome on Android prior to 85.0.4183.102 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6572 | 2021‑01‑14 21:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Media in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6571 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6570 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Information leakage in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information via a crafted WebRTC interaction. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6569 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (6) | Integer overflow in WebUSB in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6568 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in intent handling in Google Chrome on Android prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6567 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in command line handling in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6566 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in media in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6565 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Omnibox in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6564 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in permissions in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of a permission dialog via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6563 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in intent handling in Google Chrome on Android prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from disk via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6562 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6561 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Content Security Policy in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6560 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6559 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in presentation API in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6558 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in iOSWeb in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 85.0.4183.83 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6557 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in networking in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6556 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.135 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6555 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds read in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6554 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑6553 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in offline mode in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6552 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6551 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebXR in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6550 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in IndexedDB in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6549 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6548 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6547 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in media in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially obtain sensitive information via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6546 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (8) | Inappropriate implementation in installer in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a local attacker to potentially elevate privilege via a crafted filesystem. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑6545 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6544 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6543 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in task scheduling in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6542 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.125 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6541 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebUSB in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6540 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6539 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in CSS in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6538 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in WebView in Google Chrome on Android prior to 84.0.4147.105 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6537 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.105 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6536 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in PWAs in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker who had persuaded the user to install a PWA to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted PWA. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6535 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient data validation in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to inject scripts or HTML into a privileged page via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6534 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6533 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6532 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in SCTP in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.105 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6531 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Side-channel information leakage in scroll to text in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6530 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6529 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed an attacker in a privileged network position to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6528 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in basic auth in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6527 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in CSP in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6526 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in iframe sandbox in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6525 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6524 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6523 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6522 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | CRITICAL (10) | Inappropriate implementation in external protocol handlers in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6521 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Side-channel information leakage in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6520 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6519 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Policy bypass in CSP in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6518 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker who had convinced the user to use developer tools to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6517 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in history in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6516 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Policy bypass in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6515 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in tab strip in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6514 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed an attacker in a privileged network position to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted SCTP stream. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6513 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6512 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6511 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Information leak in content security policy in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6510 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | HIGH (8) | Heap buffer overflow in background fetch in Google Chrome prior to 84.0.4147.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑6509 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.116 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6507 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.106 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6506 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in WebView in Google Chrome on Android prior to 83.0.4103.106 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6505 | 2020‑07‑22 17:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in speech in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.106 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6504 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in notifications in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to bypass notification restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6503 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6502 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect implementation in permissions in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6501 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in CSP in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6500 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in interstitials in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6499 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in AppCache in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to bypass AppCache security restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6498 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect implementation in user interface in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 83.0.4103.88 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6497 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 83.0.4103.88 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted URI. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6496 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in payments in Google Chrome on MacOS prior to 83.0.4103.97 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6495 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.97 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6494 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in payments in Google Chrome on Android prior to 83.0.4103.97 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6493 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in WebAuthentication in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.97 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6492 | 2021‑11‑02 23:15:07 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.97 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6491 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in site information in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6490 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in loader in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker who had been able to write to disk to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6489 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker who had convinced the user to take certain actions in developer tools to obtain potentially sensitive information from disk via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6488 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in downloads in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6487 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in downloads in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6486 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigations in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6485 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in media router in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6484 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in ChromeDriver in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted request. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6483 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in payments in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6482 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6481 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in URL formatting in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6480 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in enterprise in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a local attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via UI actions. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6479 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in sharing in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6478 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in full screen in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6477 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | HIGH (8) | Inappropriate implementation in installer in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a local attacker to perform privilege escalation via a crafted file. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑6476 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in tab strip in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6475 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect implementation in full screen in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6474 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6473 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6472 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory or disk via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6471 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6470 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in clipboard in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a local attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via crafted clipboard contents. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6469 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6468 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6467 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6466 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6465 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in reader mode in Google Chrome on Android prior to 83.0.4103.61 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6464 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.138 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6463 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.122 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6462 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:11 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in task scheduling in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.129 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6461 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:11 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in storage in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.129 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6460 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in URL formatting in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.122 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6459 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in payments in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.122 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6458 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read and write in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.122 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6457 | 2020‑05‑21 04:15:11 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in speech recognizer in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.113 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6456 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in clipboard in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a local attacker to bypass site isolation via crafted clipboard contents. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6455 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds read in WebSQL in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6454 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6453 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.162 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6452 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in media in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.162 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6451 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.162 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6450 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.162 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6449 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.149 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6448 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6447 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker who had convinced the user to use devtools to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6446 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in trusted types in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6445 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in trusted types in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6444 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:13 | MEDIUM (6) | Uninitialized use in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6443 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker who had convinced the user to use devtools to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6442 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in cache in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6441 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to bypass security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6440 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6439 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigations in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to bypass security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6438 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6437 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebView in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted application. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6436 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in window management in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6435 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6434 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in devtools in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6433 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6432 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigations in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6431 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in full screen in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6430 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6429 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.149 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6428 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:18 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.149 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6427 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.149 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6426 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.149 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6425 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:17 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.149 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass site isolation via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6424 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.149 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6423 | 2020‑04‑13 18:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6422 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.149 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6420 | 2020‑03‑23 16:15:17 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in media in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.132 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6419 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 81.0.4044.92 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6418 | 2020‑02‑27 23:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.122 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6417 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:15 | HIGH (8) | Inappropriate implementation in installer in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a local attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted registry entry. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑6416 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in streams in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6415 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6414 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Safe Browsing in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6413 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to bypass HTML validators via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6412 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6411 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6410 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to confuse the user via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6409 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to enter a URI to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6408 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a local attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6407 | 2020‑02‑27 23:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in streams in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.122 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6406 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6405 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in SQLite in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6404 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6403 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect implementation in Omnibox in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6402 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in downloads in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to execute arbitrary code via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6401 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6400 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6399 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in AppCache in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6398 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use of uninitialized data in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6397 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in sharing in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6396 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6395 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6394 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6393 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6392 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6391 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a local attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6390 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in streams in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6389 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video stream. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6388 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds access in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6387 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video stream. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6386 | 2020‑02‑27 23:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in speech in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.116 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6385 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in storage in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6384 | 2020‑02‑27 23:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.116 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6383 | 2020‑02‑27 23:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.116 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6382 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6381 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in JavaScript in Google Chrome on ChromeOS and Android prior to 80.0.3987.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6380 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.130 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6379 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.130 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6378 | 2020‑02‑11 15:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in speech in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.130 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑6377 | 2020‑01‑10 22:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.117 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16873 | 2020‑09‑11 17:15:17 | MEDIUM (5) | <p>A spoofing vulnerability manifests in Microsoft Xamarin.Forms due to the default settings on Android WebView version prior to 83.0.4103.106. This vulnerability could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary Javascript code on a target system.</p> <p>For the attack to be successful, the targeted user would need to browse to a malicious website or a website serving the malicious code through Xamarin.Forms.</p> <p>The security update addresses this vulnerability by preventing the malicious Javascript from running in the WebView.</p> | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16046 | 2021‑01‑14 21:15:13 | MEDIUM (6) | Script injection in iOSWeb in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 84.0.4147.105 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16045 | 2021‑01‑14 21:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after Free in Payments in Google Chrome on Android prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16044 | 2021‑02‑09 14:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 88.0.4324.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted SCTP packet. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16043 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in networking in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.141 allowed a remote attacker to bypass discretionary access control via malicious network traffic. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16042 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Uninitialized Use in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16041 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds read in networking in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16040 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16039 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16038 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16037 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in clipboard in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.88 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16036 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in cookies in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to bypass cookie restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16035 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in cros-disks in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the browser process to bypass noexec restrictions via a malicious file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16034 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a local attacker to bypass policy restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16033 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in WebUSB in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16032 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in sharing in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16031 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in UI in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16030 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:14 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient data validation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16029 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16028 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16027 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information from the user's disk via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16026 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16025 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in clipboard in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16024 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in UI in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16023 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebCodecs in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16022 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in networking in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially bypass firewall controls via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16021 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (8) | Race in image burner in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the browser process to perform OS-level privilege escalation via a malicious file. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16020 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in cryptohome in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the browser process to bypass discretionary access control via a malicious file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16019 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in filesystem in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the browser process to bypass noexec restrictions via a malicious file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16018 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in payments in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16017 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in site isolation in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.198 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16016 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Inappropriate implementation in base in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.193 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16015 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in WASM in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16014 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in PPAPI in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16013 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:12 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.198 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16012 | 2021‑01‑08 19:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Side-channel information leakage in graphics in Google Chrome prior to 87.0.4280.66 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16011 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:16 | CRITICAL (10) | Heap buffer overflow in UI in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 86.0.4240.183 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16010 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in UI in Google Chrome on Android prior to 86.0.4240.185 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16009 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.183 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16008 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Stack buffer overflow in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.183 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit stack corruption via a crafted WebRTC packet. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16007 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient data validation in installer in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.183 allowed a local attacker to potentially elevate privilege via a crafted filesystem. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑16006 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.183 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16005 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.183 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16004 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in user interface in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.183 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16003 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in printing in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.111 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16002 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.111 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16001 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.111 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑16000 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.111 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15999 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow in Freetype in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.111 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15998 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in USB in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.99 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15997 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.99 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15996 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in passwords in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.99 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15995 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15994 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15993 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in printing in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.99 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15992 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in networking in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15991 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in password manager in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15990 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15989 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | MEDIUM (6) | Uninitialized data in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑15988 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient policy enforcement in downloads in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to open files to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15987 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted WebRTC stream. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15986 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflow in media in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15985 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15984 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted URL. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15983 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient data validation in webUI in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a local attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑15982 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in cache in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15981 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in audio in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15980 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:14 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a local attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via crafted Intents. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2020‑15979 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15978 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in navigation in Google Chrome on Android prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15977 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in dialogs in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from disk via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15976 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebXR in Google Chrome on Android prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15975 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15974 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15973 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass same origin policy via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15972 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15971 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in printing in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15970 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in NFC in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15969 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15968 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15967 | 2020‑11‑03 03:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in payments in Google Chrome prior to 86.0.4240.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15966 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.121 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15965 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.121 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15964 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient data validation in media in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.121 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15963 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.121 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15962 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy validation in serial in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.121 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15961 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | CRITICAL (10) | Insufficient policy validation in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.121 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15960 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in storage in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.121 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2020‑15959 | 2020‑09‑21 20:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in networking in Google Chrome prior to 85.0.4183.102 allowed an attacker who convinced the user to enable logging to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via social engineering. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑8075 | 2019‑09‑27 16:15:11 | HIGH (8) | Adobe Flash Player version 32.0.0.192 and earlier versions have a Same Origin Policy Bypass vulnerability. Successful exploitation could lead to Information Disclosure in the context of the current user. | 4 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5881 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:38 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds read in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5880 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:38 | HIGH (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5879 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:38 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to read local files via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5878 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:38 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5877 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5876 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome on Android prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5875 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in downloads in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5874 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient filtering in URI schemes in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5873 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy validation in navigation in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5872 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5871 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5870 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5869 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.132 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5868 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (6) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.100 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑5867 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.100 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5866 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | CRITICAL (10) | Out of bounds memory access in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.142 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5865 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigations in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5864 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass content security policy via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5862 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:37 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in AppCache in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5861 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to bypass anti-clickjacking policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5860 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | MEDIUM (6) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑5859 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient filtering in URI schemes in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5858 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | HIGH (9) | Incorrect security UI in MacOS services integration in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a local attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5857 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5856 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in storage in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5855 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5854 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5853 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5852 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5851 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5850 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | CRITICAL (10) | Use after free in offline mode in Google Chrome prior to 76.0.3809.87 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5849 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds read in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5848 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect font handling in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.142 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5847 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.142 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5846 | 2020‑01‑03 23:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds access in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5845 | 2020‑01‑03 23:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds access in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5844 | 2020‑01‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds access in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5843 | 2019‑12‑10 21:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5842 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:36 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5841 | 2019‑12‑10 21:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5840 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in popup blocker in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5839 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Excessive data validation in URL parser in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to input a URL to bypass website URL validation via a crafted URL. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5838 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass restrictions on file URIs via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5837 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:16 | MEDIUM (7) | Resource size information leakage in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5836 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5835 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Object lifecycle issue in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5834 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5833 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect dialog box scoping in browser in Google Chrome on Android prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to display misleading security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5832 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in XMLHttpRequest in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5831 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Object lifecycle issue in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5830 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in CORS in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5829 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in download manager in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5828 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Object lifecycle issue in ServiceWorker in Google Chrome prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5827 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in SQLite via WebSQL in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.131 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5826 | 2019‑11‑25 20:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in IndexedDB in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.86 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5825 | 2019‑11‑25 20:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds write in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.86 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5824 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Parameter passing error in media in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.131 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5823 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient policy enforcement in service workers in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5822 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5821 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5820 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5819 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient data validation in developer tools in Google Chrome on OS X prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a local attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted string copied to clipboard. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑5818 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Uninitialized data in media in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted video file. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5817 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5816 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Process lifetime issue in Chrome in Google Chrome on Android prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially persist an exploited process via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5814 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5813 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5812 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Inadequate security UI in iOS UI in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5811 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Incorrect handling of CORS in ServiceWorker in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5810 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Information leak in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5809 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in file chooser in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform privilege escalation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5808 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5807 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Object lifetime issue in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5806 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in ANGLE in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5805 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 74.0.3729.108 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5804 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (6) | Incorrect command line processing in Chrome in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a local attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted domain name. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑5803 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Content Security Policy in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5802 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of download origins in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5801 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect eliding of URLs in Omnibox in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5800 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5799 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect inheritance of a new document's policy in Content Security Policy in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5798 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Lack of correct bounds checking in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5797 | 2022‑09‑29 02:15:12 | HIGH (8) | Double free in DOMStorage in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5796 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | HIGH (8) | Data race in extensions guest view in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5795 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5794 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of cancelled requests in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5793 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to initiate the extensions installation user interface via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5792 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5791 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate optimization in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5790 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | HIGH (9) | An integer overflow leading to an incorrect capacity of a buffer in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5789 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | HIGH (9) | An integer overflow that leads to a use-after-free in WebMIDI in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5788 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | HIGH (9) | An integer overflow that leads to a use-after-free in Blink Storage in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5787 | 2019‑05‑23 20:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-garbage-collection in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5786 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Object lifetime issue in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.121 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5785 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect convexity calculations in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5784 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of deferred code in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.96 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5783 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Missing URI encoding of untrusted input in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to perform a Dangling Markup Injection attack via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5782 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect optimization assumptions in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5781 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of a confusable character in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5780 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient restrictions on what can be done with Apple Events in Google Chrome on macOS prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a local attacker to execute JavaScript via Apple Events. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑5779 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy validation in ServiceWorker in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5778 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | A missing case for handling special schemes in permission request checks in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass extension permission checks for privileged pages via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5777 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of a confusable character in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5776 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of a confusable character in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5775 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of a confusable character in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5774 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Omission of the .desktop filetype from the Safe Browsing checklist in SafeBrowsing in Google Chrome on Linux prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to download a .desktop file to execute arbitrary code via a downloaded .desktop file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5773 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient origin validation in IndexedDB in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5772 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Sharing of objects over calls into JavaScript runtime in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5771 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | An incorrect JIT of GLSL shaders in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5770 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient input validation in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5769 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of invalid end character position when front rendering in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5768 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | DevTools API not correctly gating on extension capability in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to read local files via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5767 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient protection of permission UI in WebAPKs in Google Chrome on Android prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed an attacker who convinced the user to install a malicious application to access privacy/security sensitive web APIs via a crafted APK. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5766 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of origin taint checking in Canvas in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5765 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | An exposed debugging endpoint in the browser in Google Chrome on Android prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a local attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted Intent. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5764 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect pointer management in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5763 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Failure to check error conditions in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5762 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate memory management when caching in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5761 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect object lifecycle management in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5760 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient checks of pointer validity in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5759 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect lifetime handling in HTML select elements in Google Chrome on Android and Mac prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5758 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect object lifecycle management in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5757 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | An incorrect object type assumption in SVG in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5756 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate memory management when caching in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5755 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:00 | MEDIUM (6) | Incorrect handling of negative zero in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑5754 | 2019‑02‑19 17:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Implementation error in QUIC Networking in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed an attacker running or able to cause use of a proxy server to obtain cleartext of transport encryption via malicious network proxy. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑15684 | 2019‑11‑25 16:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Kaspersky Protection extension for web browser Google Chrome prior to 30.112.62.0 was vulnerable to unauthorized access to its features remotely that could lead to removing other installed extensions. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13768 | 2023‑01‑02 23:15:10 | HIGH (7) | Use after free in FileAPI in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. (Chrome security severity: High) | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13767 | 2020‑01‑10 22:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media picker in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.88 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13766 | 2020‑01‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free in accessibility in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13765 | 2020‑01‑03 23:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free in content delivery manager in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13764 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:16 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13763 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in payments in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13762 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:16 | LOW (3) | Insufficient policy enforcement in downloads in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a local attacker to spoof downloaded files via local code. | 2 | 1 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑13761 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13759 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in interstitials in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13758 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigation in Google Chrome on Android prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13757 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13756 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in printing in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13755 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to disable extensions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13754 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13753 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in SQLite in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13752 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Out of bounds read in SQLite in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13751 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Uninitialized data in SQLite in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13750 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in SQLite in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to bypass defense-in-depth measures via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13749 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Omnibox in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13748 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a local attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13747 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Uninitialized data in rendering in Google Chrome on Android prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13746 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13745 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in audio in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13744 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in cookies in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13743 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in external protocol handling in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13742 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Omnibox in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13741 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a local attacker to bypass same origin policy via crafted clipboard content. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13740 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in sharing in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13739 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13738 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13737 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in autocomplete in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13736 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13735 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13734 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in SQLite in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13732 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13730 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13729 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free in WebSockets in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13728 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds write in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13727 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in WebSockets in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13726 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Buffer overflow in password manager in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13725 | 2019‑12‑10 22:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free in Bluetooth in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13724 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in WebBluetooth in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.108 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13723 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebBluetooth in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.108 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13722 | 2020‑01‑14 19:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 79.0.3945.79 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13721 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13720 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.87 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13719 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in full screen mode in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to hide security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13718 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13717 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in full screen mode in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to hide security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13716 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in service workers in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13715 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:34 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13714 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Color Enhancer extension in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to inject CSS into an HTML page via a crafted URL. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13713 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13711 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient policy enforcement in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 4 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13710 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in downloads in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to bypass download restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13709 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in downloads in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to bypass download restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13708 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in navigation in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13707 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in intents in Google Chrome on Android prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a local attacker to leak files via a crafted application. | 2 | 4 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑13706 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | HIGH (8) | Out of bounds memory access in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑13705 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to leak cross-origin data via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13704 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13703 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in the Omnibox in Google Chrome on Android prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13702 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | HIGH (8) | Inappropriate implementation in installer in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a local attacker to perform privilege escalation via a crafted executable. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑13701 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect implementation in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13700 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in the gamepad API in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13699 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:33 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in media in Google Chrome prior to 78.0.3904.70 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13698 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Out of bounds memory access in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.103 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13697 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in performance APIs in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.120 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13696 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.120 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13695 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in audio in Google Chrome on Android prior to 77.0.3865.120 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13694 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.120 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13693 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in IndexedDB in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.120 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13692 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in reader mode in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13691 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13690 | 2023‑08‑25 19:15:08 | CRITICAL (10) | Inappropriate implementation in OS in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to perform OS-level privilege escalation via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: High) | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13689 | 2023‑08‑25 19:15:08 | HIGH (8) | Inappropriate implementation in OS in Google Chrome on ChromeOS prior to 75.0.3770.80 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a malicious file. (Chromium security severity: Critical) | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑13688 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13687 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13686 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in offline mode in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13685 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in sharing view in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.90 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13684 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:32 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13683 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13682 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient policy enforcement in external protocol handling in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13681 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in downloads in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass download restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13680 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in TLS in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof client IP address to websites via crafted TLS connections. | 4 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13679 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | LOW (3) | Insufficient policy enforcement in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to show print dialogs via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 1 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2019‑13678 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect data validation in downloads in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13677 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in site isolation in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13676 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Chromium in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13675 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in extensions in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to disable extensions via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13674 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (4) | IDN spoofing in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13673 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | HIGH (7) | Insufficient data validation in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13672 | 2019‑12‑10 21:15:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect security UI in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page on iOS. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13671 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (4) | UI spoofing in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof security UI via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13670 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13669 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:31 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect data validation in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13668 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | HIGH (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13667 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Omnibox in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13666 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | HIGH (7) | Information leak in storage in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13665 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient filtering in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass multiple file download protection via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13664 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13663 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | MEDIUM (4) | IDN spoofing in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13662 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in navigations in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13661 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | MEDIUM (4) | UI spoofing in Chromium in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof notifications via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13660 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | MEDIUM (5) | UI spoofing in Chromium in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof notifications via a crafted HTML page. | 4 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2019‑13659 | 2019‑11‑25 15:15:30 | MEDIUM (4) | IDN spoofing in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 77.0.3865.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6179 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient enforcement of file access permission in the activeTab case in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to access files on the local file system via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6178 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Eliding from the wrong side in an infobar in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to Hide Chrome Security UI via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6177 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Information leak in media engine in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6176 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (5) | Insufficient file type enforcement in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform privilege escalation via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2018‑6175 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6174 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflows in Swiftshader in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 potentially allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6173 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6172 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6171 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | LOW (3) | Use after free in Bluetooth in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | ADJACENT_NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6170 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (7) | A bad cast in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6169 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Lack of timeout on extension install prompt in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to trigger installation of an unwanted extension via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6168 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Information leak in media engine in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6167 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6166 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6165 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of reloads in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6164 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient origin checks for CSS content in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6163 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6162 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Improper deserialization in WebGL in Google Chrome on Mac prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6161 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6160 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (4) | JavaScript alert handling in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6159 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in ServiceWorker in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6158 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (5) | A race condition in Oilpan in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6157 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Type confusion in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6156 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | HIGH (9) | Incorect derivation of a packet length in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6155 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of frames in the VP8 parser in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6154 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6153 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (7) | A precision error in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6152 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The implementation of the Page.downloadBehavior backend unconditionally marked downloaded files as safe, regardless of file type in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page and user interaction. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6151 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Bad cast in DevTools in Google Chrome on Win, Linux, Mac, Chrome OS prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6150 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of CORS in ServiceWorker in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6149 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Type confusion in JavaScript in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.87 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6148 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect implementation in Content Security Policy in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.79 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6147 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | LOW (2) | Lack of secure text entry mode in Browser UI in Google Chrome on Mac prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a local attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a local process. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2018‑6145 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in HTML parser in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6144 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Off-by-one error in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6143 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6142 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Array bounds check failure in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6141 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of an image filter in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6140 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | HIGH (9) | Allowing the chrome.debugger API to attach to Web UI pages in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to execute arbitrary code via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6139 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient target checks on the chrome.debugger API in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to execute arbitrary code via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6138 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6137 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (4) | CSS Paint API in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6136 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Missing type check in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6135 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Lack of clearing the previous site before loading alerts from a new one in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6134 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Information leak in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to bypass no-referrer policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6133 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6132 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Uninitialized data in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted video file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6131 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Object lifecycle issue in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6130 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of object lifetimes in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6129 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Out of bounds array access in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6128 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect URL parsing in WebKit in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6127 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Early free of object in use in IndexDB in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6126 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (7) | A precision error in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6125 | 2021‑11‑02 23:15:07 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in USB in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6124 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Type confusion in ReadableStreams in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6123 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:09 | MEDIUM (4) | A use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 67.0.3396.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6122 | 2021‑11‑02 23:15:07 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.139 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6121 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of input in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.170 allowed a remote attacker to perform privilege escalation via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6120 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:09 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow that could lead to an attacker-controlled heap out-of-bounds write in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.170 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6119 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6118 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | A double-eviction in the Incognito mode cache that lead to a user-after-free in cache in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.139 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6117 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Confusing settings in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6116 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | A nullptr dereference in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6115 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate setting of the SEE_MASK_FLAG_NO_UI flag in file downloads in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to potentially bypass OS malware checks via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6114 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect enforcement of CSP for <object> tags in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6113 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Improper handling of pending navigation entries in Navigation in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6112 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Making URLs clickable and allowing them to be styled in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6111 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:08 | MEDIUM (7) | An object lifetime issue in the developer tools network handler in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a local attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6110 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:08 | MEDIUM (6) | Parsing documents as HTML in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to cause Chrome to execute scripts via a local non-HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6109 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:08 | MEDIUM (4) | readAsText() can indefinitely read the file picked by the user, rather than only once at the time the file is picked in File API in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to access data on the user file system without explicit consent via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6108 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6107 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6106 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:08 | MEDIUM (7) | An asynchronous generator may return an incorrect state in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowing a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6105 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6104 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6103 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | A stagnant permission prompt in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to bypass permission policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6102 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Missing confusable characters in Internationalization in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6101 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:02 | MEDIUM (5) | A lack of host validation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page, if the user is running a remote DevTools debugging server. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6100 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:07 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome on macOS prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6099 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | A lack of CORS checks in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to leak limited cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6098 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6097 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:06 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of asynchronous methods in Fullscreen in Google Chrome on macOS prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to enter full screen without showing a warning via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6096 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:06 | MEDIUM (4) | A JavaScript focused window could overlap the fullscreen notification in Fullscreen in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to obscure the full screen warning via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6095 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate dismissal of file picker on keyboard events in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to read local files via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6094 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Inline metadata in GarbageCollection in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6093 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:06 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient origin checks in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6092 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow on 32-bit systems in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6091 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:05 | MEDIUM (4) | Service Workers can intercept any request made by an <embed> or <object> tag in Fetch API in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6090 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow that lead to a heap buffer-overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6089 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | A lack of CORS checks, after a Service Worker redirected to a cross-origin PDF, in Service Worker in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to leak limited cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6088 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | An iterator-invalidation bug in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6087 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use-after-free in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6086 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A double-eviction in the Incognito mode cache that lead to a user-after-free in Networking Disk Cache in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6085 | 2018‑12‑04 17:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Re-entry of a destructor in Networking Disk Cache in Google Chrome prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6084 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:04 | HIGH (7) | Insufficiently sanitized distributed objects in Updater in Google Chrome on macOS prior to 66.0.3359.117 allowed a local attacker to execute arbitrary code via an executable file. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2018‑6083 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Failure to disallow PWA installation from CSP sandboxed pages in AppManifest in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to access privileged APIs via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6082 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Including port 22 in the list of allowed FTP ports in Networking in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially enumerate internal host services via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6081 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | XSS vulnerabilities in Interstitials in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension or open Developer Console to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6080 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Lack of access control checks in Instrumentation in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to obtain memory metadata from privileged processes . | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6079 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate sharing of TEXTURE_2D_ARRAY/TEXTURE_3D data between tabs in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6078 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6077 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Displacement map filters being applied to cross-origin images in Blink SVG rendering in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6076 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient encoding of URL fragment identifiers in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to perform a DOM based XSS attack via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6075 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of specified filenames in file downloads in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page and user interaction. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6074 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Failure to apply Mark-of-the-Web in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to bypass OS level controls via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6073 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A heap buffer overflow in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6072 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow leading to use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6071 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6070 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Lack of CSP enforcement on WebUI pages in Bink in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass content security policy via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6069 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Stack buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6068 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Object lifecycle issue in Chrome Custom Tab in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6067 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect IPC serialization in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6066 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Lack of CORS checking by ResourceFetcher/ResourceLoader in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6065 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in computing the required allocation size when instantiating a new javascript object in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6064 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Type Confusion in the implementation of __defineGetter__ in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6063 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect use of mojo::WrapSharedMemoryHandle in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6062 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap overflow write in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6061 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (5) | A race in the handling of SharedArrayBuffers in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6060 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6057 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Lack of special casing of Android ashmem in Google Chrome prior to 65.0.3325.146 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass inter-process read only guarantees via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6056 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Type confusion could lead to a heap out-of-bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.168 allowing a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6055 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Catalog Service in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially run arbitrary code outside sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6054 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in WebUI in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6053 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in New Tab Page in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a local attacker to view website thumbnail images after clearing browser data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6052 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Lack of support for a non standard no-referrer policy value in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to obtain referrer details from a web page that had thought it had opted out of sending referrer data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6051 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:04 | MEDIUM (4) | XSS Auditor in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119, did not ensure the reporting URL was in the same origin as the page it was on, which allowed a remote attacker to obtain referrer details via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6050 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6049 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in permissions prompt in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the origin to which permission is granted via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6048 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak referrer information via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6047 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak user redirect URL via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6046 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak user cross-origin data via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6045 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak user local file data via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6043 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in External Protocol Handler in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially execute arbitrary programs on user machine via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6042 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6041 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect security UI in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6040 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6039 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak user cross-origin data via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6038 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Heap buffer overflow in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6037 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in autofill in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to obtain autofill data with insufficient user gestures via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6036 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak user data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6035 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak user local file data via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6034 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:01 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient data validation in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6033 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in Downloads in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially run arbitrary code outside sandbox via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6032 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially leak user cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑6031 | 2018‑09‑25 14:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 64.0.3282.119 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑20073 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | LOW (2) | Use of extended attributes in downloads in Google Chrome prior to 72.0.3626.81 allowed a local attacker to read download URLs via the filesystem. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2018‑20072 | 2024‑09‑23 22:15:03 | HIGH (8) | Insufficient data validation in PDF in Google Chrome prior to 73.0.3683.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted PDF file. (Chromium security severity: Low) | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2018‑20071 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficiently strict origin checks during JIT payment app installation in Payments in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to install a service worker for a domain that can host attacker controled files via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑20070 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑20069 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Failure to prevent navigation to top frame to data URLs in Navigation in Google Chrome on iOS prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to confuse the user about the origin of the current page via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑20068 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of 304 status codes in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to confuse the user about the origin of the current page via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑20067 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | A renderer initiated back navigation was incorrectly allowed to cancel a browser initiated one in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to confuse the user about the origin of the current page via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑20066 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect object lifecycle in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑20065 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Handling of URI action in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to initiate potentially unsafe navigations without a user gesture via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18359 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of Reflect.construct in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18358 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | LOW (3) | Lack of special casing of localhost in WPAD files in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed an attacker on the local network segment to proxy resources on localhost via a crafted WPAD file. | 0 | 0 | ADJACENT_NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18357 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18356 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in path handling lead to a use after free in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18355 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in URL Formatter in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18354 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validate of external protocols in Shell Integration in Google Chrome on Windows prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to launch external programs via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18353 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Failure to dismiss http auth dialogs on navigation in Network Authentication in Google Chrome on Android prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to confuse the user about the origin of an auto dialog via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18352 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Service works could inappropriately gain access to cross origin audio in Media in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy for audio content via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18351 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Lack of proper validation of ancestor frames site when sending lax cookies in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to bypass SameSite cookie policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18350 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of CSP enforcement during navigations in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18349 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Remote frame navigations was incorrectly permitted to local resources in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to access files on the local file system via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18348 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of bidirectional domain names with RTL characters in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18347 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of failed navigations with invalid URLs in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to trick a user into executing javascript in an arbitrary origin via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18346 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of alert box display in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to present confusing browser UI via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18345 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of blob URLS in Site Isolation in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to bypass site isolation protections via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18344 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate allowance of the setDownloadBehavior devtools protocol feature in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker with control of an installed extension to access files on the local file system via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18343 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handing of paths leading to a use after free in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18342 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Execution of user supplied Javascript during object deserialization can update object length leading to an out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18341 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow leading to a heap buffer overflow in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18340 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect object lifecycle in MediaRecorder in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18339 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect object lifecycle in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18338 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect, thread-unsafe use of SkImage in Canvas in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18337 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of stylesheets leading to a use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18336 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect object lifecycle in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑18335 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17481 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect object lifecycle handling in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.98 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17480 | 2018‑12‑11 16:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Execution of user supplied Javascript during array deserialization leading to an out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 71.0.3578.80 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17479 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect object lifetime calculations in GPU code in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.110 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17478 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect array position calculations in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.102 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17477 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect dialog placement in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of extension popups via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17476 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect dialog placement in Cast UI in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to obscure the full screen warning via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17475 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of history on iOS in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17474 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in HTMLImportsController in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17473 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of confusable characters in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17472 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of googlechrome:// URL scheme on iOS in Intents in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to escape the <iframe> sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17471 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect dialog placement in WebContents in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to obscure the full screen warning via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17470 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | A heap buffer overflow in GPU in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17469 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of PDF filter chains in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17468 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of timer information during navigation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to obtain cross origin URLs via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17467 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficiently quick clearing of stale rendered content in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17466 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect texture handling in Angle in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17465 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect implementation of object trimming in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17464 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of history on iOS in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17463 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:00 | HIGH (9) | Incorrect side effect annotation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.64 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17462 | 2018‑11‑14 15:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect refcounting in AppCache in Google Chrome prior to 70.0.3538.67 allowed a remote attacker to perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17461 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (7) | An out of bounds read in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17460 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in filesystem URIs in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17459 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of clicks in the omnibox in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.92 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17458 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (7) | An improper update of the WebAssembly dispatch table in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.92 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑17457 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (7) | An object lifecycle issue in Blink could lead to a use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16088 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | A missing check for JS-simulated input events in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to download arbitrary files with no user input via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16087 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Lack of proper state tracking in Permissions in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16086 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16085 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in ResourceCoordinator in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16084 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | The default selected dialog button in CustomHandlers in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to perform certain operations to open external programs via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16083 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | An out of bounds read in forward error correction code in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16082 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | An out of bounds read in Swiftshader in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16081 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Allowing the chrome.debugger API to run on file:// URLs in DevTools in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to access files on the local file system without file access permission via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16080 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | A missing check for popup window handling in Fullscreen in Google Chrome on macOS prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16079 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | LOW (3) | A race condition between permission prompts and navigations in Prompts in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16078 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Unsafe handling of credit card details in Autofill in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16077 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Object lifecycle issue in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16076 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Missing bounds check in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16075 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | LOW (3) | Insufficient file type enforcement in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to obtain local file data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16074 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in site isolation in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16073 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in site isolation in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16072 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | A missing origin check related to HLS manifests in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to bypass same origin policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16071 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16070 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflows in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16069 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Unintended floating-point error accumulation in SwiftShader in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16068 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Missing validation in Mojo in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16067 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | A use after free in WebAudio in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16066 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | A use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16065 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | A Javascript reentrancy issues that caused a use-after-free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 69.0.3497.81 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2018‑16064 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in Extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 68.0.3440.75 allowed an attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to bypass navigation restrictions via a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5133 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Off-by-one read/write on the heap in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to corrupt memory and possibly leak information and potentially execute code via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5132 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page, aka incorrect WebAssembly stack manipulation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5131 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page, aka an out-of-bounds write. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5130 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in xmlmemory.c in libxml2 before 2.9.5, as used in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 and other products, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted XML file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5129 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in WebAudio in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5128 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page, related to WebGL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5127 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5126 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5125 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5124 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect application of sandboxing in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted MHTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5122 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate use of table size handling in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.100 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to trigger out-of-bounds access via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5121 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:03 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate use of JIT optimisation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.100 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page, related to the escape analysis phase. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5120 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate use of www mismatch redirects in browser navigation in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 61.0.3163.81 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially downgrade HTTPS requests to HTTP via a crafted HTML page. In other words, Chrome could transmit cleartext even though the user had entered an https URL, because of a misdesigned workaround for cases where the domain name in a URL almost matches the domain name in an X.509 server certificate (but differs in the initial "www." substring). | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5119 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Use of an uninitialized value in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 61.0.3163.81 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5118 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 61.0.3163.81 for Android, failed to correctly propagate CSP restrictions to javascript scheme pages, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5117 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Use of an uninitialized value in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Linux and Windows allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5116 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 61.0.3163.81 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5115 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit object corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5114 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | Inappropriate use of partition alloc in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 61.0.3163.81 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit memory corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5113 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | Math overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 61.0.3163.81 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5112 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow in WebGL in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5111 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 61.0.3163.79 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit memory corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5110 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation of the web payments API on blob: and data: schemes in Web Payments in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac, Windows, Linux, and Android allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5109 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation of unload handler handling in permission prompts in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to display UI on a non attacker controlled tab via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5108 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac, Windows, Linux, and Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially maliciously modify objects via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5107 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (5) | A timing attack in SVG rendering in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to extract pixel values from a cross-origin page being iframe'd via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5106 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac, Windows, Linux, and Android allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5105 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac, Windows, Linux, and Android allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5104 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in interstitials in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the omnibox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5103 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Use of an uninitialized value in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5102 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Use of an uninitialized value in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac, Windows, Linux, and Android allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5101 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5100 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in Apps in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5099 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in PPAPI Plugins in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac allowed a remote attacker to potentially gain privilege elevation via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5098 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac, Windows, Linux, and Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5097 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Linux allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5096 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement during navigation between different schemes in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform cross origin content download via a crafted HTML page, related to intents. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5095 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | Stack overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit stack corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5094 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Type confusion in extensions JavaScript bindings in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac, Windows, Linux, and Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially maliciously modify objects via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5093 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate implementation in modal dialog handling in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Mac, Windows, Linux, and Android allowed a remote attacker to prevent a full screen warning from being displayed via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5092 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in PPAPI Plugins in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5091 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in IndexedDB in Google Chrome prior to 60.0.3112.78 for Linux, Android, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5090 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.115 for Mac allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted domain name containing a U+0620 character, aka Apple rdar problem 32458012. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5089 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.104 for Mac allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5088 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.104 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 59.0.3071.117 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5087 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.104 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 59.0.3071.117 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page, aka an IndexedDB sandbox escape. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5086 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Windows and Mac allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5085 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Bookmarks in Google Chrome prior to 59 for iOS allowed a remote attacker who convinced the user to perform certain operations to run JavaScript on chrome:// pages via a crafted bookmark. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5083 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to display UI on a non attacker controlled tab via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5082 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | LOW (2) | Failure to take advantage of available mitigations in credit card autofill in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.92 for Android allowed a local attacker to take screen shots of credit card information via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2017‑5081 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | LOW (3) | Lack of verification of an extension's locale folder in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android, allowed an attacker with local write access to modify extensions by modifying extension files. | 2 | 1 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2017‑5080 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in credit card autofill in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Linux and Windows allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5079 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to display UI on a non attacker controlled tab via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5078 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Blink's mailto: handling in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to perform command injection via a crafted HTML page, a similar issue to CVE-2004-0121. For example, characters such as * have an incorrect interaction with xdg-email in xdg-utils, and a space character can be used in front of a command-line argument. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5077 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5076 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5075 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in CSP reporting in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to obtain the value of url fragments via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5074 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (5) | A use after free in Chrome Apps in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page, related to Bluetooth. | 0 | 0 | ADJACENT_NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5073 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Use after free in print preview in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5072 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.92 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing with RTL characters via a crafted URL page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5071 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (6) | Insufficient validation of untrusted input in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5070 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 59.0.3071.86 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 59.0.3071.92 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5069 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (6) | Incorrect MIME type of XSS-Protection reports in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 58.0.3029.83 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to circumvent Cross-Origin Resource Sharing checks via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5068 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (8) | Incorrect handling of picture ID in WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.96 for Mac, Windows, and Linux allowed a remote attacker to trigger a race condition via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5067 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | An insufficient watchdog timer in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5066 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient consistency checks in signature handling in the networking stack in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 58.0.3029.83 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to incorrectly accept a badly formed X.509 certificate via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5065 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Lack of an appropriate action on page navigation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Windows and Mac allowed a remote attacker to potentially confuse a user into making an incorrect security decision via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5064 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Incorrect handling of DOM changes in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5063 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (9) | A numeric overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 58.0.3029.83 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5062 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in Chrome Apps in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 58.0.3029.83 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted Chrome extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5061 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (5) | A race condition in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Linux, Windows, and Mac allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 2 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5060 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 58.0.3029.83 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5059 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:00 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 58.0.3029.83 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially obtain code execution via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5058 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in PrintPreview in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to potentially perform out of bounds memory access via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5057 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:00 | HIGH (9) | Type confusion in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 58.0.3029.81 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 58.0.3029.83 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5056 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:00 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.133 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 57.0.2987.132 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5055 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:00 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in printing in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.133 for Linux and Windows allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5054 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:00 | HIGH (9) | An out-of-bounds read in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.133 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 57.0.2987.132 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to obtain heap memory contents via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5053 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:00 | CRITICAL (10) | An out-of-bounds read in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.133 for Linux, Windows, and Mac, and 57.0.2987.132 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page, related to Array.prototype.indexOf. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5052 | 2017‑10‑27 05:29:00 | HIGH (9) | An incorrect assumption about block structure in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.133 for Mac, Windows, and Linux, and 57.0.2987.132 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit memory corruption via a crafted HTML page that triggers improper casting. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5051 | 2017‑04‑25 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted video file, related to ChunkDemuxer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5050 | 2017‑04‑25 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted video file, related to ChunkDemuxer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5049 | 2017‑04‑25 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted video file, related to ChunkDemuxer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5048 | 2017‑04‑25 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted video file, related to ChunkDemuxer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5047 | 2017‑04‑25 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | An integer overflow in FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted video file, related to ChunkDemuxer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5046 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | V8 in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android had insufficient policy enforcement, which allowed a remote attacker to spoof the location object via a crafted HTML page, related to Blink information disclosure. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5045 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:01 | MEDIUM (6) | XSS Auditor in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed detection of a blocked iframe load, which allowed a remote attacker to brute force JavaScript variables via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5044 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:01 | MEDIUM (6) | Heap buffer overflow in filter processing in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5043 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:01 | HIGH (9) | Chrome Apps in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Linux, Windows, and Mac had a use after free bug in GuestView, which allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted Chrome extension. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5042 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:01 | MEDIUM (6) | Cast in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android sent cookies to sites discovered via SSDP, which allowed an attacker on the local network segment to initiate connections to arbitrary URLs and observe any plaintext cookies sent. | 2 | 4 | ADJACENT_NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5041 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.100 incorrectly handled back-forward navigation, which allowed a remote attacker to display incorrect information for a site via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5040 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | V8 in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android was missing a neutering check, which allowed a remote attacker to read values in memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5039 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | HIGH (8) | A use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2017‑5038 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | MEDIUM (6) | Chrome Apps in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Linux, Windows, and Mac had a use after free bug in GuestView, which allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted Chrome extension. | 3 | 3 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5037 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | HIGH (8) | An integer overflow in FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted video file, related to ChunkDemuxer. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2017‑5036 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | HIGH (8) | A use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to have an unspecified impact via a crafted PDF file. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2017‑5035 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Windows and Mac had a race condition, which could cause Chrome to display incorrect certificate information for a site. | 2 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5034 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Linux and Windows allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5033 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android failed to correctly propagate CSP restrictions to local scheme pages, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page, related to the unsafe-inline keyword. | 3 | 1 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5032 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Windows could be made to increment off the end of a buffer, which allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5031 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Windows allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5030 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | HIGH (9) | Incorrect handling of complex species in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Linux, Windows, and Mac and 57.0.2987.108 for Android allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5029 | 2017‑04‑24 23:59:00 | HIGH (9) | The xsltAddTextString function in transform.c in libxslt 1.1.29, as used in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 57.0.2987.98 for Mac, Windows, and Linux and 57.0.2987.108 for Android, lacked a check for integer overflow during a size calculation, which allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5028 | 2019‑06‑27 17:15:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5027 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, failed to properly enforce unsafe-inline content security policy, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5026 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, failed to prevent alerts from being displayed by swapped out frames, which allowed a remote attacker to show alerts on a page they don't control via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5025 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, failed to perform proper bounds checking, which allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5024 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, failed to perform proper bounds checking, which allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5023 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Type confusion in Histogram in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit a near null dereference via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5022 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, failed to properly enforce unsafe-inline content security policy, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass content security policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5021 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | A use after free in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5020 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, failed to require a user gesture for powerful download operations, which allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5019 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5018 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, had an insufficiently strict content security policy on the Chrome app launcher page, which allowed a remote attacker to inject scripts or HTML into a privileged page via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5017 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Interactions with the OS in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Mac insufficiently cleared video memory, which allowed a remote attacker to possibly extract image fragments on systems with GeForce 8600M graphics chips via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5016 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, failed to prevent certain UI elements from being displayed by non-visible pages, which allowed a remote attacker to show certain UI elements on a page they don't control via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5015 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, incorrectly handled Unicode glyphs, which allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5014 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow during image processing in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5013 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux incorrectly handled new tab page navigations in non-selected tabs, which allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5012 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | A heap buffer overflow in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5011 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Windows insufficiently sanitized DevTools URLs, which allowed a remote attacker who convinced a user to install a malicious extension to read filesystem contents via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5010 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, resolved promises in an inappropriate context, which allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5009 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | WebRTC in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, failed to perform proper bounds checking, which allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5008 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, allowed attacker controlled JavaScript to be run during the invocation of a private script method, which allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5007 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, incorrectly handled the sequence of events when closing a page, which allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑5006 | 2017‑02‑17 07:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 56.0.2924.76 for Linux, Windows and Mac, and 56.0.2924.87 for Android, incorrectly handled object owner relationships, which allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15430 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in Chromecast plugin in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15429 | 2018‑08‑28 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Inappropriate implementation in V8 WebAssembly JS bindings in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.108 allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15428 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation in V8 builtins string generator could lead to out of bounds read and write access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.94 and allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15427 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a socially engineered user to XSS themselves by dragging and dropping a javascript: URL into the URL bar. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15426 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15425 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:14 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15424 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:13 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15423 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:12 | MEDIUM (5) | Inappropriate implementation in BoringSSL SPAKE2 in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to leak the low-order bits of SHA512(password) by inspecting protocol traffic. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15422 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:12 | MEDIUM (4) | Integer overflow in international date handling in International Components for Unicode (ICU) for C/C++ before 60.1, as used in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 and other products, allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15420 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of back navigations in error pages in Navigation in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15419 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient policy enforcement in Resource Timing API in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to infer browsing history by triggering a leaked cross-origin URL via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15418 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Use of uninitialized memory in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15417 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:09 | LOW (3) | Inappropriate implementation in Skia canvas composite operations in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to leak cross-origin data via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15416 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Heap buffer overflow in Blob API in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page, aka a Blink out-of-bounds read. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15415 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:08 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect serialization in IPC in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to leak the value of a pointer via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15413 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:07 | MEDIUM (7) | Type confusion in WebAssembly in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15412 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:06 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in libxml2 before 2.9.5, as used in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 and other products, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15411 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:05 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15410 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15409 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15408 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file that is mishandled by PDFium. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15407 | 2018‑08‑28 19:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Out-of-bounds Write in the QUIC networking stack in Google Chrome prior to 63.0.3239.84 allowed a remote attacker to gain code execution via a malicious server. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15406 | 2018‑08‑28 20:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A stack buffer overflow in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.75 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15405 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Inappropriate symlink handling and a race condition in the stateful recovery feature implementation could lead to a persistance established by a malicious code running with root privileges in cryptohomed in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 61.0.3163.113 allowed a local attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2017‑15404 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:01 | HIGH (7) | An ability to process crash dumps under root privileges and inappropriate symlinks handling could lead to a local privilege escalation in Crash Reporting in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 61.0.3163.113 allowed a local attacker to perform privilege escalation via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2017‑15403 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in crosh could lead to a command injection under chronos privileges in Networking in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 61.0.3163.113 allowed a local attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2017‑15402 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Using an ID that can be controlled by a compromised renderer which allows any frame to overwrite the page_state of any other frame in the same process in Navigation in Google Chrome on Chrome OS prior to 62.0.3202.74 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15401 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | A memory corruption bug in WebAssembly could lead to out of bounds read and write through V8 in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15399 | 2018‑08‑28 20:29:01 | HIGH (9) | A use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.89 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15398 | 2018‑08‑28 20:29:00 | HIGH (8) | A stack buffer overflow in the QUIC networking stack in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.89 allowed a remote attacker to gain code execution via a malicious server. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15396 | 2018‑08‑28 20:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | A stack buffer overflow in NumberingSystem in International Components for Unicode (ICU) for C/C++ before 60.2, as used in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.75 and other products, allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15395 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | A use after free in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page, aka an ImageCapture NULL pointer dereference. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15394 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing in permission dialogs via IDN homographs in a crafted Chrome Extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15393 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Devtools remote debugging in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to obtain access to remote debugging functionality via a crafted HTML page, aka a Referer leak. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15392 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient data validation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed an attacker who can write to the Windows Registry to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted Windows Registry entry, related to PlatformIntegration. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15391 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Extensions in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to access Extension pages without authorisation via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15390 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Insufficient Policy Enforcement in Omnibox in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform domain spoofing via IDN homographs in a crafted domain name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15389 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | An insufficient watchdog timer in navigation in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15388 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Iteration through non-finite points in Skia in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15387 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient enforcement of Content Security Policy in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to open javascript: URL windows when they should not be allowed to via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2017‑15386 | 2018‑02‑07 23:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect implementation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 62.0.3202.62 allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑9652 | 2019‑11‑20 15:15:12 | CRITICAL (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 55.0.2883.75. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑9651 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | A missing check for whether a property of a JS object is private in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑9650 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android incorrectly handled iframes, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass a no-referrer policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑7549 | 2016‑09‑25 20:59:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.113 does not ensure that the recipient of a certain IPC message is a valid RenderFrame or RenderWidget, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (invalid pointer dereference and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging access to a renderer process, related to render_frame_host_impl.cc and render_widget_host_impl.cc, as demonstrated by a Password Manager message. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑7395 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:25 | MEDIUM (7) | SkPath.cpp in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, does not properly validate the return values of ChopMonoAtY calls, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (uninitialized memory access and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted graphics data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5226 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Linux, Windows and Mac executed javascript: URLs entered in the URL bar in the context of the current tab, which allowed a socially engineered user to XSS themselves by dragging and dropping a javascript: URL into the URL bar. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5225 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android incorrectly handled form actions, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass Content Security Policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5224 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | A timing attack on denormalized floating point arithmetic in SVG filters in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5223 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Integer overflow in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption or DoS via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5222 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Incorrect handling of invalid URLs in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5221 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Type confusion in libGLESv2 in ANGLE in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android possibly allowed a remote attacker to bypass buffer validation via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5220 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android incorrectly handled navigation within PDFs, which allowed a remote attacker to read local files via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5219 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A heap use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5218 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android incorrectly handled navigation within PDFs, which allowed a remote attacker to temporarily spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via a crafted HTML page containing PDF data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5217 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android incorrectly permitted access to privileged plugins, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass site isolation via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5216 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5215 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in webaudio in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5214 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Windows mishandled downloaded files, which allowed a remote attacker to prevent the downloaded file from receiving the Mark of the Web via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5213 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5212 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android insufficiently sanitized DevTools URLs, which allowed a remote attacker to read local files via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5211 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5210 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap buffer overflow during TIFF image parsing in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5209 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Bad casting in bitmap manipulation in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5208 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Linux and Windows, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed possible corruption of the DOM tree during synchronous event handling, which allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5207 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | In Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android, corruption of the DOM tree could occur during the removal of a full screen element, which allowed a remote attacker to achieve arbitrary code execution via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5206 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | The PDF plugin in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android incorrectly followed redirects, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5205 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Linux, Windows and Mac, incorrectly handles deferred page loads, which allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5204 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Leaking of an SVG shadow tree leading to corruption of the DOM tree in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5203 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | A use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 55.0.2883.75 for Mac, Windows and Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5202 | 2019‑10‑25 15:15:12 | CRITICAL (9) | browser/extensions/api/dial/dial_registry.cc in Google Chrome before 54.0.2840.98 on macOS, before 54.0.2840.99 on Windows, and before 54.0.2840.100 on Linux neglects to copy a device ID before an erase() call, which causes the erase operation to access data that that erase operation will destroy. | 4 | 5 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5201 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | A leak of privateClass in the extensions API in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.100 for Linux, and 54.0.2840.99 for Windows, and 54.0.2840.98 for Mac allowed a remote attacker to access privileged JavaScript code via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5200 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | V8 in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.98 for Mac, and 54.0.2840.99 for Windows, and 54.0.2840.100 for Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android incorrectly applied type rules, which allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5199 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | An off by one error resulting in an allocation of zero size in FFmpeg in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.98 for Mac, and 54.0.2840.99 for Windows, and 54.0.2840.100 for Linux, and 55.0.2883.84 for Android allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted video file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5198 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | HIGH (9) | V8 in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.90 for Linux, and 54.0.2840.85 for Android, and 54.0.2840.87 for Windows and Mac included incorrect optimisation assumptions, which allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write operations, leading to code execution, via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5197 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | The content view client in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.85 for Android insufficiently validated intent URLs, which allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to start arbitrary activity on the system via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5196 | 2017‑01‑19 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | The content renderer client in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.85 for Android insufficiently enforced the Same Origin Policy amongst downloaded files, which allowed a remote attacker to access any downloaded file and interact with sites, including those the user was logged into, via a crafted HTML page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5194 | 2019‑11‑20 15:15:11 | CRITICAL (10) | Unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 54.0.2840.59. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5193 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 54.0 for iOS had insufficient validation of URLs for windows open by DOM, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass restrictions on navigation to certain URL schemes via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5192 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows missed a CORS check on redirect in TextTrackLoader, which allowed a remote attacker to bypass cross-origin restrictions via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5191 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Bookmark handling in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android had insufficient validation of supplied data, which allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via crafted HTML pages, as demonstrated by an interpretation conflict between userinfo and scheme in an http://javascript:payload@example.com URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5190 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android incorrectly handled object lifecycles during shutdown, which allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5189 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android permitted navigation to blob URLs with non-canonical origins, which allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5188 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Multiple issues in Blink in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux allow a remote attacker to spoof various parts of browser UI via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5187 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.85 for Android incorrectly handled rapid transition into and out of full screen mode, which allowed a remote attacker to spoof the contents of the Omnibox (URL bar) via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5186 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Devtools in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android incorrectly handled objects after a tab crash, which allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via crafted PDF files. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5185 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android incorrectly allowed reentrance of FrameView::updateLifecyclePhasesInternal(), which allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5184 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android incorrectly handled object lifecycles in CFFL_FormFillter::KillFocusForAnnot, which allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted PDF files. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5183 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | A heap use after free in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android allows a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted PDF files. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5182 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android had insufficient validation in bitmap handling, which allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5181 | 2016‑12‑18 03:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink in Google Chrome prior to 54.0.2840.59 for Windows, Mac, and Linux; 54.0.2840.85 for Android permitted execution of v8 microtasks while the DOM was in an inconsistent state, which allowed a remote attacker to inject arbitrary scripts or HTML (UXSS) via crafted HTML pages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5178 | 2017‑05‑23 04:29:01 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.143 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5177 | 2017‑05‑23 04:29:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in V8 in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.143 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5176 | 2016‑09‑29 10:59:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.113 allows remote attackers to bypass the SafeBrowsing protection mechanism via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5175 | 2016‑09‑25 20:59:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.113 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5174 | 2016‑09‑25 20:59:07 | MEDIUM (4) | browser/ui/cocoa/browser_window_controller_private.mm in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.113 does not process fullscreen toggle requests during a fullscreen transition, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (unsuppressed popup) via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5173 | 2016‑09‑25 20:59:06 | MEDIUM (7) | The extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.113 does not properly restrict access to Object.prototype, which allows remote attackers to load unintended resources, and consequently trigger unintended JavaScript function calls and bypass the Same Origin Policy via an indirect interception attack. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5172 | 2016‑09‑25 20:59:04 | MEDIUM (7) | The parser in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.113, mishandles scopes, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information from arbitrary memory locations via crafted JavaScript code. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5171 | 2016‑09‑25 20:59:03 | MEDIUM (7) | WebKit/Source/bindings/templates/interface.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.113, does not prevent certain constructor calls, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5170 | 2016‑09‑25 20:59:02 | MEDIUM (7) | WebKit/Source/bindings/modules/v8/V8BindingForModules.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.113, does not properly consider getter side effects during array key conversion, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted Indexed Database (aka IndexedDB) API calls. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5168 | 2017‑04‑21 20:59:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.94, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and obtain sensitive information. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5167 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:24 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5166 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:23 | LOW (3) | The download implementation in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux does not properly restrict saving a file:// URL that is referenced by an http:// URL, which makes it easier for user-assisted remote attackers to discover NetNTLM hashes and conduct SMB relay attacks via a crafted web page that is accessed with the "Save page as" menu choice. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5165 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:22 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Developer Tools (aka DevTools) subsystem in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via the settings parameter in a chrome-devtools-frontend.appspot.com URL's query string. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5164 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:21 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in WebKit/Source/platform/v8_inspector/V8Debugger.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML into the Developer Tools (aka DevTools) subsystem via a crafted web site, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5163 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:20 | MEDIUM (4) | The bidirectional-text implementation in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux does not ensure left-to-right (LTR) rendering of URLs, which allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via crafted right-to-left (RTL) Unicode text, related to omnibox/SuggestionView.java and omnibox/UrlBar.java in Chrome for Android. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5162 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:19 | MEDIUM (4) | The AllowCrossRendererResourceLoad function in extensions/browser/url_request_util.cc in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux does not properly use an extension's manifest.json web_accessible_resources field for restrictions on IFRAME elements, which makes it easier for remote attackers to conduct clickjacking attacks, and trick users into changing extension settings, via a crafted web site, a different vulnerability than CVE-2016-5160. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5161 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:18 | MEDIUM (7) | The EditingStyle::mergeStyle function in WebKit/Source/core/editing/EditingStyle.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, mishandles custom properties, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site that leverages "type confusion" in the StylePropertySerializer class. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5160 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:17 | MEDIUM (4) | The AllowCrossRendererResourceLoad function in extensions/browser/url_request_util.cc in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux does not properly use an extension's manifest.json web_accessible_resources field for restrictions on IFRAME elements, which makes it easier for remote attackers to conduct clickjacking attacks, and trick users into changing extension settings, via a crafted web site, a different vulnerability than CVE-2016-5162. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5159 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JPEG 2000 data that is mishandled during opj_aligned_malloc calls in dwt.c and t1.c. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5158 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in the opj_tcd_init_tile function in tcd.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JPEG 2000 data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5157 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the opj_dwt_interleave_v function in dwt.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via crafted coordinate values in JPEG 2000 data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5156 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:12 | MEDIUM (7) | extensions/renderer/event_bindings.cc in the event bindings in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux attempts to process filtered events after failure to add an event matcher, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5155 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:11 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux does not properly validate access to the initial document, which allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5154 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple heap-based buffer overflows in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted JBig2 image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5153 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:09 | MEDIUM (7) | The Web Animations implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, improperly relies on list iteration, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-destruction) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5152 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflow in the opj_tcd_get_decoded_tile_size function in tcd.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JPEG 2000 data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5151 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:07 | MEDIUM (7) | PDFium in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux mishandles timers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document, related to fpdfsdk/javascript/JS_Object.cpp and fpdfsdk/javascript/app.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5150 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:05 | MEDIUM (7) | WebKit/Source/bindings/modules/v8/V8BindingForModules.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, has an Indexed Database (aka IndexedDB) API implementation that does not properly restrict key-path evaluation, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that leverages certain side effects. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5149 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:04 | MEDIUM (7) | The extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux relies on an IFRAME source URL to identify an associated extension, which allows remote attackers to conduct extension-bindings injection attacks by leveraging script access to a resource that initially has the about:blank URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5148 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via vectors related to widget updates, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5147 | 2016‑09‑11 10:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 53.0.2785.89 on Windows and OS X and before 53.0.2785.92 on Linux, mishandles deferred page loads, which allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via a crafted web site, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5146 | 2016‑08‑07 19:59:12 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.116 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5145 | 2016‑08‑07 19:59:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.116, does not ensure that a taint property is preserved after a structure-clone operation on an ImageBitmap object derived from a cross-origin image, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5144 | 2016‑08‑07 19:59:09 | HIGH (8) | The Developer Tools (aka DevTools) subsystem in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.116, mishandles the script-path hostname, remoteBase parameter, and remoteFrontendUrl parameter, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted URL, a different vulnerability than CVE-2016-5143. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5143 | 2016‑08‑07 19:59:08 | HIGH (8) | The Developer Tools (aka DevTools) subsystem in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.116, mishandles the script-path hostname, remoteBase parameter, and remoteFrontendUrl parameter, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted URL, a different vulnerability than CVE-2016-5144. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5142 | 2016‑08‑07 19:59:07 | HIGH (8) | The Web Cryptography API (aka WebCrypto) implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.116, does not properly copy data buffers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code, related to NormalizeAlgorithm.cpp and SubtleCrypto.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5141 | 2016‑08‑07 19:59:05 | MEDIUM (5) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.116, allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via vectors involving a provisional URL for an initially empty document, related to FrameLoader.cpp and ScopedPageLoadDeferrer.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5140 | 2016‑08‑07 19:59:03 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the opj_j2k_read_SQcd_SQcc function in j2k.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.116, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JPEG 2000 data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5139 | 2016‑08‑07 19:59:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in the opj_tcd_init_tile function in tcd.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.116, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JPEG 2000 data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5138 | 2016‑08‑01 02:59:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflow in the kbasep_vinstr_attach_client function in midgard/mali_kbase_vinstr.c in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.85 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow and use-after-free) by leveraging an unrestricted multiplication. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5137 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:21 | MEDIUM (4) | The CSPSource::schemeMatches function in WebKit/Source/core/frame/csp/CSPSource.cpp in the Content Security Policy (CSP) implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, does not apply http :80 policies to https :443 URLs and does not apply ws :80 policies to wss :443 URLs, which makes it easier for remote attackers to determine whether a specific HSTS web site has been visited by reading a CSP report. NOTE: this vulnerability is associated with a specification change after CVE-2016-1617 resolution. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5136 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:20 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in extensions/renderer/user_script_injector.cc in the Extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to script deletion. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5135 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:19 | MEDIUM (4) | WebKit/Source/core/html/parser/HTMLPreloadScanner.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, does not consider referrer-policy information inside an HTML document during a preload request, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Content Security Policy (CSP) protection mechanism via a crafted web site, as demonstrated by a "Content-Security-Policy: referrer origin-when-cross-origin" header that overrides a "<META name='referrer' content='no-referrer'>" element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5134 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:17 | MEDIUM (4) | net/proxy/proxy_service.cc in the Proxy Auto-Config (PAC) feature in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 does not ensure that URL information is restricted to a scheme, host, and port, which allows remote attackers to discover credentials by operating a server with a PAC script, a related issue to CVE-2016-3763. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5133 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 mishandles origin information during proxy authentication, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to spoof a proxy-authentication login prompt or trigger incorrect credential storage by modifying the client-server data stream. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5132 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:15 | MEDIUM (7) | The Service Workers subsystem in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 does not properly implement the Secure Contexts specification during decisions about whether to control a subframe, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via an https IFRAME element inside an http IFRAME element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5131 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:14 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in libxml2 through 2.9.4, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the XPointer range-to function. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5130 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:12 | MEDIUM (4) | content/renderer/history_controller.cc in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 does not properly restrict multiple uses of a JavaScript forward method, which allows remote attackers to spoof the URL display via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5129 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Google V8 before 5.2.361.32, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, does not properly process left-trimmed objects, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5128 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:10 | MEDIUM (7) | objects.cc in Google V8 before 5.2.361.27, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, does not prevent API interceptors from modifying a store target without setting a property, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑5127 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in WebKit/Source/core/editing/VisibleUnits.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code involving an @import at-rule in a Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequence in conjunction with a rel=import attribute of a LINK element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑3679 | 2016‑03‑29 10:59:05 | HIGH (9) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.9.385.33, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.108, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑2845 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:16 | MEDIUM (5) | The Content Security Policy (CSP) implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75, does not ignore a URL's path component in the case of a ServiceWorker fetch, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information about visited web pages by reading CSP violation reports, related to FrameFetchContext.cpp and ResourceFetcher.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑2844 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:15 | HIGH (9) | WebKit/Source/core/layout/LayoutBlock.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75, does not properly determine when anonymous block wrappers may exist, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect cast and assertion failure) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑2843 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:14 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.9.385.26, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑2052 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in HarfBuzz before 1.0.6, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via crafted data, as demonstrated by a buffer over-read resulting from an inverted length check in hb-ot-font.cc, a different issue than CVE-2015-8947. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑2051 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.8.271.17, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1711 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:08 | MEDIUM (7) | WebKit/Source/core/loader/FrameLoader.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, does not disable frame navigation during a detach operation on a DocumentLoader object, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1710 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:07 | MEDIUM (7) | The ChromeClientImpl::createWindow method in WebKit/Source/web/ChromeClientImpl.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, does not prevent window creation by a deferred frame, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1709 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:06 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the ByteArray::Get method in data/byte_array.cc in Google sfntly before 2016-06-10, as used in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted SFNT font. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1708 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:04 | MEDIUM (7) | The Chrome Web Store inline-installation implementation in the Extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 does not properly consider object lifetimes during progress observation, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1707 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:03 | MEDIUM (4) | ios/web/web_state/ui/crw_web_controller.mm in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 on iOS does not ensure that an invalid URL is replaced with the about:blank URL, which allows remote attackers to spoof the URL display via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1706 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:02 | HIGH (9) | The PPAPI implementation in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 does not validate the origin of IPC messages to the plugin broker process that should have come from the browser process, which allows remote attackers to bypass a sandbox protection mechanism via an unexpected message type, related to broker_process_dispatcher.cc, ppapi_plugin_process_host.cc, ppapi_thread.cc, and render_frame_message_filter.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1705 | 2016‑07‑23 19:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 52.0.2743.82 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1704 | 2016‑07‑03 21:59:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.103 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1703 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:33 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.79 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1702 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:32 | MEDIUM (4) | The SkRegion::readFromMemory function in core/SkRegion.cpp in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.79, does not validate the interval count, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via crafted serialized data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1701 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:31 | MEDIUM (7) | The Autofill implementation in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.79 mishandles the interaction between field updates and JavaScript code that triggers a frame deletion, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site, a different vulnerability than CVE-2016-1690. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1700 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:30 | MEDIUM (5) | extensions/renderer/runtime_custom_bindings.cc in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.79 does not consider side effects during creation of an array of extension views, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to extensions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1699 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:29 | MEDIUM (4) | WebKit/Source/devtools/front_end/devtools.js in the Developer Tools (aka DevTools) subsystem in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.79, does not ensure that the remoteFrontendUrl parameter is associated with a chrome-devtools-frontend.appspot.com URL, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1698 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:28 | MEDIUM (4) | The createCustomType function in extensions/renderer/resources/binding.js in the extension bindings in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.79 does not validate module types, which might allow attackers to load arbitrary modules or obtain sensitive information by leveraging a poisoned definition. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1697 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:27 | MEDIUM (7) | The FrameLoader::startLoad function in WebKit/Source/core/loader/FrameLoader.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.79, does not prevent frame navigations during DocumentLoader detach operations, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1696 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:26 | MEDIUM (7) | The extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.79 does not properly restrict bindings access, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1695 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:25 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1694 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:24 | MEDIUM (4) | browser/browsing_data/browsing_data_remover.cc in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 deletes HPKP pins during cache clearing, which makes it easier for remote attackers to spoof web sites via a valid certificate from an arbitrary recognized Certification Authority. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1693 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:23 | LOW (3) | browser/safe_browsing/srt_field_trial_win.cc in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 does not use the HTTPS service on dl.google.com to obtain the Software Removal Tool, which allows remote attackers to spoof the chrome_cleanup_tool.exe (aka CCT) file via a man-in-the-middle attack on an HTTP session. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1692 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:22 | MEDIUM (4) | WebKit/Source/core/css/StyleSheetContents.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, permits cross-origin loading of CSS stylesheets by a ServiceWorker even when the stylesheet download has an incorrect MIME type, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1691 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:21 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, mishandles coincidence runs, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted curves, related to SkOpCoincidence.cpp and SkPathOpsCommon.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1690 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:20 | MEDIUM (5) | The Autofill implementation in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 mishandles the interaction between field updates and JavaScript code that triggers a frame deletion, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site, a different vulnerability than CVE-2016-1701. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1689 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:19 | MEDIUM (4) | Heap-based buffer overflow in content/renderer/media/canvas_capture_handler.cc in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1688 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:18 | MEDIUM (4) | The regexp (aka regular expression) implementation in Google V8 before 5.0.71.40, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, mishandles external string sizes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1687 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:17 | MEDIUM (4) | The renderer implementation in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 does not properly restrict public exposure of classes, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via vectors related to extensions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1686 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:15 | MEDIUM (4) | The CPDF_DIBSource::CreateDecoder function in core/fpdfapi/fpdf_render/fpdf_render_loadimage.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, mishandles decoder-initialization failure, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1685 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:14 | MEDIUM (4) | core/fxge/ge/fx_ge_text.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, miscalculates certain index values, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1684 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:13 | MEDIUM (5) | numbers.c in libxslt before 1.1.29, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, mishandles the i format token for xsl:number data, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (integer overflow or resource consumption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1683 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:12 | MEDIUM (5) | numbers.c in libxslt before 1.1.29, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, mishandles namespace nodes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds heap memory access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1682 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:11 | MEDIUM (4) | The ServiceWorkerContainer::registerServiceWorkerImpl function in WebKit/Source/modules/serviceworkers/ServiceWorkerContainer.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, allows remote attackers to bypass the Content Security Policy (CSP) protection mechanism via a ServiceWorker registration. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1681 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:10 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the opj_j2k_read_SPCod_SPCoc function in j2k.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1680 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in ports/SkFontHost_FreeType.cpp in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1679 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:08 | MEDIUM (7) | The ToV8Value function in content/child/v8_value_converter_impl.cc in the V8 bindings in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 does not properly restrict use of getters and setters, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1678 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:07 | MEDIUM (7) | objects.cc in Google V8 before 5.0.71.32, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, does not properly restrict lazy deoptimization, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1677 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:06 | MEDIUM (4) | uri.js in Google V8 before 5.1.281.26, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, uses an incorrect array type, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information by calling the decodeURI function and leveraging "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1676 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:05 | MEDIUM (7) | extensions/renderer/resources/binding.js in the extension bindings in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 does not properly use prototypes, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1675 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy by leveraging the mishandling of Document reattachment during destruction, related to FrameLoader.cpp and LocalFrame.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1674 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1673 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1672 | 2016‑06‑05 23:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | The ModuleSystem::RequireForJsInner function in extensions/renderer/module_system.cc in the extension bindings in Google Chrome before 51.0.2704.63 mishandles properties, which allows remote attackers to conduct bindings-interception attacks and bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1671 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.102 on Android mishandles / (slash) and \ (backslash) characters, which allows attackers to conduct directory traversal attacks via a file: URL, related to net/base/escape.cc and net/base/filename_util.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1670 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:10 | LOW (3) | Race condition in the ResourceDispatcherHostImpl::BeginRequest function in content/browser/loader/resource_dispatcher_host_impl.cc in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.102 allows remote attackers to make arbitrary HTTP requests by leveraging access to a renderer process and reusing a request ID. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1669 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:09 | HIGH (9) | The Zone::New function in zone.cc in Google V8 before 5.0.71.47, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.102, does not properly determine when to expand certain memory allocations, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1668 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:08 | MEDIUM (7) | The forEachForBinding function in WebKit/Source/bindings/core/v8/Iterable.h in the V8 bindings in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.102, uses an improper creation context, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1667 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:07 | MEDIUM (7) | The TreeScope::adoptIfNeeded function in WebKit/Source/core/dom/TreeScope.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.102, does not prevent script execution during node-adoption operations, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1666 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:06 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.94 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1665 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:05 | MEDIUM (4) | The JSGenericLowering class in compiler/js-generic-lowering.cc in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.94, mishandles comparison operators, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1664 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:04 | MEDIUM (4) | The HistoryController::UpdateForCommit function in content/renderer/history_controller.cc in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.94 mishandles the interaction between subframe forward navigations and other forward navigations, which allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1663 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:03 | MEDIUM (7) | The SerializedScriptValue::transferArrayBuffers function in WebKit/Source/bindings/core/v8/SerializedScriptValue.cpp in the V8 bindings in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.94, mishandles certain array-buffer data structures, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1662 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:02 | HIGH (10) | extensions/renderer/gc_callback.cc in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.94 does not prevent fallback execution once the Garbage Collection callback has started, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1661 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:01 | HIGH (8) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.94, does not ensure that frames satisfy a check for the same renderer process in addition to a Same Origin Policy check, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site, related to BindingSecurity.cpp and DOMWindow.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1660 | 2016‑05‑14 21:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.94, mishandles assertions in the WTF::BitArray and WTF::double_conversion::Vector classes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds write) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1659 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:08 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1658 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:07 | MEDIUM (4) | The Extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75 incorrectly relies on GetOrigin method calls for origin comparisons, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and obtain sensitive information via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1657 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:06 | MEDIUM (4) | The WebContentsImpl::FocusLocationBarByDefault function in content/browser/web_contents/web_contents_impl.cc in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75 mishandles focus for certain about:blank pages, which allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via a crafted URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1656 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:05 | MEDIUM (5) | The download implementation in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75 on Android allows remote attackers to bypass intended pathname restrictions via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1655 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75 does not properly consider that frame removal may occur during callback execution, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1654 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:03 | MEDIUM (4) | The media subsystem in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75 does not initialize an unspecified data structure, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (invalid read operation) via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1653 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:02 | HIGH (9) | The LoadBuffer implementation in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75, mishandles data types, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers an out-of-bounds write operation, related to compiler/pipeline.cc and compiler/simplified-lowering.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1652 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the ModuleSystem::RequireForJsInner function in extensions/renderer/module_system.cc in the Extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via a crafted web site, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1651 | 2016‑04‑18 10:59:00 | MEDIUM (6) | fxcodec/codec/fx_codec_jpx_opj.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 50.0.2661.75, does not properly implement the sycc420_to_rgb and sycc422_to_rgb functions, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information from process memory or cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via crafted JPEG 2000 data in a PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1650 | 2016‑03‑29 10:59:04 | HIGH (9) | The PageCaptureSaveAsMHTMLFunction::ReturnFailure function in browser/extensions/api/page_capture/page_capture_api.cc in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.108 allows attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering an error in creating an MHTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1649 | 2016‑03‑29 10:59:03 | HIGH (9) | The Program::getUniformInternal function in Program.cpp in libANGLE, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.108, does not properly handle a certain data-type mismatch, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted shader stages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1648 | 2016‑03‑29 10:59:02 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the GetLoadTimes function in renderer/loadtimes_extension_bindings.cc in the Extensions implementation in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.108 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1647 | 2016‑03‑29 10:59:01 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the RenderWidgetHostImpl::Destroy function in content/browser/renderer_host/render_widget_host_impl.cc in the Navigation implementation in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.108 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1646 | 2016‑03‑29 10:59:00 | HIGH (9) | The Array.prototype.concat implementation in builtins.cc in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.108, does not properly consider element data types, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1645 | 2016‑03‑13 22:59:05 | HIGH (9) | Multiple integer signedness errors in the opj_j2k_update_image_data function in j2k.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.87, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect cast and out-of-bounds write) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JPEG 2000 data. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1644 | 2016‑03‑13 22:59:04 | HIGH (9) | WebKit/Source/core/layout/LayoutObject.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.87, does not properly restrict relayout scheduling, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1643 | 2016‑03‑13 22:59:03 | HIGH (9) | The ImageInputType::ensurePrimaryContent function in WebKit/Source/core/html/forms/ImageInputType.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.87, does not properly maintain the user agent shadow DOM, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that leverage "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1642 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:13 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1641 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:12 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in content/browser/web_contents/web_contents_impl.cc in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering an image download after a certain data structure is deleted, as demonstrated by a favicon.ico download. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1640 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:11 | MEDIUM (4) | The Web Store inline-installer implementation in the Extensions UI in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 does not block installations upon deletion of an installation frame, which makes it easier for remote attackers to trick a user into believing that an installation request originated from the user's next navigation target via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1639 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:10 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in browser/extensions/api/webrtc_audio_private/webrtc_audio_private_api.cc in the WebRTC Audio Private API implementation in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging incorrect reliance on the resource context pointer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1638 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:09 | MEDIUM (7) | extensions/renderer/resources/platform_app.js in the Extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 does not properly restrict use of Web APIs, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted platform app. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1637 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:08 | MEDIUM (4) | The SkATan2_255 function in effects/gradients/SkSweepGradient.cpp in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75, mishandles arctangent calculations, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1636 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:07 | HIGH (8) | The PendingScript::notifyFinished function in WebKit/Source/core/dom/PendingScript.cpp in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 relies on memory-cache information about integrity-check occurrences instead of integrity-check successes, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Subresource Integrity (aka SRI) protection mechanism by triggering two loads of the same resource. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1635 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:06 | HIGH (10) | extensions/renderer/render_frame_observer_natives.cc in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 does not properly consider object lifetimes and re-entrancy issues during OnDocumentElementCreated handling, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1634 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:05 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the StyleResolver::appendCSSStyleSheet function in WebKit/Source/core/css/resolver/StyleResolver.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site that triggers Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) style invalidation during a certain subtree-removal action. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1633 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:04 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1632 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:03 | MEDIUM (7) | The Extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 does not properly maintain own properties, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via crafted JavaScript code that triggers an incorrect cast, related to extensions/renderer/v8_helpers.h and gin/converter.h. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1631 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The PPB_Flash_MessageLoop_Impl::InternalRun function in content/renderer/pepper/ppb_flash_message_loop_impl.cc in the Pepper plugin in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75 mishandles nested message loops, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1630 | 2016‑03‑06 02:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | The ContainerNode::parserRemoveChild function in WebKit/Source/core/dom/ContainerNode.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 49.0.2623.75, mishandles widget updates, which makes it easier for remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1629 | 2016‑02‑21 18:59:01 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.116 allows remote attackers to bypass the Blink Same Origin Policy and a sandbox protection mechanism via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1628 | 2016‑02‑21 05:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | pi.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.109, does not validate a certain precision value, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted JPEG 2000 image in a PDF document, related to the opj_pi_next_rpcl, opj_pi_next_pcrl, and opj_pi_next_cprl functions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1627 | 2016‑02‑14 02:59:05 | MEDIUM (7) | The Developer Tools (aka DevTools) subsystem in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.109 does not validate URL schemes and ensure that the remoteBase parameter is associated with a chrome-devtools-frontend.appspot.com URL, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted URL, related to browser/devtools/devtools_ui_bindings.cc and WebKit/Source/devtools/front_end/Runtime.js. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1626 | 2016‑02‑14 02:59:04 | MEDIUM (4) | The opj_pi_update_decode_poc function in pi.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.109, miscalculates a certain layer index value, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1625 | 2016‑02‑14 02:59:03 | MEDIUM (4) | The Chrome Instant feature in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.109 does not ensure that a New Tab Page (NTP) navigation target is on the most-visited or suggestions list, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended restrictions via unspecified vectors, related to instant_service.cc and search_tab_helper.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1624 | 2016‑02‑14 02:59:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer underflow in the ProcessCommandsInternal function in dec/decode.c in Brotli, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.109, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted data with brotli compression. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1623 | 2016‑02‑14 02:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | The DOM implementation in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.109 does not properly restrict frame-attach operations from occurring during or after frame-detach operations, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site, related to FrameLoader.cpp, HTMLFrameOwnerElement.h, LocalFrame.cpp, and WebLocalFrameImpl.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1622 | 2016‑02‑14 02:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | The Extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.109 does not prevent use of the Object.defineProperty method to override intended extension behavior, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1620 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:09 | HIGH (9) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1619 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in the (1) sycc422_to_rgb and (2) sycc444_to_rgb functions in fxcodec/codec/fx_codec_jpx_opj.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1618 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:07 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82, does not ensure that a proper cryptographicallyRandomValues random number generator is used, which makes it easier for remote attackers to defeat cryptographic protection mechanisms via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1617 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:06 | MEDIUM (4) | The CSPSource::schemeMatches function in WebKit/Source/core/frame/csp/CSPSource.cpp in the Content Security Policy (CSP) implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82, does not apply http policies to https URLs and does not apply ws policies to wss URLs, which makes it easier for remote attackers to determine whether a specific HSTS web site has been visited by reading a CSP report. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1616 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:05 | MEDIUM (4) | The CustomButton::AcceleratorPressed function in ui/views/controls/button/custom_button.cc in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82 allows remote attackers to spoof URLs via vectors involving an unfocused custom button. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1615 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:04 | MEDIUM (4) | The Omnibox implementation in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82 allows remote attackers to spoof a document's origin via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1614 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:02 | MEDIUM (4) | The UnacceleratedImageBufferSurface class in WebKit/Source/platform/graphics/UnacceleratedImageBufferSurface.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82, mishandles the initialization mode, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information from process memory via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1613 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in the formfiller implementation in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document, related to improper tracking of the destruction of (1) IPWL_FocusHandler and (2) IPWL_Provider objects. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑1612 | 2016‑01‑25 11:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | The LoadIC::UpdateCaches function in ic/ic.cc in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 48.0.2564.82, does not ensure receiver compatibility before performing a cast of an unspecified variable, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2016‑10403 | 2019‑01‑09 19:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient data validation on image data in PDFium in Google Chrome prior to 51.0.2704.63 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory read via a crafted PDF file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑8664 | 2015‑12‑24 03:59:01 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the WebCursor::Deserialize function in content/common/cursors/webcursor.cc in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.106 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via an RGBA pixel array with crafted dimensions, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-6792. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑8548 | 2015‑12‑14 11:59:05 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.7.80.23, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.80, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors, a different issue than CVE-2015-8478. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑8480 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:28 | HIGH (10) | The VideoFramePool::PoolImpl::CreateFrame function in media/base/video_frame_pool.cc in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 does not initialize memory for a video-frame data structure, which might allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds memory access) or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper interaction with the vp3_h_loop_filter_c function in libavcodec/vp3dsp.c in FFmpeg. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑8479 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:26 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the AudioOutputDevice::OnDeviceAuthorized function in media/audio/audio_output_device.cc in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering access to an unauthorized audio output device. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑8478 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:25 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.7.80.23, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑7834 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:12 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.6.85.23, as used in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6792 | 2015‑12‑24 03:59:00 | HIGH (10) | The MIDI subsystem in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.106 does not properly handle the sending of data, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors, related to midi_manager.cc, midi_manager_alsa.cc, and midi_manager_mac.cc, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-8664. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6791 | 2015‑12‑14 11:59:04 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.80 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6790 | 2015‑12‑14 11:59:03 | MEDIUM (4) | The WebPageSerializerImpl::openTagToString function in WebKit/Source/web/WebPageSerializerImpl.cpp in the page serializer in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.80 does not properly use HTML entities, which might allow remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via a crafted document, as demonstrated by a double-quote character inside a single-quoted string. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6789 | 2015‑12‑14 11:59:02 | HIGH (9) | Race condition in the MutationObserver implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.80, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging unanticipated object deletion. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6788 | 2015‑12‑14 11:59:00 | HIGH (10) | The ObjectBackedNativeHandler class in extensions/renderer/object_backed_native_handler.cc in the extensions subsystem in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.80 improperly implements handler functions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that leverage "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6787 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:24 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6786 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:24 | MEDIUM (4) | The CSPSourceList::matches function in WebKit/Source/core/frame/csp/CSPSourceList.cpp in the Content Security Policy (CSP) implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 accepts a blob:, data:, or filesystem: URL as a match for a * pattern, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended scheme restrictions in opportunistic circumstances by leveraging a policy that relies on this pattern. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6785 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:22 | MEDIUM (4) | The CSPSource::hostMatches function in WebKit/Source/core/frame/csp/CSPSource.cpp in the Content Security Policy (CSP) implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 accepts an x.y hostname as a match for a *.x.y pattern, which might allow remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions in opportunistic circumstances by leveraging a policy that was intended to be specific to subdomains. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6784 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:21 | MEDIUM (4) | The page serializer in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 mishandles Mark of the Web (MOTW) comments for URLs containing a "--" sequence, which might allow remote attackers to inject HTML via a crafted URL, as demonstrated by an initial http://example.com?-- substring. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6783 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:21 | MEDIUM (4) | The FindStartOffsetOfFileInZipFile function in crazy_linker_zip.cpp in crazy_linker (aka Crazy Linker) in Android 5.x and 6.x, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, improperly searches for an EOCD record, which allows attackers to bypass a signature-validation requirement via a crafted ZIP archive. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6782 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:20 | MEDIUM (4) | The Document::open function in WebKit/Source/core/dom/Document.cpp in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 does not ensure that page-dismissal event handling is compatible with modal-dialog blocking, which makes it easier for remote attackers to spoof Omnibox content via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6781 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:19 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the FontData::Bound function in data/font_data.cc in Google sfntly, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted offset or length value within font data in an SFNT container. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6780 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:18 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Infobars implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site, related to browser/ui/views/website_settings/website_settings_popup_view.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6779 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:17 | MEDIUM (4) | PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, does not properly restrict use of chrome: URLs, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended scheme restrictions via a crafted PDF document, as demonstrated by a document with a link to a chrome://settings URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6778 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:16 | HIGH (8) | The CJBig2_SymbolDict class in fxcodec/jbig2/JBig2_SymbolDict.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds memory access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a PDF document containing crafted data with JBIG2 compression. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6777 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:15 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the ContainerNode::notifyNodeInsertedInternal function in WebKit/Source/core/dom/ContainerNode.cpp in the DOM implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to DOMCharacterDataModified events for certain detached-subtree insertions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6776 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:14 | MEDIUM (7) | The opj_dwt_decode_1* functions in dwt.c in OpenJPEG, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds array access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JPEG 2000 data that is mishandled during a discrete wavelet transform. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6775 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:13 | HIGH (8) | fpdfsdk/src/jsapi/fxjs_v8.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, does not use signatures, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that leverage "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6774 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:12 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the GetLoadTimes function in renderer/loadtimes_extension_bindings.cc in the Extensions implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that modifies a pointer used for reporting loadTimes data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6773 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:10 | HIGH (8) | The convolution implementation in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, does not properly constrain row lengths, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds memory access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted graphics data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6772 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:09 | HIGH (8) | The DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, does not prevent javascript: URL navigation while a document is being detached, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code that improperly interacts with a plugin. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6771 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:08 | HIGH (8) | js/array.js in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, improperly implements certain map and filter operations for arrays, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds memory access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6770 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:07 | HIGH (8) | The DOM implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-6768. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6769 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:06 | HIGH (8) | The provisional-load commit implementation in WebKit/Source/bindings/core/v8/WindowProxy.cpp in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy by leveraging a delay in window proxy clearing. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6768 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:05 | HIGH (8) | The DOM implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-6770. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6767 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:04 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in content/browser/appcache/appcache_dispatcher_host.cc in the AppCache implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging incorrect pointer maintenance associated with certain callbacks. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6766 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:03 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the AppCache implementation in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers with renderer access to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging incorrect AppCacheUpdateJob behavior associated with duplicate cache selection. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6765 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:02 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in content/browser/appcache/appcache_update_job.cc in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service by leveraging the mishandling of AppCache update jobs. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6764 | 2015‑12‑06 01:59:00 | CRITICAL (10) | The BasicJsonStringifier::SerializeJSArray function in json-stringifier.h in the JSON stringifier in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 47.0.2526.73, improperly loads array elements, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds memory access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6763 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:10 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6762 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:09 | HIGH (8) | The CSSFontFaceSrcValue::fetch function in core/css/CSSFontFaceSrcValue.cpp in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71, does not use the CORS cross-origin request algorithm when a font's URL appears to be a same-origin URL, which allows remote web servers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a redirect. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6761 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:07 | MEDIUM (7) | The update_dimensions function in libavcodec/vp8.c in FFmpeg through 2.8.1, as used in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71 and other products, relies on a coefficient-partition count during multi-threaded operation, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (race condition and memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted WebM file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6760 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:06 | HIGH (8) | The Image11::map function in renderer/d3d/d3d11/Image11.cpp in libANGLE, as used in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71, mishandles mapping failures after device-lost events, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (invalid read or write) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a removed device. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6759 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:05 | MEDIUM (5) | The shouldTreatAsUniqueOrigin function in platform/weborigin/SecurityOrigin.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71, does not ensure that the origin of a LocalStorage resource is considered unique, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via vectors involving a blob: URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6758 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:04 | MEDIUM (7) | The CPDF_Document::GetPage function in fpdfapi/fpdf_parser/fpdf_parser_document.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71, does not properly perform a cast of a dictionary object, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6757 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:03 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in content/browser/service_worker/embedded_worker_instance.cc in the ServiceWorker implementation in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging object destruction in a callback. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6756 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the CPDFSDK_PageView implementation in fpdfsdk/src/fsdk_mgr.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging mishandling of a focused annotation in a PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6755 | 2015‑10‑15 10:59:00 | HIGH (8) | The ContainerNode::parserInsertBefore function in core/dom/ContainerNode.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.71, proceeds with a DOM tree insertion in certain cases where a parent node no longer contains a child node, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6583 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:17 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85 does not display a location bar for a hosted app's window after navigation away from the installation site, which might make it easier for remote attackers to spoof content via a crafted app, related to browser.cc and hosted_app_browser_controller.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6582 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:16 | MEDIUM (7) | The decompose function in platform/transforms/TransformationMatrix.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, does not verify that a matrix inversion succeeded, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (uninitialized memory access and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6581 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:15 | HIGH (8) | Double free vulnerability in the opj_j2k_copy_default_tcp_and_create_tcd function in j2k.c in OpenJPEG before r3002, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) by triggering a memory-allocation failure. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑6580 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:14 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.5.103.29, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑5605 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:19 | MEDIUM (5) | The regular-expression implementation in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, mishandles interrupts, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via crafted JavaScript code, as demonstrated by an error in garbage collection during allocation of a stack-overflow exception message. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑4491 | 2015‑08‑16 01:59:19 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflow in the make_filter_table function in pixops/pixops.c in gdk-pixbuf before 2.31.5, as used in Mozilla Firefox before 40.0 and Firefox ESR 38.x before 38.2 on Linux, Google Chrome on Linux, and other products, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow and application crash) via crafted bitmap dimensions that are mishandled during scaling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑3910 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:20 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.3.61.21, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑3336 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 does not always ask the user before proceeding with CONTENT_SETTINGS_TYPE_FULLSCREEN and CONTENT_SETTINGS_TYPE_MOUSELOCK changes, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (UI disruption) by constructing a crafted HTML document containing JavaScript code with requestFullScreen and requestPointerLock calls, and arranging for the user to access this document with a file: URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑3335 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:15 | HIGH (8) | The NaClSandbox::InitializeLayerTwoSandbox function in components/nacl/loader/sandbox_linux/nacl_sandbox_linux.cc in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 does not have RLIMIT_AS and RLIMIT_DATA limits for Native Client (aka NaCl) processes, which might make it easier for remote attackers to conduct row-hammer attacks or have unspecified other impact by leveraging the ability to run a crafted program in the NaCl sandbox. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑3334 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:14 | MEDIUM (4) | browser/ui/website_settings/website_settings.cc in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 does not always display "Media: Allowed by you" in a Permissions table after the user has granted camera permission to a web site, which might make it easier for user-assisted remote attackers to obtain sensitive video data from a device's physical environment via a crafted web site that turns on the camera at a time when the user believes that camera access is prohibited. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑3333 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:13 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.2.77.14, as used in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑2239 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:30 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, when Instant Extended mode is used, does not properly consider the interaction between the "1993 search" features and restore-from-disk RELOAD transitions, which makes it easier for remote attackers to spoof the address bar for a search-results page by leveraging (1) a compromised search engine or (2) an XSS vulnerability in a search engine, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1231. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑2238 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:29 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 4.1.0.21, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1361 | 2015‑01‑27 20:04:16 | MEDIUM (7) | platform/image-decoders/ImageFrame.h in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, does not initialize a variable that is used in calls to the Skia SkBitmap::setAlphaType function, which might allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1205. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1360 | 2015‑01‑27 20:04:15 | HIGH (8) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (buffer over-read) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted data that is improperly handled during text drawing, related to gpu/GrBitmapTextContext.cpp and gpu/GrDistanceFieldTextContext.cpp, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1205. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1359 | 2015‑01‑27 20:04:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple off-by-one errors in fpdfapi/fpdf_font/font_int.h in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document, related to an "intra-object-overflow" issue, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1205. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1346 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:30 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 3.30.33.15, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1304 | 2015‑10‑12 01:59:17 | HIGH (8) | object-observe.js in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.101, does not properly restrict method calls on access-checked objects, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a (1) observe or (2) getNotifier call. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1303 | 2015‑10‑12 01:59:15 | HIGH (8) | bindings/core/v8/V8DOMWrapper.h in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.101, does not perform a rethrow action to propagate information about a cross-context exception, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted HTML document containing an IFRAME element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1302 | 2015‑11‑11 11:59:00 | HIGH (8) | The PDF viewer in Google Chrome before 46.0.2490.86 does not properly restrict scripting messages and API exposure, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via an unintended embedder or unintended plugin loading, related to pdf.js and out_of_process_instance.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1301 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:13 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1300 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:11 | MEDIUM (5) | The FrameFetchContext::updateTimingInfoForIFrameNavigation function in core/loader/FrameFetchContext.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, does not properly restrict the availability of IFRAME Resource Timing API times, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via crafted JavaScript code that leverages a history.back call. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1299 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:10 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the shared-timer implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging erroneous timer firing, related to ThreadTimers.cpp and Timer.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1298 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:09 | MEDIUM (4) | The RuntimeEventRouter::OnExtensionUninstalled function in extensions/browser/api/runtime/runtime_api.cc in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85 does not ensure that the setUninstallURL preference corresponds to the URL of a web site, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to trigger access to an arbitrary URL via a crafted extension that is uninstalled. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1297 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:08 | HIGH (8) | The WebRequest API implementation in extensions/browser/api/web_request/web_request_api.cc in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85 does not properly consider a request's source before accepting the request, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted (1) app or (2) extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1296 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:07 | MEDIUM (5) | The UnescapeURLWithAdjustmentsImpl implementation in net/base/escape.cc in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85 does not prevent display of Unicode LOCK characters in the omnibox, which makes it easier for remote attackers to spoof the SSL lock icon by placing one of these characters at the end of a URL, as demonstrated by the omnibox in localizations for right-to-left languages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1295 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:06 | HIGH (8) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in the PrintWebViewHelper class in components/printing/renderer/print_web_view_helper.cc in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85 allow user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering nested IPC messages during preparation for printing, as demonstrated by messages associated with PDF documents in conjunction with messages about printer capabilities. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1294 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:05 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SkMatrix::invertNonIdentity function in core/SkMatrix.cpp in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering the use of matrix elements that lead to an infinite result during an inversion calculation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1293 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:03 | HIGH (8) | The DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1292 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:02 | MEDIUM (5) | The NavigatorServiceWorker::serviceWorker function in modules/serviceworkers/NavigatorServiceWorker.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy by accessing a Service Worker. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1291 | 2015‑09‑03 22:59:00 | MEDIUM (6) | The ContainerNode::parserRemoveChild function in core/dom/ContainerNode.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 45.0.2454.85, does not check whether a node is expected, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy or cause a denial of service (DOM tree corruption) via a web site with crafted JavaScript code and IFRAME elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1290 | 2018‑01‑09 16:29:00 | HIGH (9) | The Google V8 engine, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 and QtWebEngineCore in Qt before 5.5.1, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or execute arbitrary code via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1289 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:18 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1288 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:17 | MEDIUM (7) | The Spellcheck API implementation in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 does not use an HTTPS session for downloading a Hunspell dictionary, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to deliver incorrect spelling suggestions or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted file, a related issue to CVE-2015-1263. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1287 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, enables a quirks-mode exception that limits the cases in which a Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) document is required to have the text/css content type, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site, related to core/fetch/CSSStyleSheetResource.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1286 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the V8ContextNativeHandler::GetModuleSystem function in extensions/renderer/v8_context_native_handler.cc in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML by leveraging the lack of a certain V8 context restriction, aka a Blink "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1285 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:15 | MEDIUM (5) | The XSSAuditor::canonicalize function in core/html/parser/XSSAuditor.cpp in the XSS auditor in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, does not properly choose a truncation point, which makes it easier for remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via an unspecified linear-time attack. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1284 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:14 | HIGH (8) | The LocalFrame::isURLAllowed function in core/frame/LocalFrame.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, does not properly check for a page's maximum number of frames, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (invalid count value and use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that makes many createElement calls for IFRAME elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1283 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in the XML_GetBuffer function in Expat through 2.1.0, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 and other products, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted XML data, a related issue to CVE-2015-2716. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1282 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:12 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in fpdfsdk/src/javascript/Document.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document, related to the (1) Document::delay and (2) Document::DoFieldDelay functions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1281 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:11 | MEDIUM (4) | core/loader/ImageLoader.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, does not properly determine the V8 context of a microtask, which allows remote attackers to bypass Content Security Policy (CSP) restrictions by providing an image from an unintended source. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1280 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:10 | HIGH (8) | SkPictureShader.cpp in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging access to a renderer process and providing crafted serialized data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1279 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:09 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the CJBig2_Image::expand function in fxcodec/jbig2/JBig2_Image.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via large height and stride values. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1278 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:08 | MEDIUM (4) | content/browser/web_contents/web_contents_impl.cc in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 does not ensure that a PDF document's modal dialog is closed upon navigation to an interstitial page, which allows remote attackers to spoof URLs via a crafted document, as demonstrated by the alert_dialog.pdf document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1277 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:07 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the accessibility implementation in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging lack of certain validity checks for accessibility-tree data structures. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1276 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in content/browser/indexed_db/indexed_db_backing_store.cc in the IndexedDB implementation in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging an abort action before a certain write operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1275 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:05 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in org/chromium/chrome/browser/UrlUtilities.java in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 on Android allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via a crafted intent: URL, as demonstrated by a trailing alert(document.cookie);// substring, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1274 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 does not ensure that the auto-open list omits all dangerous file types, which makes it easier for remote attackers to execute arbitrary code by providing a crafted file and leveraging a user's previous "Always open files of this type" choice, related to download_commands.cc and download_prefs.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1273 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap-based buffer overflow in j2k.c in OpenJPEG before r3002, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via invalid JPEG2000 data in a PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1272 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the GPU process implementation in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging the continued availability of a GPUChannelHost data structure during Blink shutdown, related to content/browser/gpu/browser_gpu_channel_host_factory.cc and content/renderer/render_thread_impl.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1271 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, does not properly handle certain out-of-memory conditions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap-based buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document that triggers a large memory allocation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1270 | 2015‑07‑23 00:59:00 | MEDIUM (7) | The ucnv_io_getConverterName function in common/ucnv_io.cpp in International Components for Unicode (ICU), as used in Google Chrome before 44.0.2403.89, mishandles converter names with initial x- substrings, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (read of uninitialized memory) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1269 | 2015‑06‑26 14:59:04 | MEDIUM (4) | The DecodeHSTSPreloadRaw function in net/http/transport_security_state.cc in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.130 does not properly canonicalize DNS hostnames before making comparisons to HSTS or HPKP preload entries, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a string that (1) ends in a . (dot) character or (2) is not entirely lowercase. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1268 | 2015‑06‑26 14:59:03 | MEDIUM (5) | bindings/scripts/v8_types.py in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.130, does not properly select a creation context for a return value's DOM wrapper, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code, as demonstrated by use of a data: URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1267 | 2015‑06‑26 14:59:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.130, does not properly restrict the creation context during creation of a DOM wrapper, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code that uses a Blink public API, related to WebArrayBufferConverter.cpp, WebBlob.cpp, WebDOMError.cpp, and WebDOMFileSystem.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1266 | 2015‑06‑26 14:59:00 | MEDIUM (5) | content/browser/webui/content_web_ui_controller_factory.cc in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.130 does not properly consider the scheme in determining whether a URL is associated with a WebUI SiteInstance, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a similar URL, as demonstrated by use of http://gpu when there is a WebUI class for handling chrome://gpu requests. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1265 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:17 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1264 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 allows user-assisted remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via crafted data that is improperly handled by the Bookmarks feature. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1263 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:15 | MEDIUM (4) | The Spellcheck API implementation in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 does not use an HTTPS session for downloading a Hunspell dictionary, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to deliver incorrect spelling suggestions or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1262 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:14 | HIGH (8) | platform/fonts/shaping/HarfBuzzShaper.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65, does not initialize a certain width field, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted Unicode text. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1261 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:13 | MEDIUM (5) | android/java/src/org/chromium/chrome/browser/WebsiteSettingsPopup.java in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 on Android does not properly restrict use of a URL's fragment identifier during construction of a page-info popup, which allows remote attackers to spoof the URL bar or deliver misleading popup content via crafted text. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1260 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:13 | HIGH (8) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in content/renderer/media/user_media_client_impl.cc in the WebRTC implementation in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that executes upon completion of a getUserMedia request. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1259 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:12 | HIGH (8) | PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65, does not properly initialize memory, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1258 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:11 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 relies on libvpx code that was not built with an appropriate --size-limit value, which allows remote attackers to trigger a negative value for a size field, and consequently cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact, via a crafted frame size in VP9 video data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1257 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:10 | HIGH (8) | platform/graphics/filters/FEColorMatrix.cpp in the SVG implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65, does not properly handle an insufficient number of values in an feColorMatrix filter, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (container overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1256 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:09 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SVG implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document that leverages improper handling of a shadow tree for a use element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1255 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in content/renderer/media/webaudio_capturer_source.cc in the WebAudio implementation in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper handling of a stop action for an audio track. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1254 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:07 | MEDIUM (5) | core/dom/Document.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65, enables the inheritance of the designMode attribute, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy by leveraging the availability of editing. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1253 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:06 | HIGH (8) | core/html/parser/HTMLConstructionSite.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code that appends a child to a SCRIPT element, related to the insert and executeReparentTask functions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1252 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:04 | HIGH (8) | common/partial_circular_buffer.cc in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 does not properly handle wraps, which allows remote attackers to bypass a sandbox protection mechanism or cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds write) via vectors that trigger a write operation with a large amount of data, related to the PartialCircularBuffer::Write and PartialCircularBuffer::DoWrite functions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1251 | 2015‑05‑20 10:59:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SpeechRecognitionClient implementation in the Speech subsystem in Google Chrome before 43.0.2357.65 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1250 | 2015‑05‑01 10:59:06 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.135 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1249 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:12 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1248 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:11 | MEDIUM (4) | The FileSystem API in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 allows remote attackers to bypass the SafeBrowsing for Executable Files protection mechanism by creating a .exe file in a temporary filesystem and then referencing this file with a filesystem:http: URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1247 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:11 | MEDIUM (5) | The SearchEngineTabHelper::OnPageHasOSDD function in browser/ui/search_engines/search_engine_tab_helper.cc in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 does not prevent use of a file: URL for an OpenSearch descriptor XML document, which might allow remote attackers to obtain sensitive information from local files via a crafted (1) http or (2) https web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1246 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:10 | MEDIUM (5) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1245 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:09 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the OpenPDFInReaderView::Update function in browser/ui/views/location_bar/open_pdf_in_reader_view.cc in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 might allow user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering interaction with a PDFium "Open PDF in Reader" button that has an invalid tab association. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1244 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:08 | MEDIUM (5) | The URLRequest::GetHSTSRedirect function in url_request/url_request.cc in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 does not replace the ws scheme with the wss scheme whenever an HSTS Policy is active, which makes it easier for remote attackers to obtain sensitive information by sniffing the network for WebSocket traffic. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1243 | 2015‑05‑01 10:59:05 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the MutationObserver::disconnect function in core/dom/MutationObserver.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.135, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering an attempt to unregister a MutationObserver object that is not currently registered. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1242 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:07 | HIGH (8) | The ReduceTransitionElementsKind function in hydrogen-check-elimination.cc in Google V8 before 4.2.77.8, as used in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that leverages "type confusion" in the check-elimination optimization. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1241 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:06 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 does not properly consider the interaction of page navigation with the handling of touch events and gesture events, which allows remote attackers to trigger unintended UI actions via a crafted web site that conducts a "tapjacking" attack. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1240 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:05 | MEDIUM (5) | gpu/blink/webgraphicscontext3d_impl.cc in the WebGL implementation in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted WebGL program that triggers a state inconsistency. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1239 | 2017‑10‑18 17:29:00 | MEDIUM (7) | Double free vulnerability in the j2k_read_ppm_v3 function in OpenJPEG before r2997, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (process crash) via a crafted PDF. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1238 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:04 | HIGH (8) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds write) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1237 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the RenderFrameImpl::OnMessageReceived function in content/renderer/render_frame_impl.cc in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger renderer IPC messages during a detach operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1236 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The MediaElementAudioSourceNode::process function in modules/webaudio/MediaElementAudioSourceNode.cpp in the Web Audio API implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and obtain sensitive audio sample values via a crafted web site containing a media element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1235 | 2015‑04‑19 10:59:00 | MEDIUM (5) | The ContainerNode::parserRemoveChild function in core/dom/ContainerNode.cpp in the HTML parser in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 42.0.2311.90, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted HTML document with an IFRAME element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1234 | 2015‑04‑01 21:59:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in gpu/command_buffer/service/gles2_cmd_decoder.cc in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.118 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (buffer overflow) or possibly have unspecified other impact by manipulating OpenGL ES commands. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1233 | 2015‑04‑01 21:59:00 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.118 does not properly handle the interaction of IPC, the Gamepad API, and Google V8, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1232 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:27 | HIGH (8) | Array index error in the MidiManagerUsb::DispatchSendMidiData function in media/midi/midi_manager_usb.cc in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging renderer access to provide an invalid port index that triggers an out-of-bounds write operation, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1212. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1231 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:24 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1230 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:23 | HIGH (8) | The getHiddenProperty function in bindings/core/v8/V8EventListenerList.h in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, has a name conflict with the AudioContext class, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via JavaScript code that adds an AudioContext event listener and triggers "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1229 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:22 | MEDIUM (5) | net/http/proxy_client_socket.cc in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 does not properly handle a 407 (aka Proxy Authentication Required) HTTP status code accompanied by a Set-Cookie header, which allows remote proxy servers to conduct cookie-injection attacks via a crafted response. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1228 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:21 | HIGH (8) | The RenderCounter::updateCounter function in core/rendering/RenderCounter.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, does not force a relayout operation and consequently does not initialize memory for a data structure, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequence. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1227 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:20 | HIGH (8) | The DragImage::create function in platform/DragImage.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, does not initialize memory for image drawing, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact by triggering a failed image decoding, as demonstrated by an image for which the default orientation cannot be used. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1226 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:20 | MEDIUM (5) | The DebuggerFunction::InitAgentHost function in browser/extensions/api/debugger/debugger_api.cc in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 does not properly restrict what URLs are available as debugger targets, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1225 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:19 | MEDIUM (5) | PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1224 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:18 | MEDIUM (5) | The VpxVideoDecoder::VpxDecode function in media/filters/vpx_video_decoder.cc in the vpxdecoder implementation in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 does not ensure that alpha-plane dimensions are identical to image dimensions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via crafted VPx video data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1223 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:17 | HIGH (8) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in core/html/HTMLInputElement.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger extraneous change events, as demonstrated by events for invalid input or input to read-only fields, related to the initializeTypeInParsing and updateType functions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1222 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:16 | HIGH (8) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in the ServiceWorkerScriptCacheMap implementation in content/browser/service_worker/service_worker_script_cache_map.cc in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger a ServiceWorkerContextWrapper::DeleteAndStartOver call, related to the NotifyStartedCaching and NotifyFinishedCaching functions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1221 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:15 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging incorrect ordering of operations in the Web SQL Database thread relative to Blink's main thread, related to the shutdown function in web/WebKit.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1220 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:13 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the GIFImageReader::parseData function in platform/image-decoders/gif/GIFImageReader.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted frame size in a GIF image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1219 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:12 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the SkMallocPixelRef::NewAllocate function in core/SkMallocPixelRef.cpp in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger an attempted allocation of a large amount of memory during WebGL rendering. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1218 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:11 | HIGH (8) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger movement of a SCRIPT element to different documents, related to (1) the HTMLScriptElement::didMoveToNewDocument function in core/html/HTMLScriptElement.cpp and (2) the SVGScriptElement::didMoveToNewDocument function in core/svg/SVGScriptElement.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1217 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:09 | HIGH (8) | The V8LazyEventListener::prepareListenerObject function in bindings/core/v8/V8LazyEventListener.cpp in the V8 bindings in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, does not properly compile listeners, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that leverage "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1216 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:08 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the V8Window::namedPropertyGetterCustom function in bindings/core/v8/custom/V8WindowCustom.cpp in the V8 bindings in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger a frame detachment. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1215 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:07 | HIGH (8) | The filters implementation in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1214 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:06 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the SkAutoSTArray implementation in include/core/SkTemplates.h in the filters implementation in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger a reset action with a large count value, leading to an out-of-bounds write operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1213 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:04 | HIGH (8) | The SkBitmap::ReadRawPixels function in core/SkBitmap.cpp in the filters implementation in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1212 | 2015‑02‑06 11:59:10 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.111 on Windows, OS X, and Linux and before 40.0.2214.109 on Android allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1211 | 2015‑02‑06 11:59:09 | HIGH (8) | The OriginCanAccessServiceWorkers function in content/browser/service_worker/service_worker_dispatcher_host.cc in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.111 on Windows, OS X, and Linux and before 40.0.2214.109 on Android does not properly restrict the URI scheme during a ServiceWorker registration, which allows remote attackers to gain privileges via a filesystem: URI. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1210 | 2015‑02‑06 11:59:08 | MEDIUM (5) | The V8ThrowException::createDOMException function in bindings/core/v8/V8ThrowException.cpp in the V8 bindings in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.111 on Windows, OS X, and Linux and before 40.0.2214.109 on Android, does not properly consider frame access restrictions during the throwing of an exception, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1209 | 2015‑02‑06 11:59:07 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the VisibleSelection::nonBoundaryShadowTreeRootNode function in core/editing/VisibleSelection.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.111 on Windows, OS X, and Linux and before 40.0.2214.109 on Android, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers improper handling of a shadow-root anchor. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1207 | 2017‑06‑06 18:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Double-free vulnerability in libavformat/mov.c in FFMPEG in Google Chrome 41.0.2251.0 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption and crash) via a crafted .m4a file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1206 | 2017‑10‑06 15:29:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Heap-based buffer overflow in Google Chrome before M40 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (unpaged memory write and process crash) via a crafted MP4 file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2015‑1205 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:29 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑9689 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:02 | MEDIUM (5) | content/renderer/device_sensors/device_orientation_event_pump.cc in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 does not properly restrict access to high-rate gyroscope data, which makes it easier for remote attackers to obtain speech signals from a device's physical environment via a crafted web site that listens for ondeviceorientation events, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1231. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑9654 | 2017‑04‑24 06:59:00 | HIGH (8) | The Regular Expressions package in International Components for Unicode (ICU) for C/C++ before 2014-12-03, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, calculates certain values without ensuring that they can be represented in a 24-bit field, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted string, a related issue to CVE-2014-7923. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑9648 | 2015‑01‑27 20:01:44 | MEDIUM (4) | components/navigation_interception/intercept_navigation_resource_throttle.cc in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 on Android does not properly restrict use of intent: URLs to open an application after navigation to a web site, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (loss of browser access to that site) via crafted JavaScript code, as demonstrated by pandora.com and the Pandora application, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1205. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑9647 | 2015‑01‑27 20:00:29 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document, related to fpdfsdk/src/fpdfview.cpp and fpdfsdk/src/fsdk_mgr.cpp, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1205. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑9646 | 2015‑01‑27 19:59:12 | MEDIUM (5) | Unquoted Windows search path vulnerability in the GoogleChromeDistribution::DoPostUninstallOperations function in installer/util/google_chrome_distribution.cc in the uninstall-survey feature in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 allows local users to gain privileges via a Trojan horse program in the %SYSTEMDRIVE% directory, as demonstrated by program.exe, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1205. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2014‑7967 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 3.28.71.15, as used in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7948 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:28 | MEDIUM (4) | The AppCacheUpdateJob::URLFetcher::OnResponseStarted function in content/browser/appcache/appcache_update_job.cc in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 proceeds with AppCache caching for SSL sessions even if there is an X.509 certificate error, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to spoof HTML5 application content via a crafted certificate. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7947 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:27 | MEDIUM (5) | OpenJPEG before r2944, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted PDF document, related to j2k.c, jp2.c, pi.c, t1.c, t2.c, and tcd.c. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7946 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:26 | MEDIUM (5) | The RenderTable::simplifiedNormalFlowLayout function in core/rendering/RenderTable.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, skips captions during table layout in certain situations, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors related to the Fonts implementation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7945 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:25 | MEDIUM (5) | OpenJPEG before r2908, as used in PDFium in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted PDF document, related to j2k.c, jp2.c, and t2.c. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7944 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:24 | MEDIUM (5) | The sycc422_to_rgb function in fxcodec/codec/fx_codec_jpx_opj.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, does not properly handle odd values of image width, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7943 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:23 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7942 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:23 | HIGH (8) | The Fonts implementation in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 does not initialize memory for a data structure, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7941 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:22 | MEDIUM (5) | The SelectionOwner::ProcessTarget function in ui/base/x/selection_owner.cc in the UI implementation in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 uses an incorrect data type for a certain length value, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via crafted X11 data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7940 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:21 | HIGH (8) | The collator implementation in i18n/ucol.cpp in International Components for Unicode (ICU) 52 through SVN revision 293126, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, does not initialize memory for a data structure, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted character sequence. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7939 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:20 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, when the Harmony proxy in Google V8 is enabled, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via crafted JavaScript code with Proxy.create and console.log calls, related to HTTP responses that lack an "X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff" header. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7938 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:19 | HIGH (8) | The Fonts implementation in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7937 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:18 | HIGH (8) | Multiple off-by-one errors in libavcodec/vorbisdec.c in FFmpeg before 2.4.2, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted Vorbis I data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7936 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:17 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the ZoomBubbleView::Close function in browser/ui/views/location_bar/zoom_bubble_view.cc in the Views implementation in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document that triggers improper maintenance of a zoom bubble. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7935 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:17 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in browser/speech/tts_message_filter.cc in the Speech implementation in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving utterances from a closed tab. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7934 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:16 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to unexpected absence of document data structures. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7933 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:15 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the matroska_read_seek function in libavformat/matroskadec.c in FFmpeg before 2.5.1, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted Matroska file that triggers improper maintenance of tracks data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7932 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:14 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Element::detach function in core/dom/Element.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving pending updates of detached elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7931 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:13 | HIGH (8) | factory.cc in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers improper maintenance of backing-store pointers. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7930 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:12 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in core/events/TreeScopeEventContext.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers improper maintenance of TreeScope data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7929 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:11 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the HTMLScriptElement::didMoveToNewDocument function in core/html/HTMLScriptElement.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving movement of a SCRIPT element across documents. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7928 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:10 | HIGH (8) | hydrogen.cc in Google V8, as used Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, does not properly handle arrays with holes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers an array copy. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7927 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:09 | HIGH (8) | The SimplifiedLowering::DoLoadBuffer function in compiler/simplified-lowering.cc in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, does not properly choose an integer data type, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7926 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:08 | HIGH (8) | The Regular Expressions package in International Components for Unicode (ICU) 52 before SVN revision 292944, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to a zero-length quantifier. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7925 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:07 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the WebAudio implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger an audio-rendering thread in which AudioNode data is improperly maintained. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7924 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:06 | MEDIUM (5) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the IndexedDB implementation in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering duplicate BLOB references, related to content/browser/indexed_db/indexed_db_callbacks.cc and content/browser/indexed_db/indexed_db_dispatcher_host.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7923 | 2015‑01‑22 22:59:00 | HIGH (8) | The Regular Expressions package in International Components for Unicode (ICU) 52 before SVN revision 292944, as used in Google Chrome before 40.0.2214.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to a look-behind expression. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7910 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:12 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7909 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:11 | MEDIUM (5) | effects/SkDashPathEffect.cpp in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65, computes a hash key using uninitialized integer values, which might allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service by rendering crafted data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7908 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:10 | HIGH (8) | Multiple integer overflows in the CheckMov function in media/base/container_names.cc in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a large atom in (1) MPEG-4 or (2) QuickTime .mov data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7907 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:09 | HIGH (8) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in modules/screen_orientation/ScreenOrientationController.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger improper handling of a detached frame, related to the (1) lock and (2) unlock methods. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7906 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:08 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Pepper plugins in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted Flash content that triggers an attempted PepperMediaDeviceManager access outside of the object's lifetime. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7905 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:07 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65 on Android does not prevent navigation to a URL in cases where an intent for the URL lacks CATEGORY_BROWSABLE, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7904 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:06 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7903 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:05 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in OpenJPEG before r2911 in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted JPEG image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7902 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:04 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7901 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:03 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the opj_t2_read_packet_data function in fxcodec/fx_libopenjpeg/libopenjpeg20/t2.c in OpenJPEG in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a long segment in a JPEG image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7900 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the CPDF_Parser::IsLinearizedFile function in fpdfapi/fpdf_parser/fpdf_parser_parser.cpp in PDFium, as used in Google Chrome before 39.0.2171.65, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑7899 | 2014‑11‑19 11:59:00 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101 allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar by placing a blob: substring at the beginning of the URL, followed by the original URI scheme and a long username string. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3803 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | MEDIUM (4) | The SpeechInput feature in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114, allows remote attackers to enable microphone access and obtain speech-recognition text without indication via an INPUT element with a -x-webkit-speech attribute. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3201 | 2014‑10‑10 01:55:09 | MEDIUM (5) | core/rendering/compositing/RenderLayerCompositor.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.102 on Android, does not properly handle a certain IFRAME overflow condition, which allows remote attackers to spoof content via a crafted web site that interferes with the scrollbar. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3200 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3199 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | MEDIUM (5) | The wrap function in bindings/core/v8/custom/V8EventCustom.cpp in the V8 bindings in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101, has an erroneous fallback outcome for wrapper-selection failures, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service via vectors that trigger stopping a worker process that had been handling an Event object. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3198 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | MEDIUM (5) | The Instance::HandleInputEvent function in pdf/instance.cc in the PDFium component in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101 interprets a certain -1 value as an index instead of a no-visible-page error code, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3197 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | MEDIUM (5) | The NavigationScheduler::schedulePageBlock function in core/loader/NavigationScheduler.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101, does not properly provide substitute data for pages blocked by the XSS auditor, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3196 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | HIGH (8) | base/memory/shared_memory_win.cc in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101 on Windows does not properly implement read-only restrictions on shared memory, which allows attackers to bypass a sandbox protection mechanism via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3195 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | MEDIUM (5) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101, does not properly track JavaScript heap-memory allocations as allocations of uninitialized memory and does not properly concatenate arrays of double-precision floating-point numbers, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via crafted JavaScript code, related to the PagedSpace::AllocateRaw and NewSpace::AllocateRaw functions in heap/spaces-inl.h, the LargeObjectSpace::AllocateRaw function in heap/spaces.cc, and the Runtime_ArrayConcat function in runtime.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3194 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Web Workers implementation in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3193 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:07 | HIGH (8) | The SessionService::GetLastSession function in browser/sessions/session_service.cc in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that leverage "type confusion" for callback processing. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3192 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the ProcessingInstruction::setXSLStyleSheet function in core/dom/ProcessingInstruction.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3191 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers a widget-position update that improperly interacts with the render tree, related to the FrameView::updateLayoutAndStyleForPainting function in core/frame/FrameView.cpp and the RenderLayerScrollableArea::setScrollOffset function in core/rendering/RenderLayerScrollableArea.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3190 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Event::currentTarget function in core/events/Event.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that accesses the path property of an Event object. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3189 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:06 | HIGH (8) | The chrome_pdf::CopyImage function in pdf/draw_utils.cc in the PDFium component in Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101 does not properly validate image-data dimensions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3188 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:06 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 38.0.2125.101 and Chrome OS before 38.0.2125.101 do not properly handle the interaction of IPC and Google V8, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via vectors involving JSON data, related to improper parsing of an escaped index by ParseJsonObject in json-parser.h. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3187 | 2014‑10‑08 10:55:06 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.60 and 38.x before 38.0.2125.59 on iOS does not properly restrict processing of (1) facetime:// and (2) facetime-audio:// URLs, which allows remote attackers to obtain video and audio data from a device via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3179 | 2014‑09‑10 10:55:08 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.120 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3178 | 2014‑09‑10 10:55:08 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in core/dom/Node.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.120, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper handling of render-tree inconsistencies. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3177 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:06 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94 does not properly handle the interaction of extensions, IPC, the sync API, and Google V8, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2014-3176. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3176 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:06 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94 does not properly handle the interaction of extensions, IPC, the sync API, and Google V8, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2014-3177. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3175 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:06 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors, related to the load_truetype_glyph function in truetype/ttgload.c in FreeType and other functions in other components. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3174 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:06 | MEDIUM (5) | modules/webaudio/BiquadDSPKernel.cpp in the Web Audio API implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94, does not properly consider concurrent threads during attempts to update biquad filter coefficients, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (read of uninitialized memory) via crafted API calls. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3173 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:06 | MEDIUM (5) | The WebGL implementation in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94 does not ensure that clear calls interact properly with the state of a draw buffer, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (read of uninitialized memory) via a crafted CANVAS element, related to gpu/command_buffer/service/framebuffer_manager.cc and gpu/command_buffer/service/gles2_cmd_decoder.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3172 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:06 | MEDIUM (6) | The Debugger extension API in browser/extensions/api/debugger/debugger_api.cc in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94 does not validate a tab's URL before an attach operation, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access limitations via an extension that uses a restricted URL, as demonstrated by a chrome:// URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3171 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the V8 bindings in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper use of HashMap add operations instead of HashMap set operations, related to bindings/core/v8/DOMWrapperMap.h and bindings/core/v8/SerializedScriptValue.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3170 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:06 | MEDIUM (6) | extensions/common/url_pattern.cc in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94 does not prevent use of a '\0' character in a host name, which allows remote attackers to spoof the extension permission dialog by relying on truncation after this character. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3169 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:05 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in core/dom/ContainerNode.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging script execution that occurs before notification of node removal. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3168 | 2014‑08‑27 01:55:05 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SVG implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.94, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper caching associated with animation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3167 | 2014‑08‑13 04:57:13 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 36.0.1985.143 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3166 | 2014‑08‑13 04:57:13 | MEDIUM (4) | The Public Key Pinning (PKP) implementation in Google Chrome before 36.0.1985.143 on Windows, OS X, and Linux, and before 36.0.1985.135 on Android, does not correctly consider the properties of SPDY connections, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information by leveraging the use of multiple domain names. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3165 | 2014‑08‑13 04:57:12 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in modules/websockets/WorkerThreadableWebSocketChannel.cpp in the Web Sockets implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 36.0.1985.143, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger an unexpectedly long lifetime of a temporary object during method completion. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3162 | 2014‑07‑20 11:12:50 | MEDIUM (5) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 36.0.1985.125 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3161 | 2014‑07‑20 11:12:50 | HIGH (8) | The WebMediaPlayerAndroid::load function in content/renderer/media/android/webmediaplayer_android.cc in Google Chrome before 36.0.1985.122 on Android does not properly interact with redirects, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site that hosts a video stream. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3160 | 2014‑07‑20 11:12:50 | MEDIUM (7) | The ResourceFetcher::canRequest function in core/fetch/ResourceFetcher.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 36.0.1985.125, does not properly restrict subresource requests associated with SVG files, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3159 | 2014‑07‑20 11:12:50 | MEDIUM (6) | The WebContentsDelegateAndroid::OpenURLFromTab function in components/web_contents_delegate_android/web_contents_delegate_android.cc in Google Chrome before 36.0.1985.122 on Android does not properly restrict URL loading, which allows remote attackers to spoof the URL in the Omnibox via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3157 | 2014‑06‑11 10:57:19 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the FFmpegVideoDecoder::GetVideoBuffer function in media/filters/ffmpeg_video_decoder.cc in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.153 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging VideoFrame data structures that are too small for proper interaction with an underlying FFmpeg library. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3156 | 2014‑06‑11 10:57:19 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in the clipboard implementation in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.153 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger unexpected bitmap data, related to content/renderer/renderer_clipboard_client.cc and content/renderer/webclipboard_impl.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3155 | 2014‑06‑11 10:57:19 | MEDIUM (5) | net/spdy/spdy_write_queue.cc in the SPDY implementation in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.153 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) by leveraging incorrect queue maintenance. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3154 | 2014‑06‑11 10:57:18 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the ChildThread::Shutdown function in content/child/child_thread.cc in the filesystem API in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.153 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to a Blink shutdown. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑3152 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | HIGH (8) | Integer underflow in the LCodeGen::PrepareKeyedOperand function in arm/lithium-codegen-arm.cc in Google V8 before 3.25.28.16, as used in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger a negative key value. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1749 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1748 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | MEDIUM (5) | The ScrollView::paint function in platform/scroll/ScrollView.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114, allows remote attackers to spoof the UI by extending scrollbar painting into the parent frame. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1747 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the DocumentLoader::maybeCreateArchive function in core/loader/DocumentLoader.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114, allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via crafted MHTML content, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1746 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | MEDIUM (5) | The InMemoryUrlProtocol::Read function in media/filters/in_memory_url_protocol.cc in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114 relies on an insufficiently large integer data type, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via vectors that trigger use of a large buffer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1745 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SVG implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger removal of an SVGFontFaceElement object, related to core/svg/SVGFontFaceElement.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1744 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the AudioInputRendererHost::OnCreateStream function in content/browser/renderer_host/media/audio_input_renderer_host.cc in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger a large shared-memory allocation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1743 | 2014‑05‑21 11:14:10 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the StyleElement::removedFromDocument function in core/dom/StyleElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 35.0.1916.114, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers tree mutation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1742 | 2014‑05‑14 11:13:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the FrameSelection::updateAppearance function in core/editing/FrameSelection.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.137, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper RenderObject handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1741 | 2014‑05‑14 11:13:06 | HIGH (8) | Multiple integer overflows in the replace-data functionality in the CharacterData interface implementation in core/dom/CharacterData.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.137, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to ranges. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1740 | 2014‑05‑14 11:13:06 | HIGH (8) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in net/websockets/websocket_job.cc in the WebSockets implementation in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.137 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to WebSocketJob deletion. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1736 | 2014‑05‑06 10:44:06 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in api.cc in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.131 on Windows and OS X and before 34.0.1847.132 on Linux, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a large length value. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1735 | 2014‑04‑26 10:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 3.24.35.33, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.131 on Windows and OS X and before 34.0.1847.132 on Linux, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1734 | 2014‑04‑26 10:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.131 on Windows and OS X and before 34.0.1847.132 on Linux allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1733 | 2014‑04‑26 10:55:06 | HIGH (8) | The PointerCompare function in codegen.cc in Seccomp-BPF, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.131 on Windows and OS X and before 34.0.1847.132 on Linux, does not properly merge blocks, which might allow remote attackers to bypass intended sandbox restrictions by leveraging renderer access. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1732 | 2014‑04‑26 10:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in browser/ui/views/speech_recognition_bubble_views.cc in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.131 on Windows and OS X and before 34.0.1847.132 on Linux allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via an INPUT element that triggers the presence of a Speech Recognition Bubble window for an incorrect duration. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1731 | 2014‑04‑26 10:55:05 | HIGH (8) | core/html/HTMLSelectElement.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.131 on Windows and OS X and before 34.0.1847.132 on Linux, does not properly check renderer state upon a focus event, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that leverage "type confusion" for SELECT elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1730 | 2014‑04‑26 10:55:05 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.131 on Windows and OS X and before 34.0.1847.132 on Linux, does not properly store internationalization metadata, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions by leveraging "type confusion" and reading property values, related to i18n.js and runtime.cc. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1729 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:57 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 3.24.35.22, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1728 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:57 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1727 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:57 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in content/renderer/renderer_webcolorchooser_impl.h in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to forms. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1726 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:57 | MEDIUM (4) | The drag implementation in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116 allows user-assisted remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and forge local pathnames by leveraging renderer access. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1725 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:57 | MEDIUM (5) | The base64DecodeInternal function in wtf/text/Base64.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116, does not properly handle string data composed exclusively of whitespace characters, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a window.atob method call. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1724 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:57 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Free(b)soft Laboratory Speech Dispatcher 0.7.1, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application hang) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a text-to-speech request. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1723 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:51 | HIGH (8) | The UnescapeURLWithOffsetsImpl function in net/base/escape.cc in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116 does not properly handle bidirectional Internationalized Resource Identifiers (IRIs), which makes it easier for remote attackers to spoof URLs via crafted use of right-to-left (RTL) Unicode text. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1722 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:51 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the RenderBlock::addChildIgnoringAnonymousColumnBlocks function in core/rendering/RenderBlock.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving addition of a child node. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1721 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:51 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116, does not properly implement lazy deoptimization, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code, as demonstrated by improper handling of a heap allocation of a number outside the Small Integer (aka smi) range. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1720 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:51 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the HTMLBodyElement::insertedInto function in core/html/HTMLBodyElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving attributes. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1719 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:16 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the WebSharedWorkerStub::OnTerminateWorkerContext function in content/worker/websharedworker_stub.cc in the Web Workers implementation in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger a SharedWorker termination during script loading. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1718 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:16 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the SoftwareFrameManager::SwapToNewFrame function in content/browser/renderer_host/software_frame_manager.cc in the software compositor in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger an attempted mapping of a large amount of renderer memory. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1717 | 2014‑04‑09 10:57:16 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116, does not properly use numeric casts during handling of typed arrays, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds array access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1716 | 2014‑04‑09 10:56:51 | HIGH (8) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the Runtime_SetPrototype function in runtime.cc in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 34.0.1847.116, allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via unspecified vectors, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1715 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:46 | HIGH (8) | Directory traversal vulnerability in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.152 on OS X and Linux and before 33.0.1750.154 on Windows has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1714 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:46 | HIGH (8) | The ScopedClipboardWriter::WritePickledData function in ui/base/clipboard/scoped_clipboard_writer.cc in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.152 on OS X and Linux and before 33.0.1750.154 on Windows does not verify a certain format value, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the clipboard. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1713 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:46 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the AttributeSetter function in bindings/templates/attributes.cpp in the bindings in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.152 on OS X and Linux and before 33.0.1750.154 on Windows, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving the document.location value. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1705 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:45 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.152 on OS X and Linux and before 33.0.1750.154 on Windows, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1704 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:45 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 3.23.17.18, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.149, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1703 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:45 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the WebSocketDispatcherHost::SendOrDrop function in content/browser/renderer_host/websocket_dispatcher_host.cc in the Web Sockets implementation in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.149 might allow remote attackers to bypass the sandbox protection mechanism by leveraging an incorrect deletion in a certain failure case. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1702 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:45 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the DatabaseThread::cleanupDatabaseThread function in modules/webdatabase/DatabaseThread.cpp in the web database implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.149, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper handling of scheduled tasks during shutdown of a thread. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1701 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:45 | MEDIUM (4) | The GenerateFunction function in bindings/scripts/code_generator_v8.pm in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.149, does not implement a certain cross-origin restriction for the EventTarget::dispatchEvent function, which allows remote attackers to conduct Universal XSS (UXSS) attacks via vectors involving events. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1700 | 2014‑03‑16 14:06:45 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in modules/speech/SpeechSynthesis.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.149, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper handling of a certain utterance data structure. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1681 | 2014‑01‑28 14:30:40 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 32.0.1700.102 have unknown impact and attack vectors, related to 12 "security fixes [that were not] either contributed by external researchers or particularly interesting." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2014‑1568 | 2014‑09‑25 17:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Mozilla Network Security Services (NSS) before 3.16.2.1, 3.16.x before 3.16.5, and 3.17.x before 3.17.1, as used in Mozilla Firefox before 32.0.3, Mozilla Firefox ESR 24.x before 24.8.1 and 31.x before 31.1.1, Mozilla Thunderbird before 24.8.1 and 31.x before 31.1.2, Mozilla SeaMonkey before 2.29.1, Google Chrome before 37.0.2062.124 on Windows and OS X, and Google Chrome OS before 37.0.2062.120, does not properly parse ASN.1 values in X.509 certificates, which makes it easier for remote attackers to spoof RSA signatures via a crafted certificate, aka a "signature malleability" issue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6802 | 2013‑11‑18 05:23:58 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.57 allows remote attackers to bypass intended sandbox restrictions by leveraging access to a renderer process, as demonstrated during a Mobile Pwn2Own competition at PacSec 2013, a different vulnerability than CVE-2013-6632. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6668 | 2014‑03‑05 05:11:22 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google V8 before 3.24.35.10, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.146, allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6667 | 2014‑03‑05 05:11:22 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.146 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6666 | 2014‑03‑05 05:11:22 | MEDIUM (6) | The PepperFlashRendererHost::OnNavigate function in renderer/pepper/pepper_flash_renderer_host.cc in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.146 does not verify that all headers are Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) simple headers before proceeding with a PPB_Flash.Navigate operation, which might allow remote attackers to bypass intended CORS restrictions via an inappropriate header. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6665 | 2014‑03‑05 05:11:22 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the ResourceProvider::InitializeSoftware function in cc/resources/resource_provider.cc in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.146 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a large texture size that triggers improper memory allocation in the software renderer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6664 | 2014‑03‑05 05:11:22 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the FormAssociatedElement::formRemovedFromTree function in core/html/FormAssociatedElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.146, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving FORM elements, as demonstrated by use of the speech-recognition feature. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6663 | 2014‑03‑05 05:11:22 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SVGImage::setContainerSize function in core/svg/graphics/SVGImage.cpp in the SVG implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.146, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the resizing of a view. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6662 | 2017‑04‑13 17:59:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome caches TLS sessions before certificate validation occurs. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6661 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117 allow attackers to bypass the sandbox protection mechanism after obtaining renderer access, or have other impact, via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6660 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | MEDIUM (5) | The drag-and-drop implementation in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117 does not properly restrict the information in WebDropData data structures, which allows remote attackers to discover full pathnames via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6659 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | MEDIUM (6) | The SSLClientSocketNSS::Core::OwnAuthCertHandler function in net/socket/ssl_client_socket_nss.cc in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117 does not prevent changes to server X.509 certificates during renegotiations, which allows remote SSL servers to trigger use of a new certificate chain, inconsistent with the user's expectations, by initiating a TLS renegotiation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6658 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | HIGH (8) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in the layout implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving (1) running JavaScript code during execution of the updateWidgetPositions function or (2) making a call into a plugin during execution of the updateWidgetPositions function. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6657 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | MEDIUM (6) | core/html/parser/XSSAuditor.cpp in the XSS auditor in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117, inserts the about:blank URL during certain blocking of FORM elements within HTTP requests, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and obtain sensitive information via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6656 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | MEDIUM (5) | The XSSAuditor::init function in core/html/parser/XSSAuditor.cpp in the XSS auditor in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117, processes POST requests by using the body of a redirecting page instead of the body of a redirect target, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6655 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to improper handling of overflowchanged DOM events during interaction between JavaScript and layout. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6654 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | HIGH (8) | The SVGAnimateElement::calculateAnimatedValue function in core/svg/SVGAnimateElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117, does not properly handle unexpected data types, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect cast) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6653 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the web contents implementation in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving attempted conflicting access to the color chooser. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6652 | 2014‑02‑24 04:48:10 | HIGH (8) | Directory traversal vulnerability in sandbox/win/src/named_pipe_dispatcher.cc in Google Chrome before 33.0.1750.117 on Windows allows attackers to bypass intended named-pipe policy restrictions in the sandbox via vectors related to (1) lack of checks for .. (dot dot) sequences or (2) lack of use of the \\?\ protection mechanism. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6650 | 2014‑01‑28 14:30:39 | HIGH (8) | The StoreBuffer::ExemptPopularPages function in store-buffer.cc in Google V8 before 3.22.24.16, as used in Google Chrome before 32.0.1700.102, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger incorrect handling of "popular pages." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6649 | 2014‑01‑28 14:30:34 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the RenderSVGImage::paint function in core/rendering/svg/RenderSVGImage.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 32.0.1700.102, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a zero-size SVG image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6647 | 2017‑04‑11 19:59:00 | HIGH (8) | A use-after-free in AnimationController::endAnimationUpdate in Google Chrome. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6646 | 2014‑01‑16 12:17:26 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Web Workers implementation in Google Chrome before 32.0.1700.76 on Windows and before 32.0.1700.77 on Mac OS X and Linux allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the shutting down of a worker process. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6645 | 2014‑01‑16 12:17:26 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the OnWindowRemovingFromRootWindow function in content/browser/web_contents/web_contents_view_aura.cc in Google Chrome before 32.0.1700.76 on Windows and before 32.0.1700.77 on Mac OS X and Linux allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving certain print-preview and tab-switch actions that interact with a speech input element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6644 | 2014‑01‑16 12:17:26 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 32.0.1700.76 on Windows and before 32.0.1700.77 on Mac OS X and Linux allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6643 | 2014‑01‑16 12:17:26 | HIGH (8) | The OneClickSigninBubbleView::WindowClosing function in browser/ui/views/sync/one_click_signin_bubble_view.cc in Google Chrome before 32.0.1700.76 on Windows and before 32.0.1700.77 on Mac OS X and Linux allows attackers to trigger a sync with an arbitrary Google account by leveraging improper handling of the closing of an untrusted signin confirm dialog. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6642 | 2014‑01‑16 12:17:26 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome through 32.0.1700.23 on Android allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6641 | 2014‑01‑16 12:17:26 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the FormAssociatedElement::formRemovedFromTree function in core/html/FormAssociatedElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 32.0.1700.76 on Windows and before 32.0.1700.77 on Mac OS X and Linux, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper handling of the past names map of a FORM element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6640 | 2013‑12‑07 00:55:04 | HIGH (8) | The DehoistArrayIndex function in hydrogen-dehoist.cc (aka hydrogen.cc) in Google V8 before 3.22.24.7, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.63, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via JavaScript code that sets a variable to the value of an array element with a crafted index. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6639 | 2013‑12‑07 00:55:04 | HIGH (8) | The DehoistArrayIndex function in hydrogen-dehoist.cc (aka hydrogen.cc) in Google V8 before 3.22.24.7, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.63, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds write) or possibly have unspecified other impact via JavaScript code that sets the value of an array element with a crafted index. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6638 | 2013‑12‑07 00:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Multiple buffer overflows in runtime.cc in Google V8 before 3.22.24.7, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.63, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger a large typed array, related to the (1) Runtime_TypedArrayInitialize and (2) Runtime_TypedArrayInitializeFromArrayLike functions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6637 | 2013‑12‑07 00:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.63 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6636 | 2013‑12‑07 00:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | The FrameLoader::notifyIfInitialDocumentAccessed function in core/loader/FrameLoader.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.63, makes an incorrect check for an empty document during presentation of a modal dialog, which allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via vectors involving the document.write method. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6635 | 2013‑12‑07 00:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the editing implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.63, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via JavaScript code that triggers removal of a node during processing of the DOM tree, related to CompositeEditCommand.cpp and ReplaceSelectionCommand.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6634 | 2013‑12‑07 00:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | The OneClickSigninHelper::ShowInfoBarIfPossible function in browser/ui/sync/one_click_signin_helper.cc in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.63 uses an incorrect URL during realm validation, which allows remote attackers to conduct session fixation attacks and hijack web sessions by triggering improper sync after a 302 (aka Found) HTTP status code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6632 | 2013‑11‑18 05:23:58 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.57 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unspecified vectors, as demonstrated during a Mobile Pwn2Own competition at PacSec 2013. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6631 | 2013‑11‑19 04:50:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Channel::SendRTCPPacket function in voice_engine/channel.cc in libjingle in WebRTC, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48 and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger the absence of certain statistics initialization, leading to the skipping of a required DeRegisterExternalTransport call. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6630 | 2013‑11‑19 04:50:56 | MEDIUM (5) | The get_dht function in jdmarker.c in libjpeg-turbo through 1.3.0, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48 and other products, does not set all elements of a certain Huffman value array during the reading of segments that follow Define Huffman Table (DHT) JPEG markers, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information from uninitialized memory locations via a crafted JPEG image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6629 | 2013‑11‑19 04:50:56 | MEDIUM (5) | The get_sos function in jdmarker.c in (1) libjpeg 6b and (2) libjpeg-turbo through 1.3.0, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48, Ghostscript, and other products, does not check for certain duplications of component data during the reading of segments that follow Start Of Scan (SOS) JPEG markers, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information from uninitialized memory locations via a crafted JPEG image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6628 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | net/socket/ssl_client_socket_nss.cc in the TLS implementation in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48 does not ensure that a server's X.509 certificate is the same during renegotiation as it was before renegotiation, which might allow remote web servers to interfere with trust relationships by renegotiating a session. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6627 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:04 | MEDIUM (5) | net/http/http_stream_parser.cc in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48 does not properly process HTTP Informational (aka 1xx) status codes, which allows remote web servers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted response. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6626 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | The WebContentsImpl::AttachInterstitialPage function in content/browser/web_contents/web_contents_impl.cc in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48 does not cancel JavaScript dialogs upon generating an interstitial warning, which allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6625 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in core/dom/ContainerNode.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper handling of DOM range objects in circumstances that require child node removal after a (1) mutation or (2) blur event. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6624 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving the string values of id attributes. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6623 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | The SVG implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) by leveraging the use of tree order, rather than transitive dependency order, for layout. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6622 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the HTMLMediaElement::didMoveToNewDocument function in core/html/HTMLMediaElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving the movement of a media element between documents. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6621 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the x-webkit-speech attribute in a text INPUT element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑6166 | 2014‑02‑15 14:57:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 29 sends HTTP Cookie headers without first validating that they have the required character-set restrictions, which allows remote attackers to conduct the equivalent of a persistent Logout CSRF attack via a crafted parameter that forces a web application to set a malformed cookie within an HTTP response. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2931 | 2013‑11‑13 15:55:03 | HIGH (10) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 31.0.1650.48 allow attackers to execute arbitrary code or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2928 | 2013‑10‑16 20:55:07 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.101 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2927 | 2013‑10‑16 20:55:07 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the HTMLFormElement::prepareForSubmission function in core/html/HTMLFormElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.101, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to submission for FORM elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2926 | 2013‑10‑16 20:55:06 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the IndentOutdentCommand::tryIndentingAsListItem function in core/editing/IndentOutdentCommand.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.101, allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to list elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2925 | 2013‑10‑16 20:55:05 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in core/xml/XMLHttpRequest.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.101, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger multiple conflicting uses of the same XMLHttpRequest object. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2924 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:36 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in International Components for Unicode (ICU), as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66 and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2923 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2922 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in core/html/HTMLTemplateElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that operates on a TEMPLATE element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2921 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (7) | Double free vulnerability in the ResourceFetcher::didLoadResource function in core/fetch/ResourceFetcher.cpp in the resource loader in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by triggering certain callback processing during the reporting of a resource entry. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2920 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (5) | The DoResolveRelativeHost function in url/url_canon_relative.cc in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a relative URL containing a hostname, as demonstrated by a protocol-relative URL beginning with a //www.google.com/ substring. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2919 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2918 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the RenderBlock::collapseAnonymousBlockChild function in core/rendering/RenderBlock.cpp in the DOM implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging incorrect handling of parent-child relationships for anonymous blocks. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2917 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (5) | The ReverbConvolverStage::ReverbConvolverStage function in core/platform/audio/ReverbConvolverStage.cpp in the Web Audio implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via vectors related to the impulseResponse array. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2916 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (4) | Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via vectors involving a response with a 204 (aka No Content) status code, in conjunction with a delay in notifying the user of an attempted spoof. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2915 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66 preserves pending NavigationEntry objects in certain invalid circumstances, which allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via a URL with a malformed scheme, as demonstrated by a nonexistent:12121 URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2914 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the color-chooser dialog in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66 on Windows allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to color_chooser_dialog.cc and color_chooser_win.cc in browser/ui/views/. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2913 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the XMLDocumentParser::append function in core/xml/parser/XMLDocumentParser.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving an XML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2912 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the PepperInProcessRouter::SendToHost function in content/renderer/pepper/pepper_in_process_router.cc in the Pepper Plug-in API (PPAPI) in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a resource-destruction message. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2911 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the XSLStyleSheet::compileStyleSheet function in core/xml/XSLStyleSheetLibxslt.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging improper handling of post-failure recompilation in unspecified libxslt versions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2910 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in modules/webaudio/AudioScheduledSourceNode.cpp in the Web Audio implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2909 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to inline-block rendering for bidirectional Unicode text in an element isolated from its siblings. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2908 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66 uses incorrect function calls to determine the values of NavigationEntry objects, which allows remote attackers to spoof the address bar via vectors involving a response with a 204 (aka No Content) status code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2907 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:35 | MEDIUM (5) | The Window.prototype object implementation in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2906 | 2013‑10‑02 10:35:33 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple race conditions in the Web Audio implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 30.0.1599.66, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to threading in core/html/HTMLMediaElement.cpp, core/platform/audio/AudioDSPKernelProcessor.cpp, core/platform/audio/HRTFElevation.cpp, and modules/webaudio/ConvolverNode.cpp. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2905 | 2013‑08‑21 12:17:57 | MEDIUM (5) | The SharedMemory::Create function in memory/shared_memory_posix.cc in Google Chrome before 29.0.1547.57 uses weak permissions under /dev/shm/, which allows attackers to obtain sensitive information via direct access to a POSIX shared-memory file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2904 | 2013‑08‑21 12:17:57 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Document::finishedParsing function in core/dom/Document.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 29.0.1547.57, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via an onload event that changes an IFRAME element so that its src attribute is no longer an XML document, leading to unintended garbage collection of this document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2903 | 2013‑08‑21 12:17:57 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the HTMLMediaElement::didMoveToNewDocument function in core/html/HTMLMediaElement.cpp in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 29.0.1547.57, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving moving a (1) AUDIO or (2) VIDEO element between documents. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2902 | 2013‑08‑21 12:17:57 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the XSLT ProcessingInstruction implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 29.0.1547.57, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to an applyXSLTransform call involving (1) an HTML document or (2) an xsl:processing-instruction element that is still in the process of loading. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2901 | 2013‑08‑21 12:17:57 | HIGH (8) | Multiple integer overflows in (1) libGLESv2/renderer/Renderer9.cpp and (2) libGLESv2/renderer/Renderer11.cpp in Almost Native Graphics Layer Engine (ANGLE), as used in Google Chrome before 29.0.1547.57, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2900 | 2013‑08‑21 12:17:57 | HIGH (8) | The FilePath::ReferencesParent function in files/file_path.cc in Google Chrome before 29.0.1547.57 on Windows does not properly handle pathname components composed entirely of . (dot) and whitespace characters, which allows remote attackers to conduct directory traversal attacks via a crafted directory name. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2887 | 2013‑08‑21 12:17:54 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 29.0.1547.57 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2886 | 2013‑07‑31 13:20:14 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.95 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2885 | 2013‑07‑31 13:20:14 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.95 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to not properly considering focus during the processing of JavaScript events in the presence of a multiple-fields input type. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2884 | 2013‑07‑31 13:20:14 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the DOM implementation in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.95 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to improper tracking of which document owns an Attr object. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2883 | 2013‑07‑31 13:20:14 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.95 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to deleting the registration of a MutationObserver object. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2882 | 2013‑07‑31 13:20:14 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.95, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that leverage "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2881 | 2013‑07‑31 13:20:14 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.95 does not properly handle frames, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2880 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2879 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 does not properly determine the circumstances in which a renderer process can be considered a trusted process for sign-in and subsequent sync operations, which makes it easier for remote attackers to conduct phishing attacks via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2878 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via vectors related to the handling of text. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2877 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | parser.c in libxml2 before 2.9.0, as used in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a document that ends abruptly, related to the lack of certain checks for the XML_PARSER_EOF state. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2876 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | browser/extensions/api/tabs/tabs_api.cc in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 does not properly enforce restrictions on the capture of screenshots by extensions, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information about the content of a previous page via vectors involving an interstitial page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2875 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | core/rendering/svg/SVGInlineTextBox.cpp in the SVG implementation in Blink, as used in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2874 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 on Windows, when an Nvidia GPU is used, allows remote attackers to bypass intended restrictions on access to screen data via vectors involving IPC transmission of GL textures. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2873 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a 404 HTTP status code during the loading of resources. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2872 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 on Mac OS X does not ensure a sufficient source of entropy for renderer processes, which might make it easier for remote attackers to defeat cryptographic protection mechanisms in third-party components via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2871 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of input. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2870 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 allows remote servers to execute arbitrary code via crafted response traffic after a URL request. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2869 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted JPEG2000 image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2868 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | common/extensions/sync_helper.cc in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 proceeds with sync operations for NPAPI extensions without checking for a certain plugin permission setting, which might allow remote attackers to trigger unwanted extension changes via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2867 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 does not properly prevent pop-under windows, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2866 | 2013‑06‑19 20:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The Flash plug-in in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.116, as used on Google Chrome OS before 27.0.1453.116 and separately, does not properly determine whether a user wishes to permit camera or microphone access by a Flash application, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information from a machine's physical environment via a clickjacking attack, as demonstrated by an attack using a crafted Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) opacity property. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2865 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2864 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (invalid free operation) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2863 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 does not properly handle SSL sockets, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2862 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110, does not properly handle GPU acceleration, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2861 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SVG implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2860 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving access to a database API by a worker process. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2859 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and trigger namespace pollution via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2858 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the HTML5 Audio implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2857 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of images. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2856 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of input. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2855 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | The Developer Tools API in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2854 | 2013‑06‑05 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.110 on Windows provides an incorrect handle to a renderer process in unspecified circumstances, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2853 | 2013‑07‑10 10:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The HTTPS implementation in Google Chrome before 28.0.1500.71 does not ensure that headers are terminated by \r\n\r\n (carriage return, newline, carriage return, newline), which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to have an unspecified impact via vectors that trigger header truncation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2849 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | MEDIUM (4) | Multiple cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allow user-assisted remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via vectors involving a (1) drag-and-drop or (2) copy-and-paste operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2848 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | MEDIUM (5) | The XSS Auditor in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 might allow remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2847 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in the workers implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2846 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the media loader in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2013-2840. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2845 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | The Web Audio implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2844 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to style resolution. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2843 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of speech data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2842 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of widgets. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2841 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of Pepper resources. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2840 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the media loader in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2013-2846. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2839 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of clipboard data, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2838 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | MEDIUM (5) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2837 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SVG implementation in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2836 | 2013‑05‑22 13:29:56 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 27.0.1453.93 allow attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2632 | 2013‑03‑21 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google V8 before 3.17.13, as used in Google Chrome before 27.0.1444.3, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code, as demonstrated by the Bejeweled game. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑2268 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Unspecified vulnerability in the MathML implementation in WebKit in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, has unknown impact and remote attack vectors, related to a "high severity security issue." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑1489 | 2013‑01‑31 14:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Unspecified vulnerability in the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) component in Oracle Java SE 7 Update 10 and Update 11, when running on Windows using Internet Explorer, Firefox, Opera, and Google Chrome, allows remote attackers to bypass the "Very High" security level of the Java Control Panel and execute unsigned Java code without prompting the user via unknown vectors, aka "Issue 53" and the "Java Security Slider" vulnerability. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0926 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 does not properly handle active content in an EMBED element during a copy-and-paste operation, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0925 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 does not ensure that an extension has the tabs (aka APIPermission::kTab) permission before providing a URL to this extension, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0924 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | HIGH (8) | The extension functionality in Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 does not verify that use of the permissions API is consistent with file permissions, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0923 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | MEDIUM (5) | The USB Apps API in Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0922 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 does not properly restrict brute-force access attempts against web sites that require HTTP Basic Authentication, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0921 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | MEDIUM (7) | The Isolated Sites feature in Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 does not properly enforce the use of separate processes, which makes it easier for remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0920 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the extension bookmarks API in Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0919 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 on Linux allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging the presence of an extension that creates a pop-up window. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0918 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 does not prevent navigation to developer tools in response to a drag-and-drop operation, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0917 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:52 | MEDIUM (5) | The URL loader in Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0916 | 2013‑03‑28 12:18:44 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Web Audio implementation in Google Chrome before 26.0.1410.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0912 | 2013‑03‑11 10:55:01 | HIGH (8) | WebKit in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.160 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via vectors that leverage "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0911 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:24 | HIGH (8) | Directory traversal vulnerability in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via vectors related to databases. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0910 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:24 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 does not properly manage the interaction between the browser process and renderer processes during authorization of the loading of a plug-in, which makes it easier for remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via vectors involving a blocked plug-in. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0909 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:12 | MEDIUM (5) | The XSS Auditor in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive HTTP Referer information via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0908 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:11 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 does not properly manage bindings of extension processes, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0907 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:11 | HIGH (8) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of media threads. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0906 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:11 | HIGH (8) | The IndexedDB implementation in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0905 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:11 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving an SVG animation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0904 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:11 | HIGH (8) | The Web Audio implementation in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0903 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:11 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of browser navigation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0902 | 2013‑03‑05 21:55:11 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the frame-loader implementation in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.152 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0900 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in the International Components for Unicode (ICU) functionality in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0899 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Integer overflow in the padding implementation in the opus_packet_parse_impl function in src/opus_decoder.c in Opus before 1.0.2, as used in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a long packet. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0898 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0897 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Off-by-one error in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0896 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, does not properly manage memory during message handling for plug-ins, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0895 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, does not properly handle pathnames during copy operations, which might make it easier for remote attackers to execute arbitrary programs via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0894 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in the vorbis_parse_setup_hdr_floors function in the Vorbis decoder in vorbisdec.c in libavcodec in FFmpeg through 1.1.3, as used in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (divide-by-zero error or out-of-bounds array access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a zero value for a bark map size. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0893 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to media. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0892 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in the IPC layer in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0891 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a blob. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0890 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in the IPC layer in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0889 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, does not properly enforce a user gesture requirement before proceeding with a file download, which might make it easier for remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0888 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via vectors related to a "user gesture check for dangerous file downloads." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0887 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | The developer-tools process in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, does not properly restrict privileges during interaction with a connected server, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0886 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X does not properly implement signal handling for Native Client (aka NaCl) code, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0885 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, does not properly restrict API privileges during interaction with the Chrome Web Store, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0884 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, does not properly load Native Client (aka NaCl) code, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0883 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect read operation) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0882 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect memory access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a large number of SVG parameters. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0881 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect read operation) via crafted data in the Matroska container format. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0880 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to databases. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0879 | 2013‑02‑23 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 25.0.1364.97 on Windows and Linux, and before 25.0.1364.99 on Mac OS X, does not properly implement web audio nodes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0843 | 2013‑01‑24 21:55:06 | HIGH (8) | content/renderer/media/webrtc_audio_renderer.cc in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.56 on Mac OS X does not use an appropriate buffer size for the 96 kHz sampling rate, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a web site that provides WebRTC audio. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0842 | 2013‑01‑24 21:55:06 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.56 does not properly handle %00 characters in pathnames, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0841 | 2013‑01‑24 21:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Array index error in the content-blocking functionality in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.56 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0840 | 2013‑01‑24 21:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.56 does not validate URLs during the opening of new windows, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0839 | 2013‑01‑24 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.56 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of fonts in CANVAS elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0838 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 on Linux uses weak permissions for shared memory segments, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0837 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of extension tabs. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0836 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google V8 before 3.14.5.3, as used in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52, does not properly implement garbage collection, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0835 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in the Geolocation implementation in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0834 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via vectors involving glyphs. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0833 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via vectors related to printing. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0832 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to printing. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0831 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Directory traversal vulnerability in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact by leveraging access to an extension process. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0830 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | The IPC layer in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 on Windows omits a NUL character required for termination of an unspecified data structure, which has unknown impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0829 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 does not properly maintain database metadata, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended file-access restrictions via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2013‑0828 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during processing of the root of the structure tree, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5851 | 2012‑11‑15 11:58:40 | MEDIUM (4) | html/parser/XSSAuditor.cpp in WebCore in WebKit, as used in Google Chrome through 22 and Safari 5.1.7, does not consider all possible output contexts of reflected data, which makes it easier for remote attackers to bypass a cross-site scripting (XSS) protection mechanism via a crafted string, aka rdar problem 12019108. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5376 | 2012‑10‑11 10:51:57 | CRITICAL (10) | The Inter-process Communication (IPC) implementation in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.94 allows remote attackers to bypass intended sandbox restrictions and write to arbitrary files by leveraging access to a renderer process, a different vulnerability than CVE-2012-5112. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5157 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 does not properly handle image data in PDF documents, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5156 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving PDF fields. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5155 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 on Mac OS X does not use an appropriate sandboxing approach for worker processes, which makes it easier for remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5154 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 on Windows allows attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to allocation of shared memory. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5153 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google V8 before 3.14.5.3, as used in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers an out-of-bounds access to stack memory. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5152 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via vectors involving seek operations on video data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5151 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code in a PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5150 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving seek operations on video data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5149 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the audio IPC layer in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5148 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | The hyphenation functionality in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 does not properly validate file names, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5147 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to DOM handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5146 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a malformed URL. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5145 | 2013‑01‑15 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 24.0.1312.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to SVG layout. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5144 | 2012‑12‑12 11:38:45 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.97, and Libav 0.7.x before 0.7.7 and 0.8.x before 0.8.5, do not properly perform AAC decoding, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (stack memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to "an off-by-one overwrite when switching to LTP profile from MAIN." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5143 | 2012‑12‑12 11:38:45 | HIGH (10) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.97 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to PPAPI image buffers. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5142 | 2012‑12‑12 11:38:45 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.97 does not properly handle history navigation, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5141 | 2012‑12‑12 11:38:45 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.97 does not properly restrict instantiation of the Chromoting client plug-in, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5140 | 2012‑12‑12 11:38:45 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.97 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the URL loader. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5139 | 2012‑12‑12 11:38:45 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.97 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to visibility events. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5138 | 2012‑12‑04 06:05:56 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.95 does not properly handle file paths, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5137 | 2012‑12‑04 06:05:55 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.95 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the Media Source API. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5136 | 2012‑11‑28 01:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.91 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of the INPUT element, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5135 | 2012‑11‑28 01:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to printing. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5134 | 2012‑11‑28 01:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap-based buffer underflow in the xmlParseAttValueComplex function in parser.c in libxml2 2.9.0 and earlier, as used in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.91 and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly execute arbitrary code via crafted entities in an XML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5133 | 2012‑11‑28 01:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to SVG filters. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5132 | 2012‑11‑28 01:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via a response with chunked transfer coding. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5131 | 2012‑11‑28 01:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.91 on Mac OS X does not properly mitigate improper rendering behavior in the Intel GPU driver, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5130 | 2012‑11‑28 01:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.91, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5129 | 2012‑12‑04 06:05:55 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the WebGL subsystem in Google Chrome OS before 23.0.1271.94 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (GPU process crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5128 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:16 | HIGH (8) | Google V8 before 3.13.7.5, as used in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64, does not properly perform write operations, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5127 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:16 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted WebP image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5126 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:16 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of plug-in placeholders. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5125 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:16 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of extension tabs. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5124 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:16 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 does not properly handle textures, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5123 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:16 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5122 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:16 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of input, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5121 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:16 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to video layout. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5120 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:15 | HIGH (8) | Google V8 before 3.13.7.5, as used in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64, on 64-bit Linux platforms allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers an out-of-bounds access to an array. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5119 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in Pepper, as used in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to buffers. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5118 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:15 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 on Mac OS X does not properly validate an integer value during the handling of GPU command buffers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5117 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:15 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 does not properly restrict the loading of an SVG subresource in the context of an IMG element, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5116 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:15 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of SVG filters. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5115 | 2012‑11‑07 11:43:15 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 23.0.1271.64 on Mac OS X does not properly mitigate improper write behavior in graphics drivers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger "wild writes." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5112 | 2012‑10‑11 10:51:57 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the SVG implementation in WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.94, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5111 | 2012‑10‑09 11:13:10 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.92 does not monitor for crashes of Pepper plug-ins, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5110 | 2012‑10‑09 11:13:10 | MEDIUM (5) | The compositor in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.92 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5109 | 2012‑10‑09 11:13:10 | MEDIUM (5) | The International Components for Unicode (ICU) functionality in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.92 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via vectors related to a regular expression. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑5108 | 2012‑10‑09 11:13:10 | HIGH (9) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.92 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via vectors related to audio devices. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4930 | 2012‑09‑15 18:55:03 | LOW (3) | The SPDY protocol 3 and earlier, as used in Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, and other products, can perform TLS encryption of compressed data without properly obfuscating the length of the unencrypted data, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to obtain plaintext HTTP headers by observing length differences during a series of guesses in which a string in an HTTP request potentially matches an unknown string in an HTTP header, aka a "CRIME" attack. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4929 | 2012‑09‑15 18:55:03 | LOW (3) | The TLS protocol 1.2 and earlier, as used in Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Qt, and other products, can encrypt compressed data without properly obfuscating the length of the unencrypted data, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to obtain plaintext HTTP headers by observing length differences during a series of guesses in which a string in an HTTP request potentially matches an unknown string in an HTTP header, aka a "CRIME" attack. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4909 | 2012‑09‑13 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025308 on Android allows remote attackers to obtain cookie information via a crafted application. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4908 | 2012‑09‑13 20:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025308 on Android allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and obtain access to local files via vectors involving a symlink. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4907 | 2012‑09‑13 20:55:02 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025308 on Android does not properly restrict access from JavaScript code to Android APIs, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted web page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4906 | 2012‑09‑13 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025308 on Android does not properly restrict access to file: URLs, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via unspecified vectors, as demonstrated by obtaining credential data, a different vulnerability than CVE-2012-4903. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4905 | 2012‑09‑13 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025308 on Android allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via an extra in an Intent object, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4904 | 2012‑09‑13 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-application scripting vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025308 on Android allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script via unspecified vectors, as demonstrated by "Universal XSS (UXSS)" attacks against the current tab. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑4903 | 2012‑09‑13 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025308 on Android does not properly restrict access to file: URLs, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via unspecified vectors, as demonstrated by obtaining credential data, a different vulnerability than CVE-2012-4906. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2900 | 2012‑10‑09 11:13:05 | HIGH (8) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.92, does not properly render text, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2899 | 2014‑01‑05 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.82 on iOS makes certain incorrect calls to WebView methods that trigger use of an applewebdata: URL, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and conduct Universal XSS (UXSS) attacks via vectors involving the document.write method. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2898 | 2014‑01‑05 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.82 on iOS on iPad devices allows remote attackers to spoof the Omnibox URL via vectors involving SSL error messages, a related issue to CVE-2012-0674. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2897 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | HIGH (10) | The kernel-mode drivers in Microsoft Windows XP SP2 and SP3, Windows Server 2003 SP2, Windows Vista SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2, R2, and R2 SP1, Windows 7 Gold and SP1, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, and Windows RT, as used by Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 and other programs, do not properly handle objects in memory, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted TrueType font file, aka "Windows Font Parsing Vulnerability" or "TrueType Font Parsing Vulnerability." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2896 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the WebGL implementation in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 on Mac OS X allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2895 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (7) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger out-of-bounds write operations. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2894 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 does not properly handle graphics-context data structures, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2893 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (7) | Double free vulnerability in libxslt, as used in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to XSL transforms. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2892 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to bypass the pop-up blocker via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2891 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (5) | The IPC implementation in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows attackers to obtain potentially sensitive information about memory addresses via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2890 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2889 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via vectors involving frames, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2888 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving SVG text references. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2887 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving onclick events. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2886 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via vectors related to the Google V8 bindings, aka "Universal XSS (UXSS)." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2885 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | HIGH (8) | Double free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to application exit. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2884 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2883 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | HIGH (8) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write operation, a different vulnerability than CVE-2012-2874. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2882 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:05 | MEDIUM (7) | FFmpeg, as used in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79, does not properly handle OGG containers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, related to a "wild pointer" issue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2881 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:04 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 does not properly handle plug-ins, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (DOM tree corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2880 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:04 | HIGH (8) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the plug-in paint buffer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2879 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (DOM topology corruption) via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2878 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:04 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to plug-in handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2877 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:04 | MEDIUM (5) | The extension system in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 does not properly handle modal dialogs, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2876 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:04 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in the SSE2 optimization functionality in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2875 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79 allow remote attackers to have an unknown impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2874 | 2012‑09‑26 10:56:04 | HIGH (8) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 22.0.1229.79, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write operation, a different vulnerability than CVE-2012-2883. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2872 | 2012‑08‑31 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in an SSL interstitial page in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.89 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2871 | 2012‑08‑31 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | libxml2 2.9.0-rc1 and earlier, as used in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.89, does not properly support a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of XSL transforms, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document, related to the _xmlNs data structure in include/libxml/tree.h. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2870 | 2012‑08‑31 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | libxslt 1.1.26 and earlier, as used in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.89, does not properly manage memory, which might allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted XSLT expression that is not properly identified during XPath navigation, related to (1) the xsltCompileLocationPathPattern function in libxslt/pattern.c and (2) the xsltGenerateIdFunction function in libxslt/functions.c. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2869 | 2012‑08‑31 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.89 does not properly load URLs, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger a "stale buffer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2868 | 2012‑08‑31 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.89 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving improper interaction between worker processes and an XMLHttpRequest (aka XHR) object. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2867 | 2012‑08‑31 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | The SPDY implementation in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.89 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2866 | 2012‑08‑31 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.89 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of run-in elements, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2865 | 2012‑08‑31 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.89 does not properly perform line breaking, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2863 | 2012‑08‑09 10:29:47 | HIGH (8) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.75 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger out-of-bounds write operations. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2862 | 2012‑08‑09 10:29:47 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.75 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2860 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The date-picker implementation in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2859 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Linux does not properly handle tabs, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2858 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Buffer overflow in the WebP decoder in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted WebP image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2857 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) DOM implementation in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2856 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger out-of-bounds write operations. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2855 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2854 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allows remote attackers to obtain potentially sensitive information about pointer values by leveraging access to a WebUI renderer process. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2853 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The webRequest API in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, does not properly interact with the Chrome Web Store, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2852 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, does not properly handle object linkage, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (use-after-free) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2851 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2850 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allow remote attackers to have an unknown impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2849 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Off-by-one error in the GIF decoder in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2848 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The drag-and-drop implementation in Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, allows user-assisted remote attackers to bypass intended file access restrictions via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2847 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Mac OS X and Linux, and before 21.0.1180.60 on Windows and Chrome Frame, does not request user confirmation before continuing a large series of downloads, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (resource consumption) via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2846 | 2012‑08‑06 15:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 21.0.1180.57 on Linux does not properly isolate renderer processes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (cross-process interference) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2844 | 2012‑07‑12 21:55:06 | HIGH (9) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.57 does not properly handle JavaScript code, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect object access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2843 | 2012‑07‑12 21:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.57 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to layout height tracking. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2842 | 2012‑07‑12 21:55:06 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.57 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to counter handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2834 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted data in the Matroska container format. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2833 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in the JS API in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2832 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | MEDIUM (7) | The image-codec implementation in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 does not initialize an unspecified pointer, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2831 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to SVG references. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2830 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 does not properly set array values, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect pointer use) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2829 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the :first-letter pseudo-element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2828 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2827 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the UI in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 on Mac OS X allows attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2826 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 does not properly implement texture conversion, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2825 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | MEDIUM (5) | The XSL implementation in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect read operation) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2824 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to SVG painting. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2823 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to SVG resources. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2822 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | MEDIUM (5) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2821 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | The autofill implementation in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 does not properly display text, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2820 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 does not properly implement SVG filters, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2819 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | MEDIUM (7) | The texSubImage2D implementation in the WebGL subsystem in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 does not properly handle uploads to floating-point textures, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (assertion failure and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web page, as demonstrated by certain WebGL performance tests, aka rdar problem 11520387. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2818 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:39 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the layout of documents that use the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) counters feature. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2817 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:38 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to tables that have sections. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2816 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:38 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 on Windows does not properly isolate sandboxed processes, which might allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (process interference) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2815 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:38 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 allows remote attackers to obtain potentially sensitive information from a fragment identifier by leveraging access to an IFRAME element associated with a different domain. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2807 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:38 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in libxml2, as used in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 and other products, on 64-bit Linux platforms allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑2764 | 2012‑06‑27 10:18:38 | HIGH (7) | Untrusted search path vulnerability in Google Chrome before 20.0.1132.43 on Windows might allow local users to gain privileges via a Trojan horse Metro DLL in the current working directory. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2012‑1846 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome 17.0.963.66 and earlier allows remote attackers to bypass the sandbox protection mechanism by leveraging access to a sandboxed process, as demonstrated by VUPEN during a Pwn2Own competition at CanSecWest 2012. NOTE: the primary affected product may be clarified later; it was not identified by the researcher, who reportedly stated "it really doesn't matter if it's third-party code." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑1845 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:02 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome 17.0.963.66 and earlier allows remote attackers to bypass the DEP and ASLR protection mechanisms, and execute arbitrary code, via unspecified vectors, as demonstrated by VUPEN during a Pwn2Own competition at CanSecWest 2012. NOTE: the primary affected product may be clarified later; it was not identified by the researcher, who reportedly stated "it really doesn't matter if it's third-party code." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑1521 | 2012‑05‑01 10:12:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the XML parser in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.168 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑0725 | 2012‑04‑06 20:55:01 | HIGH (9) | Adobe Flash Player before 11.2.202.229 in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allow attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2012-0724. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2012‑0724 | 2012‑04‑06 20:55:01 | HIGH (9) | Adobe Flash Player before 11.2.202.229 in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allow attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2012-0725. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑5319 | 2015‑03‑09 00:59:00 | MEDIUM (5) | content/renderer/device_sensors/device_motion_event_pump.cc in Google Chrome before 41.0.2272.76 does not properly restrict access to high-rate accelerometer data, which makes it easier for remote attackers to capture keystrokes via a crafted web site that listens for ondevicemotion events, a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1231. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑4692 | 2011‑12‑07 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (5) | WebKit, as used in Apple Safari 5.1.1 and earlier and Google Chrome 15 and earlier, does not prevent capture of data about the time required for image loading, which makes it easier for remote attackers to determine whether an image exists in the browser cache via crafted JavaScript code, as demonstrated by visipisi. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑4691 | 2011‑12‑07 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome 15.0.874.121 and earlier does not prevent capture of data about the times of Same Origin Policy violations during IFRAME loading attempts, which makes it easier for remote attackers to determine whether a document exists in the browser cache via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3972 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (5) | The shader translator implementation in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3971 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to mousemove events. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3970 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (4) | libxslt, as used in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3969 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to layout of SVG documents. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3968 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (4) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequences. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3967 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted certificate. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3966 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to error handling for Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token-sequence data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3965 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 does not properly check signatures, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3964 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 does not properly implement the drag-and-drop feature, which makes it easier for remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3963 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 does not properly handle PDF FAX images, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3962 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 does not properly perform path clipping, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3961 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | HIGH (9) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via vectors that trigger a crash of a utility process. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3960 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 does not properly decode audio data, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3959 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in the locale implementation in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3958 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 does not properly perform casts of variables during handling of a column span, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3957 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the garbage-collection functionality in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving PDF documents. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3956 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (7) | The extension implementation in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 does not properly handle sandboxed origins, which might allow remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3955 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger the aborting of an IndexedDB transaction. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3954 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:29 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via vectors that trigger a large amount of database usage. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3953 | 2012‑02‑09 04:10:28 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.46 does not prevent monitoring of the clipboard after a paste event, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3928 | 2012‑01‑24 04:03:37 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.77 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to DOM handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3927 | 2012‑01‑24 04:03:36 | HIGH (8) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.77, does not perform all required initialization of values, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3926 | 2012‑01‑24 04:03:36 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the tree builder in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.77 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3925 | 2012‑01‑24 04:03:36 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Safe Browsing feature in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.75 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to a navigation entry and an interstitial page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3924 | 2012‑01‑24 04:03:36 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.77 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to DOM selections. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3922 | 2012‑01‑07 11:55:15 | HIGH (8) | Stack-based buffer overflow in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.75 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to glyph handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3921 | 2012‑01‑07 11:55:15 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.75 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving animation frames. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3919 | 2012‑01‑07 11:55:13 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in libxml2, as used in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.75, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3917 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Stack-based buffer overflow in FileWatcher in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3916 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 does not properly handle PDF cross references, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3915 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to PDF fonts. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3914 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:02 | HIGH (8) | The internationalization (aka i18n) functionality in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3913 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to Range handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3912 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to SVG filters. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3911 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 does not properly handle PDF documents, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3910 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 does not properly handle YUV video frames, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3909 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 on 64-bit platforms does not properly manage property arrays, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3908 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 does not properly parse SVG documents, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3907 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The view-source feature in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 allows remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3906 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | The PDF parser in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3905 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | libxml2, as used in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3904 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to bidirectional text (aka bidi) handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3903 | 2011‑12‑13 21:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 16.0.912.63 does not properly perform regex matching, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3900 | 2011‑11‑17 23:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.121, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3898 | 2011‑11‑11 11:55:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.120, when Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 7 is used, does not request user confirmation before applet execution begins, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted applet. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3897 | 2011‑11‑11 11:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.120 allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to editing. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3896 | 2011‑11‑11 11:55:03 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.120 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to shader variable mapping. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3895 | 2011‑11‑11 11:55:03 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the Vorbis decoder in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.120 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted stream. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3894 | 2011‑11‑11 11:55:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.120 does not properly perform VP8 decoding, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted stream. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3893 | 2011‑11‑11 11:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.120 does not properly implement the MKV and Vorbis media handlers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3892 | 2011‑11‑11 11:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Double free vulnerability in the Theora decoder in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.120 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted stream. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3891 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 does not properly restrict access to internal Google V8 functions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3890 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to video source handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3889 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the Web Audio implementation in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3888 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to editing operations in conjunction with an unknown plug-in. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3887 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 does not properly handle javascript: URLs, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions and read cookies via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3886 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that triggers out-of-bounds write operations. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3885 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to stale Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token-sequence data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3884 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 does not properly address timing issues during DOM traversal, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3883 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to counters. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3882 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to media buffers. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3881 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 and Android before 4.4, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and conduct Universal XSS (UXSS) attacks via vectors related to (1) the DOMWindow::clear function and use of a selection object, (2) the Object::GetRealNamedPropertyInPrototypeChain function and use of an __proto__ property, (3) the HTMLPlugInImageElement::allowedToLoadFrameURL function and use of a javascript: URL, (4) incorrect origins for XSLT-generated documents in the XSLTProcessor::createDocumentFromSource function, and (5) improper handling of synchronous frame loads in the ScriptController::executeIfJavaScriptURL function. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3880 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 does not prevent use of an unspecified special character as a delimiter in HTTP headers, which has unknown impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3879 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 does not prevent redirects to chrome: URLs, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3878 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to worker process initialization. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3877 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the appcache internals page in Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3876 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 does not properly handle downloading files that have whitespace characters at the end of a filename, which has unspecified impact and user-assisted remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3875 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 does not properly handle drag and drop operations on URL strings, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3873 | 2011‑10‑04 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.202 does not properly implement shader translation, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3640 | 2011‑10‑28 02:49:53 | HIGH (7) | Untrusted search path vulnerability in Mozilla Network Security Services (NSS), as used in Google Chrome before 17 on Windows and Mac OS X, might allow local users to gain privileges via a Trojan horse pkcs11.txt file in a top-level directory. NOTE: the vendor's response was "Strange behavior, but we're not treating this as a security bug." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3389 | 2011‑09‑06 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (4) | The SSL protocol, as used in certain configurations in Microsoft Windows and Microsoft Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Opera, and other products, encrypts data by using CBC mode with chained initialization vectors, which allows man-in-the-middle attackers to obtain plaintext HTTP headers via a blockwise chosen-boundary attack (BCBA) on an HTTPS session, in conjunction with JavaScript code that uses (1) the HTML5 WebSocket API, (2) the Java URLConnection API, or (3) the Silverlight WebClient API, aka a "BEAST" attack. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3234 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:57 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly handle boxes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3115 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger "type corruption." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3114 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Multiple buffer overflows in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger unknown function calls. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3113 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | HIGH (8) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of color spaces, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3112 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via an invalid encrypted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3111 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (invalid read operation) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3110 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | HIGH (8) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger out-of-bounds write operations. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3109 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 on Linux does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact by leveraging an error in the GTK implementation of the UI. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3108 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via vectors related to the browser cache. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3107 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 does not properly implement JavaScript bindings for plug-ins, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3106 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | HIGH (10) | The WebSockets implementation in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 does not properly handle use of SSL, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3105 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the :first-letter pseudo-element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3104 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3103 | 2012‑05‑24 18:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.52, does not properly perform garbage collection, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3102 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Off-by-one error in libxml2, as used in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds write) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3101 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:04 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 on Linux does not properly mitigate an unspecified flaw in an NVIDIA driver, which has unknown impact and attack vectors. NOTE: see CVE-2012-3105 for the related MFSA 2012-34 issue in Mozilla products. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3100 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 does not properly draw dash paths, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3099 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a malformed name for the font encoding. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3098 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | HIGH (7) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 on Windows uses an incorrect search path for the Windows Media Player plug-in, which might allow local users to gain privileges via a Trojan horse plug-in in an unspecified directory. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2011‑3097 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | HIGH (10) | The PDF functionality in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging an out-of-bounds write error in the implementation of sampled functions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3096 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 on Linux allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact by leveraging an error in the GTK implementation of the omnibox. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3095 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | HIGH (10) | The OGG container in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3094 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 does not properly handle Tibetan text, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3093 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 does not properly handle glyphs, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3092 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:03 | HIGH (10) | The regex implementation in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (invalid write operation) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3091 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the IndexedDB implementation in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3090 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to worker processes. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3089 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving tables. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3088 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 does not properly draw hairlines, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3087 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 does not properly perform window navigation, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3086 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a STYLE element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3085 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | The Autofill feature in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 does not properly restrict field values, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (UI corruption) and possibly conduct spoofing attacks via vectors involving long values. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3084 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 does not use a dedicated process for the loading of links found on an internal page, which might allow attackers to bypass intended sandbox restrictions via a crafted page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3083 | 2012‑05‑16 00:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | browser/profiles/profile_impl_io_data.cc in Google Chrome before 19.0.1084.46 does not properly handle a malformed ftp URL in the SRC attribute of a VIDEO element, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and application crash) via a crafted web page. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3081 | 2012‑05‑01 10:12:04 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.168 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the floating of elements, a different vulnerability than CVE-2011-3078. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3080 | 2012‑05‑01 10:12:04 | HIGH (8) | Race condition in the Inter-process Communication (IPC) implementation in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.168 allows attackers to bypass intended sandbox restrictions via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3079 | 2012‑05‑01 10:12:04 | HIGH (10) | The Inter-process Communication (IPC) implementation in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.168, as used in Mozilla Firefox before 38.0 and other products, does not properly validate messages, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3078 | 2012‑05‑01 10:12:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.168 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the floating of elements, a different vulnerability than CVE-2011-3081. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3077 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving the script bindings, related to a "read-after-free" issue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3076 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to focus handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3075 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to style-application commands. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3074 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of media. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3073 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of SVG resources. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3072 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via vectors related to pop-up windows. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3071 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the HTMLMediaElement implementation in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3070 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the Google V8 bindings. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3069 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to line boxes. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3068 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to run-in boxes. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3067 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via vectors related to replacement of IFRAME elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3066 | 2012‑04‑05 22:02:08 | MEDIUM (7) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.151, does not properly perform clipping, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3065 | 2012‑03‑30 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.142, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3064 | 2012‑03‑30 22:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.142 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to SVG clipping. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3063 | 2012‑03‑30 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.142 does not properly validate the renderer's navigation requests, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3062 | 2012‑03‑30 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Off-by-one error in the OpenType Sanitizer in Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.142 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted OpenType file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3061 | 2012‑03‑30 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.142 does not properly check X.509 certificates before use of a SPDY proxy, which might allow man-in-the-middle attackers to spoof servers or obtain sensitive information via a crafted certificate. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3060 | 2012‑03‑30 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.142 does not properly handle text fragments, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3059 | 2012‑03‑30 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.142 does not properly handle SVG text elements, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3058 | 2012‑03‑30 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 18.0.1025.142 does not properly handle the EUC-JP encoding system, which might allow remote attackers to conduct cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3057 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service via vectors that trigger an invalid read operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3056 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via vectors involving a "magic iframe." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3055 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The browser native UI in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 does not require user confirmation before an unpacked extension installation, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3054 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The WebUI privilege implementation in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 does not properly perform isolation, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3053 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to block splitting. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3052 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | The WebGL implementation in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 does not properly handle CANVAS elements, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3051 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the cross-fade function. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3050 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the :first-letter pseudo-element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3049 | 2012‑03‑23 10:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 does not properly restrict the extension web request API, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (disrupted system requests) via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3047 | 2012‑03‑10 19:55:01 | HIGH (9) | The GPU process in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.79 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) by leveraging an error in the plug-in loading mechanism. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3046 | 2012‑03‑09 00:55:01 | HIGH (10) | The extension subsystem in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.78 does not properly handle history navigation, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code by leveraging a "Universal XSS (UXSS)" issue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3045 | 2012‑03‑22 16:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer signedness error in the png_inflate function in pngrutil.c in libpng before 1.4.10beta01, as used in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.83 and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly execute arbitrary code via a crafted PNG file, a different vulnerability than CVE-2011-3026. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3044 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving SVG animation elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3043 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a flexbox (aka flexible box) in conjunction with the floating of elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3042 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of table sections. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3041 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of class attributes. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3040 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 does not properly handle text, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3039 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to quote handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3038 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to multi-column handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3037 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 does not properly perform casts of unspecified variables during the splitting of anonymous blocks, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3036 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of line boxes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3035 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving SVG use elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3034 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving an SVG document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3033 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Buffer overflow in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3032 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of SVG values. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3031 | 2012‑03‑05 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the element wrapper in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.65, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3027 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of columns, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3026 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Integer overflow in libpng, as used in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger an integer truncation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3025 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 does not properly parse H.264 data, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3024 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via an empty X.509 certificate. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3023 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to drag-and-drop operations. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3022 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (5) | translate/translate_manager.cc in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 and 19.x before 19.0.1036.7 uses an HTTP session to exchange data for translation, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information by sniffing the network. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3021 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to subframe loading. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3020 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Unspecified vulnerability in the Native Client validator implementation in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 has unknown impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3019 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Heap-based buffer overflow in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted Matroska video (aka MKV) file. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3018 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Heap-based buffer overflow in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to path rendering. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3017 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to database handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3016 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving counter nodes, related to a "read-after-free" issue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑3015 | 2012‑02‑16 20:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in the PDF codecs in Google Chrome before 17.0.963.56 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2881 | 2011‑10‑04 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.202 does not properly handle Google V8 hidden objects, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2880 | 2011‑10‑04 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.202 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the Google V8 bindings. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2879 | 2011‑10‑04 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.202 does not properly consider object lifetimes and thread safety during the handling of audio nodes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2878 | 2011‑10‑04 20:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.202 does not properly restrict access to the window prototype, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2877 | 2011‑10‑04 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.202 does not properly handle SVG text, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to "stale font." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2876 | 2011‑10‑04 20:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.202 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a text line box. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2875 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:57 | MEDIUM (7) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163, does not properly perform object sealing, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that leverage "type confusion." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2874 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not perform an expected pin operation for a self-signed certificate during a session, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2864 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly handle Tibetan characters, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2863 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Insufficient policy enforcement in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 14.0.0.0 allowed a remote attacker to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2862 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163, does not properly restrict access to built-in objects, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2861 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly handle strings in PDF documents, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted document that triggers an incorrect read operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2860 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to table styles. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2859 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 uses incorrect permissions for non-gallery pages, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2858 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly handle triangle arrays, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2857 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the focus controller. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2856 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2855 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly handle Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequences, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale node." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2854 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to "ruby / table style handing." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2853 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to plug-in handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2852 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Off-by-one error in Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2851 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly handle video, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2850 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly handle Khmer characters, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2849 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (4) | The WebSockets implementation in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2848 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows user-assisted remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via vectors related to the forward button. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2847 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the document loader in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2846 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to unload event handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2845 | 2011‑10‑25 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 15.0.874.102 does not properly handle history data, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2844 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly process MP3 files, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2843 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly handle media buffers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2842 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | HIGH (8) | The installer in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 on Mac OS X does not properly handle lock files, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2841 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly perform garbage collection during the processing of PDF documents, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2840 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows user-assisted remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via vectors related to "unusual user interaction." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2839 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | The PDF implementation in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 on Linux does not properly use the memset library function, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2838 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not properly consider the MIME type during the loading of a plug-in, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2837 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 on Linux does not use the PIC and PIE compiler options for position-independent code, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2836 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 does not require Infobar interaction before use of the Windows Media Player plug-in, which makes it easier for remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via crafted Flash content. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2835 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163 allows attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the certificate cache. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2834 | 2011‑09‑19 12:02:56 | MEDIUM (7) | Double free vulnerability in libxml2, as used in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to XPath handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2830 | 2011‑10‑28 02:49:53 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 14.0.835.163, does not properly implement script object wrappers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2829 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 on 32-bit platforms allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving uniform arrays. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2828 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2827 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to text searching. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2826 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via vectors related to empty origins. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2825 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving custom fonts. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2824 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving counter nodes. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2823 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a line box. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2822 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 on Windows does not properly parse URLs located on the command line, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2821 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Double free vulnerability in libxml2, as used in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted XPath expression. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2819 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via vectors related to handling of the base URI. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2818 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to display box rendering. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2806 | 2011‑08‑29 15:55:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.215 on Windows does not properly handle vertex data, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2805 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and conduct script injection attacks via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2804 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not properly handle nested functions in PDF documents, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2803 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not properly handle Skia paths, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2802 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107, does not properly perform const lookups, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2801 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the frame loader. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2800 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to obtain potentially sensitive information about client-side redirect targets via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2799 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to HTML range handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2798 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not properly restrict access to internal schemes, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2797 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to resource caching. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2796 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2795 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not prevent calls to functions in other frames, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via a crafted web site, related to a "cross-frame function leak." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2794 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not properly perform text iteration, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2793 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to media selectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2792 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to float removal. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2791 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | The International Components for Unicode (ICU) functionality in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2790 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving floating styles. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2789 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to instantiation of the Pepper plug-in. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2788 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Buffer overflow in the inspector serialization functionality in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows user-assisted remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2787 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not properly address re-entrancy issues associated with the GPU lock, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2786 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not ensure that the speech-input bubble is shown on the product's screen, which might make it easier for remote attackers to make audio recordings via a crafted web page containing an INPUT element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2785 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | The extensions implementation in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not properly validate the URL for the home page, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2784 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | LOW (2) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via a request for the GL program log, which reveals a local path in an unspecified log entry. | 0 | 0 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2011‑2783 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not ensure that developer-mode NPAPI extension installations are confirmed by a browser dialog, which makes it easier for remote attackers to modify the product's functionality via a Trojan horse extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2782 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (4) | The drag-and-drop implementation in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 on Linux does not properly enforce permissions for files, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2761 | 2011‑07‑18 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome 14.0.794.0 does not properly handle a reload of a page generated in response to a POST, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted web site, related to GetWidget methods. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2599 | 2011‑06‑30 15:55:05 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome 11 does not block use of a cross-domain image as a WebGL texture, which allows remote attackers to obtain approximate copies of arbitrary images via a timing attack involving a crafted WebGL fragment shader. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2361 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The Basic Authentication dialog implementation in Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not properly handle strings, which might make it easier for remote attackers to capture credentials via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2360 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not ensure that the user is prompted before download of a dangerous file, which makes it easier for remote attackers to bypass intended content restrictions via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2359 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not properly track line boxes during rendering, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2358 | 2011‑08‑03 00:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 13.0.782.107 does not ensure that extension installations are confirmed by a browser dialog, which makes it easier for remote attackers to modify the product's functionality via a Trojan horse extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2351 | 2011‑06‑29 17:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.112 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving SVG use elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2350 | 2011‑06‑29 17:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | The HTML parser in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.112 does not properly address "lifetime and re-entrancy issues," which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2349 | 2011‑06‑29 17:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.112 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to text selection. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2348 | 2011‑06‑29 17:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.112, performs an incorrect bounds check, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2347 | 2011‑06‑29 17:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 12.0.742.112 does not properly handle Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequences, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2346 | 2011‑06‑29 17:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.112 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving SVG fonts. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2345 | 2011‑06‑29 17:55:04 | MEDIUM (4) | The NPAPI implementation in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.112 does not properly handle strings, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2342 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (4) | The DOM implementation in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2332 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑2075 | 2011‑05‑10 18:55:03 | HIGH (9) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome 11.0.696.65 on Windows 7 SP1 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unknown vectors. NOTE: as of 20110510, the only disclosure is a vague advisory that possibly relates to multiple vulnerabilities or multiple products. However, because it is from a well-known researcher, it is being assigned a CVE identifier for tracking purposes. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1819 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 allows remote attackers to perform unspecified injection into a chrome:// page via vectors related to extensions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1818 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the image loader in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1817 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 does not properly implement history deletion, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1816 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the developer tools in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1815 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 allows remote attackers to inject script into a tab page via vectors related to extensions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1814 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 attempts to read data from an uninitialized pointer, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1813 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 does not properly implement the framework for extensions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1812 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 allows remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via vectors related to extensions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1811 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 does not properly handle a large number of form submissions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1810 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:03 | MEDIUM (4) | The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 does not properly restrict access to the visit history, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1809 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the accessibility feature in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1808 | 2011‑06‑09 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 12.0.742.91 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to incorrect integer calculations during float handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1807 | 2011‑05‑26 16:55:05 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.71 does not properly handle blobs, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1806 | 2011‑05‑26 16:55:05 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.71 does not properly implement the GPU command buffer, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1805 | 2020‑06‑03 23:15:11 | HIGH (9) | Bad cast in CSS in Google Chrome prior to 11.0.0.0 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1804 | 2011‑05‑26 16:55:05 | HIGH (8) | rendering/RenderBox.cpp in WebCore in WebKit before r86862, as used in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.71, does not properly render floats, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1801 | 2011‑05‑26 16:55:05 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.71 allows remote attackers to bypass the pop-up blocker via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1800 | 2011‑05‑16 17:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Multiple integer overflows in the SVG Filters implementation in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.68 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1799 | 2011‑05‑16 17:55:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.68 does not properly perform casts of variables during interaction with the WebKit engine, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1798 | 2014‑12‑26 02:59:04 | HIGH (8) | rendering/svg/RenderSVGText.cpp in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.65 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during an attempt to handle a block child, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted text element in an SVG document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1796 | 2014‑12‑26 02:59:03 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the FrameView::calculateScrollbarModesForLayout function in page/FrameView.cpp in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted JavaScript code that calls the removeChild method during interaction with a FRAME element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1795 | 2014‑12‑26 02:59:03 | HIGH (8) | Integer underflow in the HTMLFormElement::removeFormElement function in html/HTMLFormElement.cpp in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document containing a FORM element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1794 | 2014‑12‑26 02:59:02 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in the FilterEffect::copyImageBytes function in platform/graphics/filters/FilterEffect.cpp in the SVG filter implementation in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via crafted dimensions. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1793 | 2014‑12‑26 02:59:00 | HIGH (8) | rendering/svg/RenderSVGResourceFilter.cpp in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.65 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted SVG document that leads to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1691 | 2011‑04‑15 00:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | The counterToCSSValue function in CSSComputedStyleDeclaration.cpp in the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in WebCore in WebKit before r82222, as used in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.43 and other products, does not properly handle access to the (1) counterIncrement and (2) counterReset attributes of CSSStyleDeclaration data provided by a getComputedStyle method call, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and application crash) via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1465 | 2011‑03‑20 02:00:04 | MEDIUM (5) | The SPDY implementation in net/http/http_network_transaction.cc in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.14 drains the bodies from SPDY responses, which might allow remote SPDY servers to cause a denial of service (application exit) by canceling a stream. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1456 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly handle PDF forms, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to "stale pointers." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1455 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly handle PDF documents with multipart encoding, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1454 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the DOM id handling functionality in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1452 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 allows user-assisted remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via vectors involving a redirect and a manual reload. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1451 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly handle DOM id maps, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to "dangling pointers." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1450 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly present file dialogs, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to "dangling pointers." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1449 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the WebSockets implementation in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1448 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly perform height calculations, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1447 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly handle drop-down lists, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1446 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (6) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 allows remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via vectors involving (1) a navigation error or (2) an interrupted load. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1445 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly handle SVG documents, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1444 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in the sandbox launcher implementation in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 on Linux allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1443 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly implement layering, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to "stale pointers." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1442 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly handle mutation events, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (node tree corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1441 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:02 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of floating select lists, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1440 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the ruby element and Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequences. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1439 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 on Linux does not properly isolate renderer processes, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1438 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via vectors involving blobs. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1437 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Multiple integer overflows in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to float rendering. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1436 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 on Linux does not properly interact with the X Window System, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1435 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly implement the tabs permission for extensions, which allows remote attackers to read local files via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1434 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not ensure thread safety during handling of MIME data, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1413 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:21 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 on Linux does not properly mitigate an unspecified flaw in an X server, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via vectors involving long messages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1305 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 on Linux and Mac OS X allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to linked lists and a database. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1304 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 allows remote attackers to bypass the pop-up blocker via vectors related to plug-ins. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1303 | 2011‑05‑03 22:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 11.0.696.57 does not properly handle floating objects, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1302 | 2011‑04‑15 19:55:01 | HIGH (9) | Heap-based buffer overflow in the GPU process in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.205 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1301 | 2011‑04‑15 19:55:01 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the GPU process in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.205 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1300 | 2011‑04‑15 19:55:01 | HIGH (10) | The Program::getActiveUniformMaxLength function in libGLESv2/Program.cpp in libGLESv2.dll in the WebGLES library in Almost Native Graphics Layer Engine (ANGLE), as used in Mozilla Firefox 4.x before 4.0.1 on Windows and in the GPU process in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.205 on Windows, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors, related to an "off-by-three" error. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1296 | 2011‑03‑25 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.204 does not properly handle SVG text, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1295 | 2011‑03‑25 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.204 and Apple Safari before 5.0.6, does not properly handle node parentage, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (DOM tree corruption), conduct cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1294 | 2011‑03‑25 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.204 does not properly handle Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequences, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1293 | 2011‑03‑25 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the HTMLCollection implementation in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.204 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1292 | 2011‑03‑25 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the frame-loader implementation in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.204 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1291 | 2011‑03‑25 19:55:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.204 does not properly handle base strings, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, related to a "buffer error." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1286 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:21 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger incorrect access to memory. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1285 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | HIGH (8) | The regular-expression functionality in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not properly implement reentrancy, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1204 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not properly handle attributes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (DOM tree corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1203 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not properly handle SVG cursors, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1202 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | MEDIUM (4) | The xsltGenerateIdFunction function in functions.c in libxslt 1.1.26 and earlier, as used in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 and other products, allows remote attackers to obtain potentially sensitive information about heap memory addresses via an XML document containing a call to the XSLT generate-id XPath function. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1201 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | HIGH (8) | The context implementation in WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1200 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during text rendering, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unknown other impact via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1199 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not properly handle DataView objects, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1198 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | HIGH (8) | The video functionality in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger use of a malformed "out-of-bounds structure." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1197 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not properly perform table painting, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1196 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | HIGH (8) | The OGG container implementation in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that trigger an out-of-bounds write. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1195 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:20 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to "document script lifetime handling." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1194 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | MEDIUM (5) | Multiple unspecified vulnerabilities in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 allow remote attackers to bypass the pop-up blocker via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1193 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | HIGH (8) | Google V8, as used in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1192 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 on Linux does not properly handle Unicode ranges, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1191 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the handling of DOM URLs. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1190 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | MEDIUM (5) | The Web Workers implementation in Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors, related to an "error message leak." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1189 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not properly perform box layout, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale node." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1188 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not properly handle counter nodes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1187 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors, related to an "error message leak." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1186 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:19 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 on Linux does not properly handle parallel execution of calls to the print method, which might allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via crafted JavaScript code. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1185 | 2011‑03‑11 02:01:18 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 10.0.648.127 does not prevent (1) navigation and (2) close operations on the top location of a sandboxed frame, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1125 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:04 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly perform layout, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1124 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:04 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to blocked plug-ins. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1123 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:04 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly restrict access to internal extension functions, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1122 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:04 | MEDIUM (5) | The WebGL implementation in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors, aka Issue 71960. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1121 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:04 | HIGH (8) | Integer overflow in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving a TEXTAREA element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1120 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:04 | MEDIUM (5) | The WebGL implementation in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors, aka Issue 71717. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1119 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:04 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly determine device orientation, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1118 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly handle TEXTAREA elements, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1117 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly handle XHTML documents, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to "stale nodes." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1116 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly handle SVG animations, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1115 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly render tables, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1114 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly handle tables, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale node." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1113 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 on 64-bit Linux platforms does not properly perform pickle deserialization, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1112 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly perform SVG rendering, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1111 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly implement forms controls, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1110 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly implement key frame rules, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1109 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly process nodes in Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) stylesheets, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1108 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 does not properly implement JavaScript dialogs, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1107 | 2011‑03‑01 23:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.107 allows remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑1059 | 2011‑02‑22 19:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Use-after-free vulnerability in WebCore in WebKit before r77705, as used in Google Chrome before 11.0.672.2 and other products, allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that entice a user to resubmit a form, related to improper handling of provisional items by the HistoryController component, aka rdar problem 8938557. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0985 | 2011‑02‑10 19:00:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.94 does not properly perform process termination upon memory exhaustion, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0984 | 2011‑02‑10 19:00:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.94 does not properly handle plug-ins, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0983 | 2011‑02‑10 19:00:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.94 does not properly handle anonymous blocks, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0982 | 2011‑02‑10 19:00:02 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.94 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving SVG font faces. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0981 | 2011‑02‑10 19:00:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.94 does not properly perform event handling for animations, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0784 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Race condition in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via vectors related to audio. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0783 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via vectors involving a "bad volume setting." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0782 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 on Mac OS X does not properly mitigate an unspecified flaw in the Mac OS X 10.5 SSL libraries, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0781 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 does not properly handle autofill profile merging, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0780 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (7) | The PDF event handler in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 does not properly interact with print operations, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0779 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 does not properly handle a missing key in an extension, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0778 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 does not properly restrict drag and drop operations, which might allow remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0777 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to image loading. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0776 | 2011‑02‑04 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | The sandbox implementation in Google Chrome before 9.0.597.84 on Mac OS X might allow remote attackers to obtain potentially sensitive information about local files via vectors related to the stat system call. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0611 | 2011‑04‑13 14:55:01 | HIGH (9) | Adobe Flash Player before 10.2.154.27 on Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and Solaris and 10.2.156.12 and earlier on Android; Adobe AIR before 2.6.19140; and Authplay.dll (aka AuthPlayLib.bundle) in Adobe Reader 9.x before 9.4.4 and 10.x through 10.0.1 on Windows, Adobe Reader 9.x before 9.4.4 and 10.x before 10.0.3 on Mac OS X, and Adobe Acrobat 9.x before 9.4.4 and 10.x before 10.0.3 on Windows and Mac OS X allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via crafted Flash content; as demonstrated by a Microsoft Office document with an embedded .swf file that has a size inconsistency in a "group of included constants," object type confusion, ActionScript that adds custom functions to prototypes, and Date objects; and as exploited in the wild in April 2011. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0609 | 2011‑03‑15 17:55:04 | HIGH (8) | Unspecified vulnerability in Adobe Flash Player 10.2.154.13 and earlier on Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and Solaris; 10.1.106.16 and earlier on Android; Adobe AIR 2.5.1 and earlier; and Authplay.dll (aka AuthPlayLib.bundle) in Adobe Reader and Acrobat 9.x through 9.4.2 and 10.x through 10.0.1 on Windows and Mac OS X, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via crafted Flash content, as demonstrated by a .swf file embedded in an Excel spreadsheet, and as exploited in the wild in March 2011. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2011‑0485 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly handle speech data, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0484 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly perform DOM node removal, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale rendering node." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0483 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of video, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0482 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during handling of anchors, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0481 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Buffer overflow in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to PDF shading. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0480 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Multiple buffer overflows in vorbis_dec.c in the Vorbis decoder in FFmpeg, as used in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted WebM file, related to buffers for (1) the channel floor and (2) the channel residue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0479 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly interact with extensions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service via a crafted extension that triggers an uninitialized pointer. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0478 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly handle SVG use elements, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0477 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly handle a mismatch in video frame sizes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (incorrect memory access) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0476 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (stack memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a PDF document that triggers an out-of-memory error. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0475 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a PDF document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0474 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly handle Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequences in conjunction with cursors, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0473 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly handle Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequences in conjunction with CANVAS elements, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to a "stale pointer." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0472 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly handle the printing of PDF documents, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a multi-page document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0471 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | HIGH (10) | The node-iteration implementation in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 does not properly handle pointers, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2011‑0470 | 2011‑01‑14 17:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.237 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.344 do not properly handle extensions notification, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑5073 | 2011‑12‑07 19:55:02 | MEDIUM (5) | The JavaScript implementation in Google Chrome 4 does not properly restrict the set of values contained in the object returned by the getComputedStyle method, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information about visited web pages by calling this method. NOTE: this may overlap CVE-2010-5070. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑5069 | 2011‑12‑07 19:55:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome 4 does not properly handle the :visited pseudo-class, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information about visited web pages via a crafted HTML document. NOTE: this may overlap CVE-2010-2264. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4578 | 2010‑12‑22 01:00:03 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.224 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.343 do not properly perform cursor handling, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors that lead to "stale pointers." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4577 | 2010‑12‑22 01:00:03 | HIGH (8) | The CSSParser::parseFontFaceSrc function in WebCore/css/CSSParser.cpp in WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.224, Chrome OS before 8.0.552.343, webkitgtk before 1.2.6, and other products does not properly parse Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) token sequences, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted local font, related to "Type Confusion." | 4 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4576 | 2010‑12‑22 01:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | browser/worker_host/message_port_dispatcher.cc in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.224 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.343 does not properly handle certain postMessage calls, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and application crash) via crafted JavaScript code that creates a web worker. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4575 | 2010‑12‑22 01:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | The ThemeInstalledInfoBarDelegate::Observe function in browser/extensions/theme_installed_infobar_delegate.cc in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.224 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.343 does not properly handle incorrect tab interaction by an extension, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4574 | 2010‑12‑22 01:00:03 | HIGH (8) | The Pickle::Pickle function in base/pickle.cc in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.224 and Chrome OS before 8.0.552.343 on 64-bit Linux platforms does not properly perform pointer arithmetic, which allows remote attackers to bypass message deserialization validation, and cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact, via invalid pickle data. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4494 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:10 | HIGH (8) | Double free vulnerability in libxml2 2.7.8 and other versions, as used in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to XPath handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4493 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service via vectors related to the handling of mouse dragging events. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4492 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:10 | HIGH (8) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving SVG animations. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4491 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:10 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 does not properly restrict privileged extensions, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted extension. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4490 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:09 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via malformed video content that triggers an indexing error. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4489 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:09 | MEDIUM (4) | libvpx, as used in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 and possibly other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via a crafted WebM video. NOTE: this vulnerability exists because of a regression. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4488 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:09 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 does not properly handle HTTP proxy authentication, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4487 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:09 | HIGH (8) | Incomplete blacklist vulnerability in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 on Linux and Mac OS X allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a "dangerous file." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4486 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:09 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to history handling. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4485 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 does not properly restrict the generation of file dialogs, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (reduced usability and possible application crash) via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4484 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:09 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 does not properly handle HTML5 databases, which allows attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4483 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:09 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 does not properly restrict read access to videos derived from CANVAS elements, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and obtain potentially sensitive video data via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4482 | 2010‑12‑07 21:00:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 8.0.552.215 allows remote attackers to bypass the pop-up blocker via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4206 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Array index error in the FEBlend::apply function in WebCore/platform/graphics/filters/FEBlend.cpp in WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44, webkitgtk before 1.2.6, and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service and possibly execute arbitrary code via a crafted SVG document, related to effects in the application of filters. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4205 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | CRITICAL (10) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44 does not properly handle the data types of event objects, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4204 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | CRITICAL (10) | WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44, webkitgtk before 1.2.6, and other products, accesses a frame object after this object has been destroyed, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4203 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | CRITICAL (10) | WebM libvpx (aka the VP8 Codec SDK) before 0.9.5, as used in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly execute arbitrary code via invalid frames. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4202 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | CRITICAL (10) | Multiple integer overflows in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44 on Linux allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted font. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4201 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | CRITICAL (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving text control selections. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4199 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44 does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable during processing of an SVG use element, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted SVG document. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4198 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | HIGH (9) | WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44, webkitgtk before 1.2.6, and other products, does not properly handle large text areas, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4197 | 2010‑11‑06 00:00:03 | CRITICAL (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44, webkitgtk before 1.2.6, and other products, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors involving text editing. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4042 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | CRITICAL (10) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 does not properly handle element maps, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to "stale elements." | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4041 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | CRITICAL (10) | The sandbox implementation in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 on Linux does not properly constrain worker processes, which might allow remote attackers to bypass intended access restrictions via unspecified vectors. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4040 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 does not properly handle animated GIF images, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted image. | 2 | 6 | LOCAL |
| CVE‑2010‑4039 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | CRITICAL (10) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 on Linux does not properly set the PATH environment variable, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4038 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | HIGH (8) | The Web Sockets implementation in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 does not properly handle a shutdown action, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 4 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4037 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | MEDIUM (4) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 allows remote attackers to bypass the pop-up blocker via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4036 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 does not properly handle the unloading of a page, which allows remote attackers to spoof URLs via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4035 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 does not properly perform autofill operations for forms, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4034 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 does not properly handle forms, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4033 | 2010‑10‑21 19:00:05 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 7.0.517.41 does not properly implement the autofill and autocomplete functionality, which allows remote attackers to conduct "profile spamming" attacks via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑4008 | 2010‑11‑17 01:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | libxml2 before 2.7.8, as used in Google Chrome before 7.0.517.44, Apple Safari 5.0.2 and earlier, and other products, reads from invalid memory locations during processing of malformed XPath expressions, which allows context-dependent attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted XML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3917 | 2020‑02‑06 13:15:11 | MEDIUM (7) | Google Chrome before 3.0 does not properly handle XML documents, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via a crafted web site. | 3 | 4 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3730 | 2010‑10‑05 18:00:32 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.62 does not properly use information about the origin of a document to manage properties, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via a crafted web site, related to a "property pollution" issue. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3729 | 2010‑10‑05 18:00:32 | CRITICAL (10) | The SPDY protocol implementation in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.62 does not properly manage buffers, which might allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via unspecified vectors. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3417 | 2010‑09‑16 21:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59 does not prompt the user before granting access to the extension history, which allows attackers to obtain potentially sensitive information via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3416 | 2010‑09‑16 21:00:03 | CRITICAL (10) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59 on Linux does not properly implement the Khmer locale, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 4 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3415 | 2010‑09‑16 21:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59 does not properly implement Geolocation, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3414 | 2010‑09‑16 21:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59 on Mac OS X does not properly implement file dialogs, which allows attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. NOTE: this issue exists because of an incorrect fix for CVE-2010-3112 on Mac OS X. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3413 | 2010‑09‑16 21:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in the pop-up blocking functionality in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3412 | 2010‑09‑16 21:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Race condition in the console implementation in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59 has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3411 | 2010‑09‑16 21:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59 on Linux does not properly handle cursors, which might allow attackers to cause a denial of service (assertion failure) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3259 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | WebKit, as used in Apple Safari before 4.1.3 and 5.0.x before 5.0.3, Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53, and webkitgtk before 1.2.6, does not properly restrict read access to images derived from CANVAS elements, which allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy and obtain potentially sensitive image data via a crafted web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3258 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | HIGH (9) | The sandbox implementation in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 does not properly deserialize parameters, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3257 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in WebKit, as used in Apple Safari before 4.1.3 and 5.0.x before 5.0.3, Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53, and webkitgtk before 1.2.6, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via vectors involving element focus. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3256 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 does not properly limit the number of stored autocomplete entries, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3255 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 and webkitgtk before 1.2.6 do not properly handle counter nodes, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3254 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | HIGH (10) | The WebSockets implementation in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 does not properly handle integer values, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3253 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | HIGH (10) | The implementation of notification permissions in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3252 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Notifications presenter in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 allows attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3251 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | The WebSockets implementation in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3250 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 allows remote attackers to enumerate the set of installed extensions via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3249 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 does not properly implement SVG filters, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors, related to a "stale pointer" issue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3248 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 does not properly restrict copying to the clipboard, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3247 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 does not properly restrict the characters in URLs, which allows remote attackers to spoof the appearance of the URL bar via homographic sequences. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3246 | 2010‑09‑07 18:00:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 does not properly handle the _blank value for the target attribute of unspecified elements, which allows remote attackers to bypass the pop-up blocker via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3120 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127 does not properly implement the Geolocation feature, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3119 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127 and webkitgtk before 1.2.6 do not properly support the Ruby language, which allows attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3118 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:03 | MEDIUM (5) | The autosuggest feature in the Omnibox implementation in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127 does not anticipate entry of passwords, which might allow remote attackers to obtain sensitive information by reading the network traffic generated by this feature. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3117 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:03 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127 does not properly implement the notifications feature, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) and possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3116 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:02 | HIGH (10) | Multiple use-after-free vulnerabilities in WebKit, as used in Apple Safari before 4.1.3 and 5.0.x before 5.0.3, Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127, and webkitgtk before 1.2.6, allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via vectors related to improper handling of MIME types by plug-ins. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3115 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127, and webkitgtk before 1.2.6, does not properly implement the history feature, which might allow remote attackers to spoof the address bar via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3114 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:02 | HIGH (10) | The text-editing implementation in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127, and webkitgtk before 1.2.6, does not check a node type before performing a cast, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors related to (1) DeleteSelectionCommand.cpp, (2) InsertLineBreakCommand.cpp, or (3) InsertParagraphSeparatorCommand.cpp in WebCore/editing/. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3113 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127, and webkitgtk before 1.2.5, does not properly handle SVG documents, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors related to state changes when using DeleteButtonController. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3112 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.127 does not properly implement file dialogs, which allows attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑3111 | 2010‑08‑24 20:00:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 6.0.472.53 does not properly mitigate an unspecified flaw in the Windows kernel, which has unknown impact and attack vectors, a different vulnerability than CVE-2010-2897. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2903 | 2010‑07‑28 20:00:10 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.125 performs unexpected truncation and improper eliding of hostnames, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2902 | 2010‑07‑28 20:00:10 | HIGH (10) | The SVG implementation in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.125 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2901 | 2010‑07‑28 20:00:10 | HIGH (10) | The rendering implementation in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.125 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2900 | 2010‑07‑28 20:00:10 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.125 does not properly handle a large canvas, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2899 | 2010‑07‑28 20:00:10 | MEDIUM (5) | Unspecified vulnerability in the layout implementation in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.125 allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information from process memory via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2898 | 2010‑07‑28 20:00:10 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.125 does not properly mitigate an unspecified flaw in the GNU C Library, which has unknown impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2897 | 2010‑07‑28 20:00:10 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.125 does not properly mitigate an unspecified flaw in the Windows kernel, which has unknown impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2652 | 2010‑07‑06 17:17:15 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.99 does not properly implement modal dialogs, which allows attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2651 | 2010‑07‑06 17:17:15 | HIGH (9) | The Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) implementation in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.99 does not properly perform style rendering, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2650 | 2010‑07‑06 17:17:15 | HIGH (9) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.99 has unknown impact and attack vectors, related to an "annoyance with print dialogs." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2649 | 2010‑07‑06 17:17:15 | MEDIUM (4) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.99 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via an invalid image. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2648 | 2010‑07‑06 17:17:15 | HIGH (9) | The implementation of the Unicode Bidirectional Algorithm (aka Bidi algorithm or UBA) in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.99 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2647 | 2010‑07‑06 17:17:15 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.99 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via an invalid SVG document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2646 | 2010‑07‑06 17:17:15 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.99 does not properly isolate sandboxed IFRAME elements, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2645 | 2010‑07‑06 17:17:15 | MEDIUM (7) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.99, when WebGL is used, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (out-of-bounds read) via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2302 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) or possibly execute arbitrary code via vectors involving remote fonts in conjunction with shadow DOM trees, aka rdar problem 8007953. NOTE: this might overlap CVE-2010-1771. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2301 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in editing/markup.cpp in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via vectors related to the node.innerHTML property of a TEXTAREA element. NOTE: this might overlap CVE-2010-1762. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2300 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | HIGH (10) | Use-after-free vulnerability in the Element::normalizeAttributes function in dom/Element.cpp in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via vectors related to handlers for DOM mutation events, aka rdar problem 7948784. NOTE: this might overlap CVE-2010-1759. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2299 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | HIGH (10) | The Clipboard::DispatchObject function in app/clipboard/clipboard.cc in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 does not properly handle CBF_SMBITMAP objects in a ViewHostMsg_ClipboardWriteObjectsAsync message, which might allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via vectors involving crafted data from the renderer process, related to a "Type Confusion" issue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2298 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | HIGH (10) | browser/renderer_host/database_dispatcher_host.cc in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 on Linux does not properly handle ViewHostMsg_DatabaseOpenFile messages in chroot-based sandboxing, which allows remote attackers to bypass intended sandbox restrictions via vectors involving fchdir and chdir calls. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2297 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | HIGH (9) | rendering/FixedTableLayout.cpp in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly execute arbitrary code via an HTML document that has a large colspan attribute within a table. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2296 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | HIGH (9) | The implementation of unspecified DOM methods in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2295 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | MEDIUM (4) | page/EventHandler.cpp in WebCore in WebKit in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 does not properly handle a change of the focused frame during the dispatching of keydown, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to redirect keystrokes via a crafted HTML document, aka rdar problem 7018610. NOTE: this might overlap CVE-2010-1422. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2179 | 2010‑06‑15 18:00:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Adobe Flash Player before 9.0.277.0 and 10.x before 10.1.53.64, and Adobe AIR before 2.0.2.12610, when Firefox or Chrome is used, allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via unspecified vectors related to URL parsing. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2120 | 2010‑06‑01 20:30:03 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome 1.0.154.48 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (resource consumption) via JavaScript code containing an infinite loop that creates IFRAME elements for invalid news:// URIs. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2110 | 2010‑05‑28 18:30:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.55 does not properly execute JavaScript code in the extension context, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2109 | 2010‑05‑28 18:30:02 | HIGH (8) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.55 allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory error) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the "drag + drop" functionality. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2108 | 2010‑05‑28 18:30:02 | HIGH (8) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.55 allows remote attackers to bypass the whitelist-mode plugin blocker via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2107 | 2010‑05‑28 18:30:02 | HIGH (10) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.55 allows attackers to cause a denial of service (memory error) or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to the Safe Browsing functionality. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2106 | 2010‑05‑28 18:30:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.55 might allow remote attackers to spoof the URL bar via vectors involving unload event handlers. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑2105 | 2010‑05‑28 18:30:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 5.0.375.55 does not properly follow the Safe Browsing specification's requirements for canonicalization of URLs, which has unspecified impact and remote attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1992 | 2010‑05‑20 17:30:02 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome 1.0.154.48 executes a mail application in situations where an IFRAME element has a mailto: URL in its SRC attribute, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (excessive application launches) via an HTML document with many IFRAME elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1851 | 2010‑05‑07 18:24:16 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome, when the Invisible Hand extension is enabled, uses cookies during background HTTP requests in a possibly unexpected manner, which might allow remote web servers to identify specific persons and their product searches via HTTP request logging, related to a "cross-site data leakage" issue. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1825 | 2010‑09‑24 19:00:04 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors related to nested SVG elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1824 | 2010‑09‑24 19:00:04 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in WebKit, as used in Apple iTunes before 10.2 on Windows, Apple Safari, and Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service via vectors related to SVG styles, the DOM tree, and error messages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1823 | 2010‑09‑24 19:00:04 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in WebKit before r65958, as used in Google Chrome before 6.0.472.59, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via vectors that trigger use of document APIs such as document.close during parsing, as demonstrated by a Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) file referencing an invalid SVG font, aka rdar problem 8442098. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1822 | 2010‑10‑04 21:00:04 | HIGH (9) | WebKit, as used in Apple Safari before 4.1.3 and 5.0.x before 5.0.3 and Google Chrome before 6.0.472.62, does not properly perform a cast of an unspecified variable, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via an SVG element in a non-SVG document. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1773 | 2010‑09‑24 19:00:04 | HIGH (9) | Off-by-one error in the toAlphabetic function in rendering/RenderListMarker.cpp in WebCore in WebKit before r59950, as used in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70, allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information, cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash), or possibly execute arbitrary code via vectors related to list markers for HTML lists, aka rdar problem 8009118. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1772 | 2010‑09‑24 19:00:04 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in page/Geolocation.cpp in WebCore in WebKit before r59859, as used in Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (application crash) via a crafted web site, related to failure to stop timers associated with geolocation upon deletion of a document. | 3 | 6 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1770 | 2010‑06‑11 19:30:20 | HIGH (9) | WebKit in Apple Safari before 5.0 on Mac OS X 10.5 through 10.6 and Windows, Apple Safari before 4.1 on Mac OS X 10.4, and Google Chrome before 5.0.375.70 does not properly handle a transformation of a text node that has the IBM1147 character set, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via a crafted HTML document containing a BR element, related to a "type checking issue." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1767 | 2010‑09‑24 19:00:04 | MEDIUM (7) | Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in loader/DocumentThreadableLoader.cpp in WebCore in WebKit before r57041, as used in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1059, allows remote attackers to hijack the authentication of unspecified victims via a crafted synchronous preflight XMLHttpRequest operation. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1731 | 2010‑05‑06 14:53:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome on the HTC Hero allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) via JavaScript that writes <marquee> sequences in an infinite loop. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1665 | 2010‑05‑03 13:51:53 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1064 does not properly handle fonts, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) and possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1664 | 2010‑05‑03 13:51:53 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1064 does not properly handle HTML5 media, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) and possibly have unspecified other impact via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1663 | 2010‑05‑03 13:51:53 | HIGH (10) | The Google URL Parsing Library (aka google-url or GURL) in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1064 allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via unspecified vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1506 | 2010‑04‑23 14:30:02 | HIGH (8) | The Google V8 bindings in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1059 allow attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1505 | 2010‑04‑23 14:30:02 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1059 does not prevent pages from loading with the New Tab page's privileges, which has unknown impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1504 | 2010‑04‑23 14:30:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1059 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via vectors related to a chrome://downloads URI. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1503 | 2010‑04‑23 14:30:02 | MEDIUM (4) | Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1059 allows remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via vectors related to a chrome://net-internals URI. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1502 | 2010‑04‑23 14:30:02 | HIGH (9) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1059 allows remote attackers to access local files via vectors related to "developer tools." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1500 | 2010‑04‑23 14:30:02 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1059 does not properly support forms, which has unknown impact and attack vectors, related to a "type confusion error." | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1237 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome 4.1 BETA before 4.1.249.1036 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory error) or possibly have unspecified other impact via an empty SVG element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1236 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | MEDIUM (4) | The protocolIs function in platform/KURLGoogle.cpp in WebCore in WebKit before r55822, as used in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 and Flock Browser 3.x before 3.0.0.4112, does not properly handle whitespace at the beginning of a URL, which allows remote attackers to conduct cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks via a crafted javascript: URL, as demonstrated by a \x00javascript:alert sequence. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1235 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | MEDIUM (4) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 allows remote attackers to trigger the omission of a download warning dialog via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1234 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | HIGH (8) | Unspecified vulnerability in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 allows remote attackers to truncate the URL shown in the HTTP Basic Authentication dialog via unknown vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1233 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | HIGH (10) | Multiple integer overflows in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 allow remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via vectors involving WebKit JavaScript objects. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1232 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory error) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a malformed SVG document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1231 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | HIGH (8) | Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 processes HTTP headers before invoking the SafeBrowsing feature, which allows remote attackers to have an unspecified impact via crafted headers. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1230 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | HIGH (10) | Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 does not have the expected behavior for attempts to delete Web SQL Databases and clear the Strict Transport Security (STS) state, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1229 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:01 | HIGH (10) | The sandbox infrastructure in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 does not properly use pointers, which has unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1228 | 2010‑04‑01 22:30:00 | HIGH (10) | Multiple race conditions in the sandbox infrastructure in Google Chrome before 4.1.249.1036 have unspecified impact and attack vectors. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑1029 | 2010‑03‑19 21:30:00 | MEDIUM (5) | Stack consumption vulnerability in the WebCore::CSSSelector function in WebKit, as used in Apple Safari 4.0.4, Apple Safari on iPhone OS and iPhone OS for iPod touch, and Google Chrome 4.0.249, allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly execute arbitrary code via a STYLE element composed of a large number of *> sequences. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0664 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Stack consumption vulnerability in the ChildProcessSecurityPolicy::CanRequestURL function in browser/child_process_security_policy.cc in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78 allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (memory consumption and application crash) via a URL that specifies multiple protocols, as demonstrated by a URL that begins with many repetitions of the view-source: substring. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0663 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | MEDIUM (5) | The ParamTraits<SkBitmap>::Read function in common/common_param_traits.cc in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78 does not initialize the memory locations that will hold bitmap data, which might allow remote attackers to obtain potentially sensitive information from process memory by providing insufficient data, related to use of a (1) thumbnail database or (2) HTML canvas. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0662 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | MEDIUM (5) | The ParamTraits<SkBitmap>::Read function in common/common_param_traits.cc in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78 does not use the correct variables in calculations designed to prevent integer overflows, which allows attackers to leverage renderer access to cause a denial of service or possibly have unspecified other impact via bitmap data, related to deserialization. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0661 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | MEDIUM (7) | WebCore/bindings/v8/custom/V8DOMWindowCustom.cpp in WebKit before r52401, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78, allows remote attackers to bypass the Same Origin Policy via vectors involving the window.open method. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0660 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | MEDIUM (5) | Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78 sends an https URL in the Referer header of an http request in certain circumstances involving https to http redirection, which allows remote HTTP servers to obtain potentially sensitive information via standard HTTP logging. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0659 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | HIGH (9) | The image decoder in WebKit before r52833, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78, does not properly handle a failure of memory allocation, which allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code in the Chrome sandbox via a malformed GIF file that specifies a large size. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0658 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | HIGH (9) | Multiple integer overflows in Skia, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78, allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code in the Chrome sandbox or cause a denial of service (memory corruption and application crash) via vectors involving CANVAS elements. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0657 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | HIGH (9) | Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78 on Windows does not perform the expected encoding, escaping, and quoting for the URL in the --app argument in a desktop shortcut, which allows user-assisted remote attackers to execute arbitrary programs or obtain sensitive information by tricking a user into creating a crafted shortcut. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0656 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | MEDIUM (4) | WebKit before r51295, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78, presents a directory-listing page in response to an XMLHttpRequest for a file:/// URL that corresponds to a directory, which allows attackers to obtain sensitive information or possibly have unspecified other impact via a crafted local HTML document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0655 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | HIGH (9) | Use-after-free vulnerability in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78 allows user-assisted remote attackers to cause a denial of service (application crash) or possibly execute arbitrary code via vectors involving the display of a blocked popup window during navigation to a different web site. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0651 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | MEDIUM (4) | WebKit before r52784, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78 and Apple Safari before 4.0.5, permits cross-origin loading of CSS stylesheets even when the stylesheet download has an incorrect MIME type and the stylesheet document is malformed, which allows remote attackers to obtain sensitive information via a crafted document. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0650 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | LOW (3) | WebKit, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.78 and Apple Safari, allows remote attackers to bypass intended restrictions on popup windows via crafted use of a mouse click event. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0649 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | HIGH (9) | Integer overflow in the CrossCallParamsEx::CreateFromBuffer function in sandbox/src/crosscall_server.cc in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.89 allows attackers to leverage renderer access to cause a denial of service (heap memory corruption) or possibly have unspecified other impact via a malformed message, related to deserializing of sandbox messages. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0647 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:01 | HIGH (9) | WebKit before r53525, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.89, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code in the Chrome sandbox via a malformed RUBY element, as demonstrated by a <ruby>><table><rt> sequence. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0646 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:00 | HIGH (10) | Multiple integer signedness errors in factory.cc in Google V8 before r3560, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.89, allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code in the Chrome sandbox via crafted use of JavaScript arrays. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0645 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:00 | HIGH (9) | Multiple integer overflows in factory.cc in Google V8 before r3560, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.89, allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code in the Chrome sandbox via crafted use of JavaScript arrays. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0644 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 4.0.249.89, when a SOCKS 5 proxy server is configured, sends DNS queries directly, which allows remote DNS servers to obtain potentially sensitive information about the identity of a client user via request logging, as demonstrated by a proxy server that was configured for the purpose of anonymity. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0643 | 2010‑02‑18 18:00:00 | MEDIUM (4) | Google Chrome before 4.0.249.89 attempts to make direct connections to web sites when all configured proxy servers are unavailable, which allows remote HTTP servers to obtain potentially sensitive information about the identity of a client user via standard HTTP logging, as demonstrated by a proxy server that was configured for the purpose of anonymity. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0556 | 2010‑02‑18 17:30:01 | MEDIUM (4) | browser/login/login_prompt.cc in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.89 populates an authentication dialog with credentials that were stored by Password Manager for a different web site, which allows user-assisted remote HTTP servers to obtain sensitive information via a URL that requires authentication, as demonstrated by a URL in the SRC attribute of an IMG element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |
| CVE‑2010‑0315 | 2010‑01‑14 19:30:01 | MEDIUM (5) | WebKit before r53607, as used in Google Chrome before 4.0.249.89, allows remote attackers to discover a redirect's target URL, for the session of a specific user of a web site, by placing the site's URL in the HREF attribute of a stylesheet LINK element, and then reading the document.styleSheets[0].href property value, related to an IFRAME element. | 0 | 0 | NETWORK |


Get the IT stuff done that nobody wants to do.
Patch more applications, achieve compliance, and prevent problems while reducing stress with Lavawall®.
Security First
A security tool by security auditors. From Passkeys and Argon2i to source validation and MVSP principles, Lavawall® has you covered.
Constant Improvement
More features and more security added nearly every day.
More patchable programs added every week
While Ninite and other patching tools have had the same patch offerings for decades, we're monitoring stats to keep adding the most useful programs (currently over 7,463)!
Details matter
From wrapping TLS communications in extra encryption and uninstalling remote support tools when they aren't used to detailed statistical analysis of system and network performance, Lavawall® goes in-depth.
Human and automated support
Get immediate fixes, user notifications, admin notifications -- and even security-certified human level 3 support when our advanced statistical analysis confirms a problem or anomaly.
| 2025‑01‑17 | 0.12.29.216 | Enhanced compliance and non-standard AV |
| 2025‑01‑13 | 0.12.28.215 | Improved process graphs |
| 2025‑01‑07 | 0.12.27.214 | Antivirus details, compliance |
| 2024‑12‑27 | 0.12.24.211 | |
| 2024‑12‑02 | 0.12.19.206 | |
| 2024‑11‑22 | 0.12.18.205 | |
| 2024‑10‑30 | 0.12.8.195 | Mac update refinements |
| 2024‑10‑25 | 0.12.3.190 | |
| 2024‑10‑21 | 0.12.0.187 | Macos implementaiton, linux and windows improvements |
| 2024‑10‑16 | 0.11.128.186 | Linux stats and system information improvements, improvements for application shutdown |
| 2024‑09‑12 | 0.11.113.171 | CPU Optimizations and Packages reliability improvements |
| 2024‑09‑05 | 0.11.106.164 | Phased deployment enhancements |
| 2024‑09‑04 | 0.11.103.161 | |
| 2024‑09‑02 | 0.11.102.160 | CPU Optimizations and Packages reliability improvements |
| 2024‑08‑30 | 0.11.99.157 | CPU Optimizations and Packages reliability improvements |
| 2024‑08‑29 | 0.11.98.156 | CPU utilization and console event optimization |
| 2024‑08‑28 | 0.11.97.155 | Reliability to detect unusual updates like redistributables. |
| 2024‑08‑27 | 0.11.96.154 | |
| 2024‑08‑26 | 0.11.95.153 | Faster response for reboot requests |
| 2024‑08‑20 | 0.11.92.150 | Additional package upgrade pre-requisites |
| 2024‑08‑15 | 0.11.89.147 | |
| 2024‑08‑06 | 0.11.87.145 | |
| 2024‑07‑26 | 0.11.83.141 | Add resiliency for MAC duplicates and uptime |
| 2024‑07‑25 | 0.11.82.140 | Changes to facilitate cross-platform use. Bitlocker and Windows key refinements |
| 2024‑07‑15 | 0.11.80.138 | Antivirus and temperature added to configuration checks |
| 2024‑07‑15 | 0.11.79.137 | Add configuration checks for execution policy and secure boot |
| 2024‑07‑11 | 0.11.77.135 | load balancing refinements |
| 2024‑07‑10 | 0.11.76.134 | Add additional load balancing and data residency capabilities, add randomness to recurring task timings to decrease server load |
| 2024‑07‑05 | 0.11.74.132 | changes to graph and residual work on user imporsonation |
| 2024‑07‑04 | 0.11.73.131 | Add configuration checks for execution policy and secure boot. |
| 2024‑07‑03 | 0.11.72.130 | Enhanced event log monitoring |
| 2024‑07‑02 | 0.11.71.129 | Add details to Windows updates, enhanced risk metrics for application patches |
| 2024‑06‑19 | 0.11.65.123 | Update resiliancy and garbage collection |
| 2024‑06‑13 | 0.11.60.118 | Enhanced logging |
| 2024‑06‑12 | 0.11.55.113 | Include the primary drive serial number; MAC addresses for built-in wireless, Bluetooth, and ethernet into the device hash to restore uninstalled and reinstalled devices in cases where the motherboard serial is not unique |
| 2024‑06‑07 | 0.11.54.112 | Patch and package uninstall data addition |
| 2024‑06‑05 | 0.11.47.105 | refine per-user registry application listing |
| 2024‑06‑02 | 0.11.45.103 | uninstall and reinstall refinements, refine local logging, refine self-update and uninstall timing |
| 2024‑05‑30 | 0.11.21.79 | various bug fixes and improvements |
| 2024‑05‑28 | 0.11.16.74 | Error logging, registration, and uninstall improvements. |
| 2024‑05‑24 | 0.11.14.72 | applied changes for devices and login commands, changes for registration as well |
| 2024‑05‑22 | 0.11.13.71 | Add Windows computer model, improve Operating System parsing |
| 2024‑05‑21 | 0.11.11.69 | Added additional states for Windows update, flexibility for non-standard program file configurations, support for network diagrams at the switch level, details for Windows editions |
| 2024‑05‑21 | 0.11.10.68 | Add specific cases for Defender patterns and Composer versions. |
| 2024‑05‑17 | 0.11.3.61 | Change Log storage location to c:\program files\Lavawall |
| 2024‑05‑17 | 0.11.1.59 | self-update improvements. |
| 2024‑05‑16 | 0.8.0.55 | error log reporting and management. |
| 2024‑05‑15 | 0.7.0.54 | Websocket resiliency improvements |
| 2024‑05‑09 | 0.6.0.53 | Error log reporting and management. |
| 2024‑05‑01 | 0.5.44.52 | Even more improvements to scheduler |
NOTE: changes after June 2024 are incorportated into the Windows Changelog as the codebases for Windows, Linux, and Mac were combined
| 2024‑05‑20 | 253 | Added cleanup of old .json files during a re-install |
| 2024‑05‑13 | 252 | Added apt-get update to install |
| 2024‑05‑06 | 248 | Allow restart to use /var/run/reboot-required if needrestart is not installed |
| 2024‑04‑22 | 239 | Improve internal update and version tracking |
| 2024‑04‑15 | 235 | Add support for Yum packages |
| 2024‑04‑08 | 233 | Align patching with Windows patch reporting |
| 2024‑04‑02 | 228 | Add support for needrestart |
| 2024‑03‑04 | 224 | Schedule restarts |
| 2024‑03‑25 | 221 | Add support for apt packages |
| 2024‑03‑18 | 212 | Implement release management |
| 2024‑03‑11 | 202 | Add user login monitoring |
| 2024‑03‑04 | 189 | Enhance installation reliability |
| 2024‑02‑26 | 187 | Exapand triggers to identify if the instance needs to be restarted |
| 2024‑02‑19 | 146 | Improve compatibility for non-AWS instances |
| 2024‑02‑14 | 138 | Add self-uninstall capabilities |
| 2024‑02‑12 | 135 | Enhance scheduling flexibility |
| 2024‑02‑07 | 132 | Add kernel version tracking |
| 2024‑02‑05 | 124 | Add device hash to cryptographic self-update script validation |
| 2024‑01‑29 | 107 | Enhance encryption of patch data |
| 2024‑01‑22 | 98 | Improve how available storage is calculated |
| 2024‑01‑15 | 97 | Move initial tasks from installation file to sub scripts |
| 2024‑05‑21 | 91 | Improve multi-distribution compatibility |
| 2024‑05‑21 | 79 | Improve encryption reliability |
| 2023‑12‑11 | 68 | Enhance cryptographic validation of new scripts before updating |
| 2023‑11‑20 | 62 | Add inner layer of AES encryption in case TLS inspection doesn't allow for a secure connection |
| 2023‑11‑27 | 56 | Additional base cases for resiliancy |
| 2023‑11‑20 | 54 | Additional headers added to authentication process during installation. |
| 2023‑11‑20 | 53 | Enhanced key management |
| 2023‑11‑15 | 51 | Add insecure installation parameter to allow installation in environments with TLS inspection or other machine-in-the-middle situations. |
| 2023‑11‑06 | 42 | Enhance redundant encryption during installation. |
| 2023‑10‑30 | 33 | Improve install-over compatibility |
| 2023‑10‑23 | 18 | Add reboot configuration and scheduling |
| 2023‑10‑23 | 17 | Add self-updating functionality. |
| 2023‑10‑16 | 15 | Add Linux patching information for apt |
| 2023‑10‑09 | 14 | Collect system information |
| 2023‑10‑09 | 13 | Add Linux distribution information |
| 2023‑09‑30 | 12 | Add memory monitoring |
| 2023‑09‑30 | 10 | Add hardware information |
| 2023‑09‑23 | 9 | Add AWS information |
| 2023‑09‑23 | 8 | Add customized schedule capability for configuration updates |
| 2023‑09‑23 | 7 | Add support for package monitoring using package and dpkg logs |
| 2023‑09‑16 | 6 | Add storage data configuration gathering |
| 2023‑09‑16 | 5 | Add CPU information |
Lavawall® was built from the ground up with these concerns and the Minimum Viable Secure Product requirements in mind.
Some of the controls we implemented include:
- PassKeys as the preferred primary authentication at no additional cost
- Single Sign-on using modern, maintained, and industry-standard protocols for all customers at no additional cost
- Multi-Factor Authentication as a non-negotiable default
- Encrypting communications the same way as TLS again within the TLS tunnel, so we can allow TLS inspection without breaking like Huntress or disclosing security vulnerabilities to eavesdroppers.
- Encouraging external vulnerability reports and customer testing
- Passwords checked against popular disclosed passwords, hashed before they leave your computer, and then stored using Argon2id
- Not requiring the use of passwords at all. We consider them a temporary backup authentication in case you can't use passkeys or SSO.
Lavawall® databases and front-end systems are hosted with AWS in Montréal, Québec, Canada.
We send emails through AWS in Ireland and dedicated servers in Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
We send text messages for additional identity verification through Twilio in the United States.
We store executables and pass requests through Cloudflare at your nearest edge location.
We use Cloudflare for risk management, turnstile, and web application firewall services.
We use LeadPages for landing pages.
We use Google and Facebook for analytics on our public-facing pages, but they do not have access to the console.
We integrate with third-party tools, such as Microsoft, Google, Huntress, Screen Connect, Axcient, and Datto in their respective locations. However, you must initiate these integrations through single sign-on or by enabling them in your Lavawall® console.
Active security by design
Lavawall® is under active development with the latest release including:
7,463+
Monitored Applications
23+
System Metrics
Actively manage your IT with Lavawall®
Patching
Updates Beyond Windows
Lavawall® prevents the 80% of breaches and failed audits due to missing patches and updates.
You can reduce application patching delays from 67 days to nearly immediate with the 350+ applications that Lavawall® monitors and patches.
Patch release monitoring
Monitor everything without having to select packages or “managed applications”
Patch impact classification
Standard and optional Windows patches
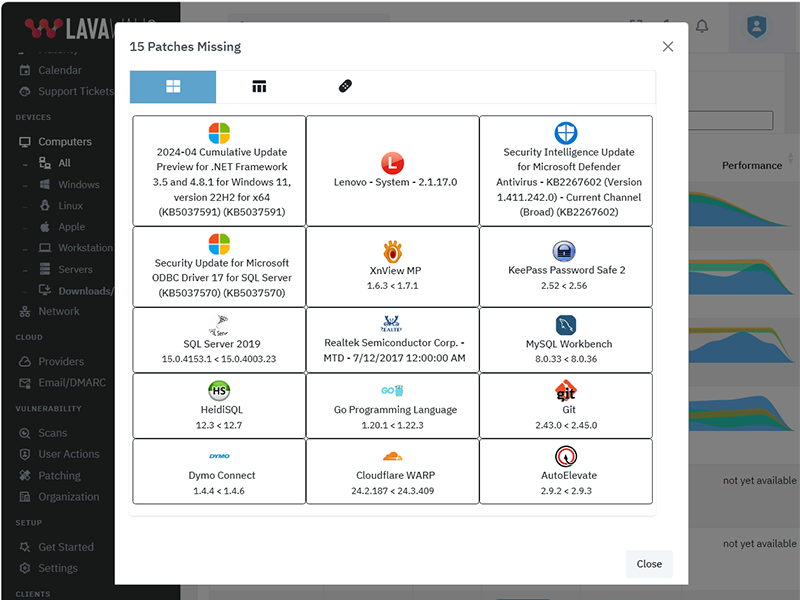
Application Patching
Some of the applications that Lavawall® monitors and audits include:
Logos are property of their respective trademark holders and are not affiliated with ThreeShield or Lavawall. We have not audited the security of most of the listed tools.
The above listing includes products that Lavawall® monitors through public information and/or proprietary statistical analysis.
Although we do have a partner relationship with some of the listed products and companies, they do not necessarily endorse Lavawall® or have integrations with our systems.
Learn More
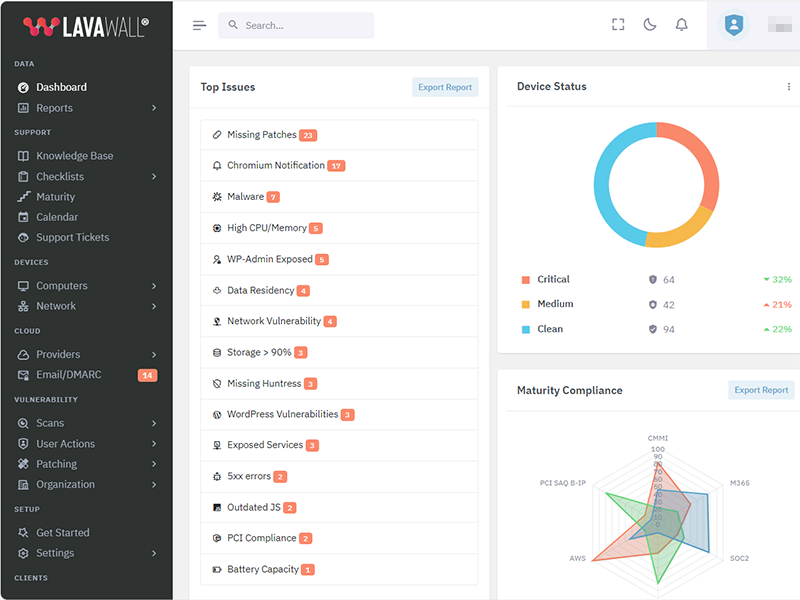
Flexible Term; Flexible Service
Flexibility for your dynamic business
You need to get your arms around compliance and security and don't want to get locked into “high watermark” monthly invoices or multi-year contracts.
Pay-as-you-need monthly pricing
DIY, full management, and coaching options
CMMI, PCI, SOC2, Canadian Cybersecurity, Minimum Viable Secure Product, and other compliance support
Choose the plan that's right for you
Simple pricing. No hidden fees. Advanced features for you business.
Month
Annual
Get 2 months free with Annual!
DIY
Security-focused RMM
C$3.25 /computer/Month
C$32.50 /computer/Year
-
1 computer
or 1 of the following cloud integrations:
AWS, Axcient, Connectwise, Datto, Google, Huntress, M365, Sophos Central integrations
(each integration counts as 1 computer) -
50+ application patches
-
30-day Logs
-
Security configuration monitoring
-
Anomaly detection
-
CMMI, MVSP, CyberCanda compliance
-
Lavawall® support
-
Sophos MDR: C$13.50/desktopSophos MDR: C$162/desktop
-
Huntress: C$5.40/deviceHuntress: C$64.80/device
-
Available white-label support for end users
-
Level 3+ IT support for IT
-
Weekly IT coaching sessions
Managed Security & Support
Unlimited end-user support
C$160 /user/Month
C$1,600 /user/Year
-
1 computer/user
Additional devices charged at DIY prices -
AWS, Axcient, Connectwise, Datto, Google, Huntress, M365, Sophos Central integrations
-
350+ application patches
-
90-day Logs
-
Security configuration monitoring
-
Anomaly detection
-
CMMI, MVSP, CyberCanda compliance
-
Lavawall® support
-
Sophos MDR Essentials
-
Huntress
-
White-label email and phone support for end users
-
Level 3+ IT support for IT
-
Weekly IT coaching sessions
-
Automatic discount and upgrade to Support & Coaching after 15 users
Support & Coaching
Improve your IT performance
$2,250 /Month
$22,500 /Year
-
25 computers included
Additional computers charged at DIY prices -
AWS, Axcient, Connectwise, Datto, Google, Huntress, M365, Sophos Central integrations
-
350+ application patches
-
90-day Logs
-
Security configuration monitoring
-
Anomaly detection
-
CMMI, MVSP, CyberCanda compliance
-
Lavawall®-only support
-
Sophos MDR Essentials
-
Huntress
-
White-label email and phone support for 15 users included Additional: C$150/user Additional: C$1,500/user
-
L3 IT support for IT
-
Weekly IT coaching sessions
Frequently Asked Questions
If you can not find answer to your question in our FAQ, you can always contact us or email us. We will answer you shortly!
General Questions
- Two years after a missing Plex Media Server led to the LastPass breach, the
Remote Monitorign and Management (RMM) tools availabel for Manged IT Service Providers (MSPs)
still didn't monitor for it.
Going through industry-specific applications, we noticed many were missing from the big RMM and patching providers. MSPs, insurance providers, and organizations that put their cleints at risk need to know about these risks, which lead to the largest number of critical audit findings and breaches - After 20 years of writing the same audit findings about system configurations, Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliance, and missing patches, our technical co-founder wanted to make it easier fo avoid these findings
- The existing risk visibility tools for insurance underwriters took a shallow look at Internet-facing risks. They -- along with all businesses -- need a deeper view of the threats that could actually lead to breaches.
- Domain risks
- Operating System (OS) patches
- Application patches
- Network vulnerabilities
- Cloud vulnerabilities
- OS configurations
You can use your own logo for the console and notifications. You can also use a CNAME to automatically brand your console.
Note: you cannot currently re-proxy the CNAME to Lavawall® through Cloudflare.
Lavawall® supports the following operating systems:
Lavawall® does not currently support non systemd distributions, such as Devuan, Artix Linux, PCLinuxOS, OpenWRT, and DD-WRT. However, we will support them by the end of 2024.
In June 2024, we combined the Windows and Linux systems for a consistent experience. This added support for RedHat and MacOS.
Privacy & Security
However, we do allow passwords and use passwords as part of the zero-knowledge encryption for your clients' sensitive data, such as Bitlocker keys and Personally-Identifiable Information (PII).
These passwords use Argon2id slow hashes with individual salts and peppers.
We have added an additional secure tunnel that mimics the TLS process within the public TLS tunnel. This extra tunnel provides authentication and privacy for the workstations and the Lavawall® servers to prevent attacks such as the one that took down Solar Winds.
Remote access is not enabled for read-only and audit situations.
Get In Touch
Have a quick question and don't want to talk? Send us a quick note with the form below and we'll reply within one business day.
NW Calgary:
ThreeShield Information Security Corporation
600 Crowfoot Crescent N.W., Suite 340
Calgary, Alberta
T3G 0B4
SE Calgary:
ThreeShield Information Security Corporation
105, 11500 - 29th St. SE
Calgary, Alberta
T2Z 3W9
Canada